arviz.plot_khat — ArviZ dev documentation (original) (raw)
arviz.plot_khat(khats, color='C0', xlabels=False, show_hlines=False, show_bins=False, bin_format='{1:.1f}%', annotate=False, threshold=None, hover_label=False, hover_format='{1}', figsize=None, textsize=None, coords=None, legend=False, markersize=None, ax=None, hlines_kwargs=None, backend=None, backend_kwargs=None, show=None, **kwargs)[source]#
Plot Pareto tail indices \(\hat{k}\) for diagnosing convergence in PSIS-LOO.
Parameters:
khatsELPDData
The input Pareto tail indices to be plotted.
colorstr or array_like, default “C0”
Colors of the scatter plot, if color is a str all dots will have the same color, if it is the size of the observations, each dot will have the specified color, otherwise, it will be interpreted as a list of the dims to be used for the color code. If Matplotlib c argument is passed, it will override the color argument.
Use coords as xticklabels.
show_hlinesbool, default False
Show the horizontal lines, by default at the values [0, 0.5, 0.7, 1].
Show the percentage of khats falling in each bin, as delimited by hlines.
bin_formatstr, optional
The string is used as formatting guide calling bin_format.format(count, pct).
thresholdfloat, optional
Show the labels of k values larger than threshold. If None (default), no observations will be highlighted.
hover_labelbool, default False
Show the datapoint label when hovering over it with the mouse. Requires an interactive backend.
hover_formatstr, default “{1}”
String used to format the hover label via hover_format.format(idx, coord_label)
figsize(float, float), optional
Figure size. If None it will be defined automatically.
textsizefloat, optional
Text size scaling factor for labels, titles and lines. If None it will be autoscaled based on figsize.
coordsmapping, optional
Coordinates of points to plot. All values are used for computation, but only a a subset can be plotted for convenience. See this section for usage examples.
Include a legend to the plot. Only taken into account when color argument is a dim name.
markersizeint, optional
markersize for scatter plot. Defaults to None in which case it will be chosen based on autoscaling for figsize.
axaxes, optional
Matplotlib axes or bokeh figures.
hlines_kwargsdict, optional
Additional keywords passed tomatplotlib.axes.Axes.hlines().
backend{“matplotlib”, “bokeh”}, default “matplotlib”
Select plotting backend.
backend_kwargsdict, optional
These are kwargs specific to the backend being used, passed tomatplotlib.pyplot.subplots() or bokeh.plotting.figure. For additional documentation check the plotting method of the backend.
showbool, optional
Call backend show function.
kwargs
Additional keywords passed tomatplotlib.axes.Axes.scatter().
Returns:
axesmatplotlib Axes or bokeh_figures
See also
Pareto smoothed importance sampling (PSIS).
Notes
The Generalized Pareto distribution (GPD) diagnoses convergence rates for importance sampling. GPD has parameters offset, scale, and shape. The shape parameter (\(k\)) tells the distribution’s number of finite moments. The pre-asymptotic convergence rate of importance sampling can be estimated based on the fractional number of finite moments of the importance ratio distribution. GPD is fitted to the largest importance ratios and interprets the estimated shape parameter \(k\), i.e., \(\hat{k}\) can then be used as a diagnostic (most importantly if \(\hat{k} > 0.7\), then the convergence rate is impractically low). See [1].
References
[1]
Vehtari, A., Simpson, D., Gelman, A., Yao, Y., Gabry, J. (2024). Pareto Smoothed Importance Sampling. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 25(72):1-58.
Examples
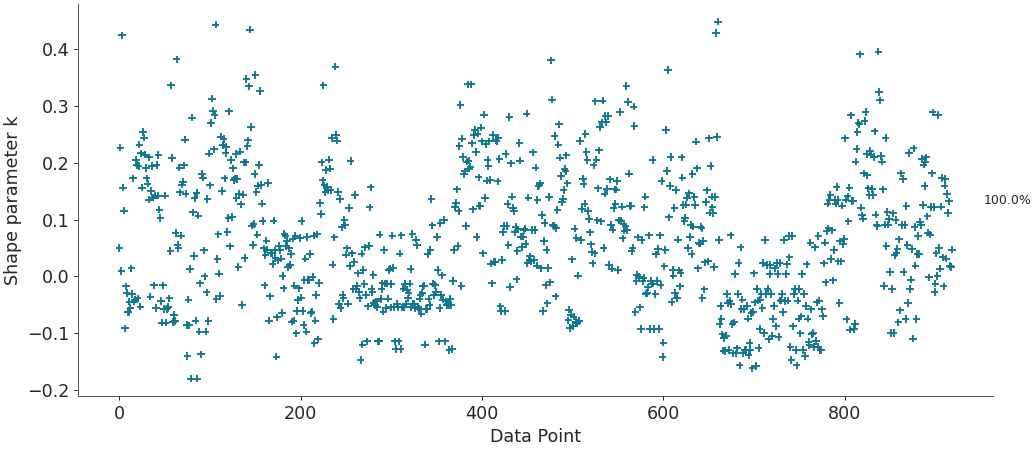
Plot estimated pareto shape parameters showing how many fall in each category.
