Faces recognition example using eigenfaces and SVMs (original) (raw)
Note
Go to the endto download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via JupyterLite or Binder
The dataset used in this example is a preprocessed excerpt of the “Labeled Faces in the Wild”, aka LFW:https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/jessicali9530/lfw-dataset
Authors: The scikit-learn developers
SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
Download the data, if not already on disk and load it as numpy arrays
lfw_people = fetch_lfw_people(min_faces_per_person=70, resize=0.4)
introspect the images arrays to find the shapes (for plotting)
n_samples, h, w = lfw_people.images.shape
for machine learning we use the 2 data directly (as relative pixel
positions info is ignored by this model)
X = lfw_people.data n_features = X.shape[1]
the label to predict is the id of the person
y = lfw_people.target target_names = lfw_people.target_names n_classes = target_names.shape[0]
print("Total dataset size:") print("n_samples: %d" % n_samples) print("n_features: %d" % n_features) print("n_classes: %d" % n_classes)
Total dataset size: n_samples: 1288 n_features: 1850 n_classes: 7
Split into a training set and a test and keep 25% of the data for testing.
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split( X, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=42 )
scaler = StandardScaler() X_train = scaler.fit_transform(X_train) X_test = scaler.transform(X_test)
Compute a PCA (eigenfaces) on the face dataset (treated as unlabeled dataset): unsupervised feature extraction / dimensionality reduction
n_components = 150
print( "Extracting the top %d eigenfaces from %d faces" % (n_components, X_train.shape[0]) ) t0 = time() pca = PCA(n_components=n_components, svd_solver="randomized", whiten=True).fit(X_train) print("done in %0.3fs" % (time() - t0))
eigenfaces = pca.components_.reshape((n_components, h, w))
print("Projecting the input data on the eigenfaces orthonormal basis") t0 = time() X_train_pca = pca.transform(X_train) X_test_pca = pca.transform(X_test) print("done in %0.3fs" % (time() - t0))
Extracting the top 150 eigenfaces from 966 faces done in 0.083s Projecting the input data on the eigenfaces orthonormal basis done in 0.005s
Train a SVM classification model
print("Fitting the classifier to the training set") t0 = time() param_grid = { "C": loguniform(1e3, 1e5), "gamma": loguniform(1e-4, 1e-1), } clf = RandomizedSearchCV( SVC(kernel="rbf", class_weight="balanced"), param_grid, n_iter=10 ) clf = clf.fit(X_train_pca, y_train) print("done in %0.3fs" % (time() - t0)) print("Best estimator found by grid search:") print(clf.best_estimator_)
Fitting the classifier to the training set done in 5.438s Best estimator found by grid search: SVC(C=np.float64(76823.03433306457), class_weight='balanced', gamma=np.float64(0.0034189458230957995))
Quantitative evaluation of the model quality on the test set
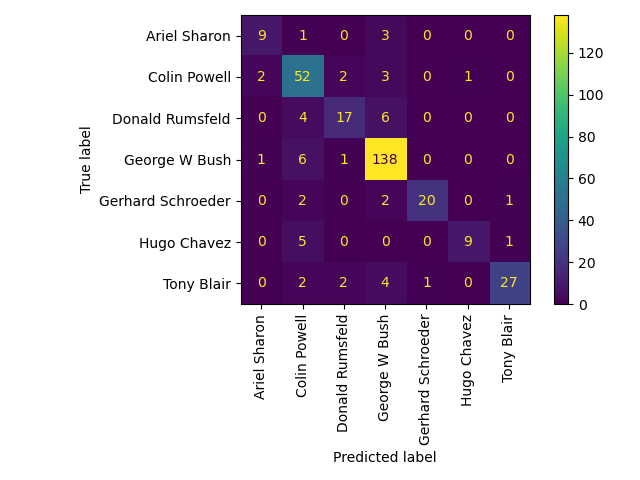
Predicting people's names on the test set done in 0.051s precision recall f1-score support
Ariel Sharon 0.75 0.69 0.72 13
Colin Powell 0.72 0.87 0.79 60Donald Rumsfeld 0.77 0.63 0.69 27 George W Bush 0.88 0.95 0.91 146 Gerhard Schroeder 0.95 0.80 0.87 25 Hugo Chavez 0.90 0.60 0.72 15 Tony Blair 0.93 0.75 0.83 36
accuracy 0.84 322
macro avg 0.84 0.75 0.79 322
weighted avg 0.85 0.84 0.84 322Qualitative evaluation of the predictions using matplotlib
def plot_gallery(images, titles, h, w, n_row=3, n_col=4): """Helper function to plot a gallery of portraits""" plt.figure(figsize=(1.8 * n_col, 2.4 * n_row)) plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0, left=0.01, right=0.99, top=0.90, hspace=0.35) for i in range(n_row * n_col): plt.subplot(n_row, n_col, i + 1) plt.imshow(images[i].reshape((h, w)), cmap=plt.cm.gray) plt.title(titles[i], size=12) plt.xticks(()) plt.yticks(())
plot the result of the prediction on a portion of the test set
def title(y_pred, y_test, target_names, i): pred_name = target_names[y_pred[i]].rsplit(" ", 1)[-1] true_name = target_names[y_test[i]].rsplit(" ", 1)[-1] return "predicted: %s\ntrue: %s" % (pred_name, true_name)
prediction_titles = [ title(y_pred, y_test, target_names, i) for i in range(y_pred.shape[0]) ]
plot_gallery(X_test, prediction_titles, h, w)

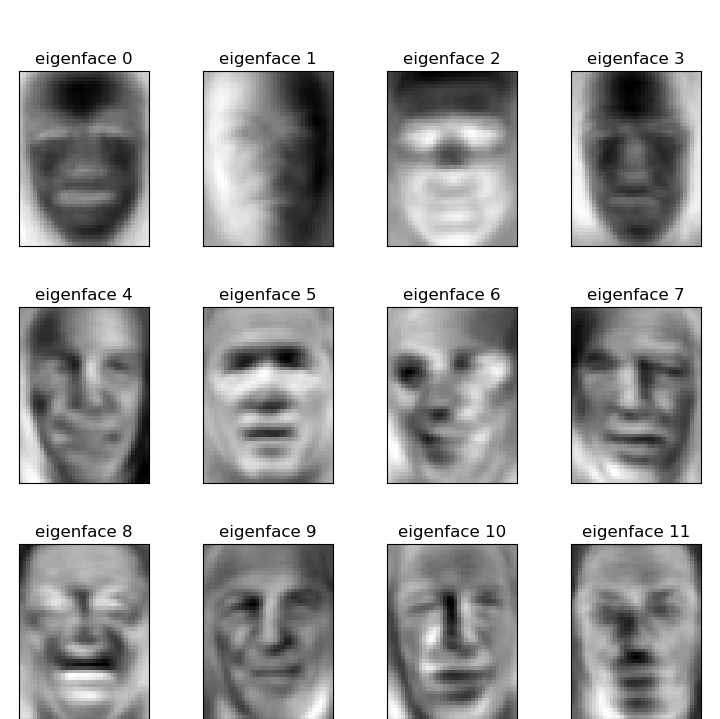
plot the gallery of the most significative eigenfaces
eigenface_titles = ["eigenface %d" % i for i in range(eigenfaces.shape[0])] plot_gallery(eigenfaces, eigenface_titles, h, w)
plt.show()

Face recognition problem would be much more effectively solved by training convolutional neural networks but this family of models is outside of the scope of the scikit-learn library. Interested readers should instead try to use pytorch or tensorflow to implement such models.
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 6.254 seconds)
Related examples