import arviz as az radon = az.load_arviz_data("radon") loo_radon = az.loo(radon, pointwise=True) az.plot_khat(loo_radon, show_bins=True)
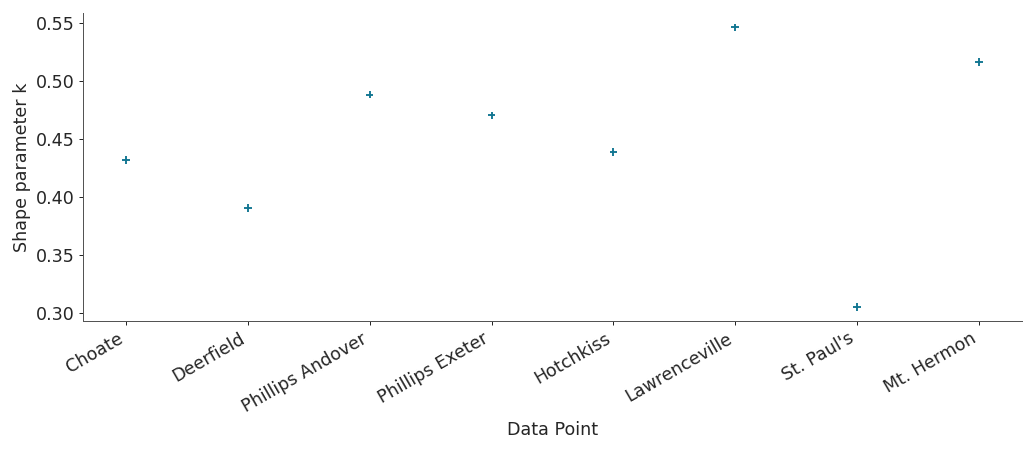
Show xlabels
centered_eight = az.load_arviz_data("centered_eight") khats = az.loo(centered_eight, pointwise=True).pareto_k az.plot_khat(khats, xlabels=True, threshold=1)
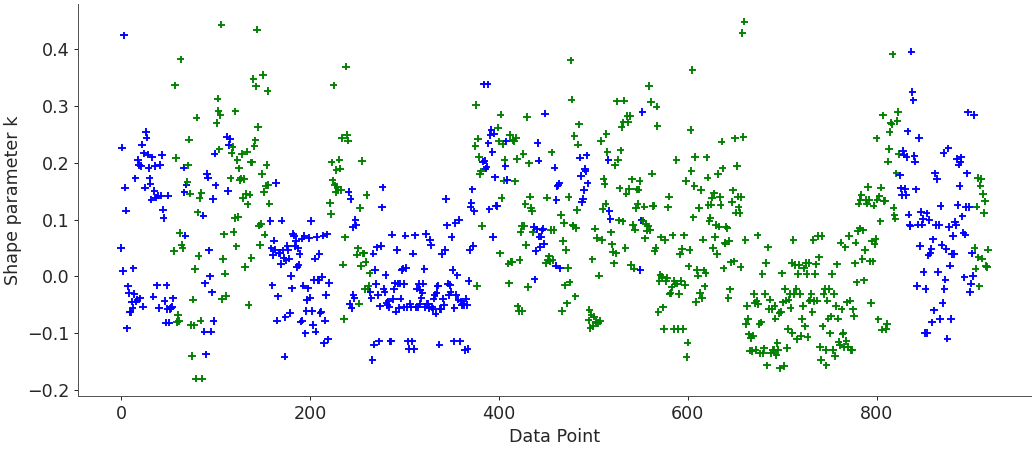
Use custom color scheme
counties = radon.posterior.County[radon.constant_data.county_idx].values colors = [ ... "blue" if county[-1] in ("A", "N") else "green" for county in counties ... ] az.plot_khat(loo_radon, color=colors)