Psoriasis pathophysiology: current concepts of pathogenesis (original) (raw)
Abstract
Psoriasis vulgaris is a common skin disorder characterised by focal formation of inflamed, raised plaques that constantly shed scales derived from excessive growth of skin epithelial cells. The disease is defined by a series of linked cellular changes in the skin: hyperplasia of epidermal keratinocytes, vascular hyperplasia and ectasia, and infiltration of T lymphocytes, neutrophils, and other types of leucocyte in affected skin. In a relatively short period, psoriasis vulgaris has been conceptualised as a T lymphocyte mediated autoimmune disease and new biological therapies that target T cells have just entered routine clinical practice. Similarly, rapid progress has been made towards dissecting cellular and molecular pathways of inflammation that contribute to disease pathogenesis. This short review presents current pathogenic concepts that have emerged from genetic, genomic, and cellular information obtained in basic studies and from clinical studies of selective immune targeting drugs.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (494.6 KB).
Figure 1.
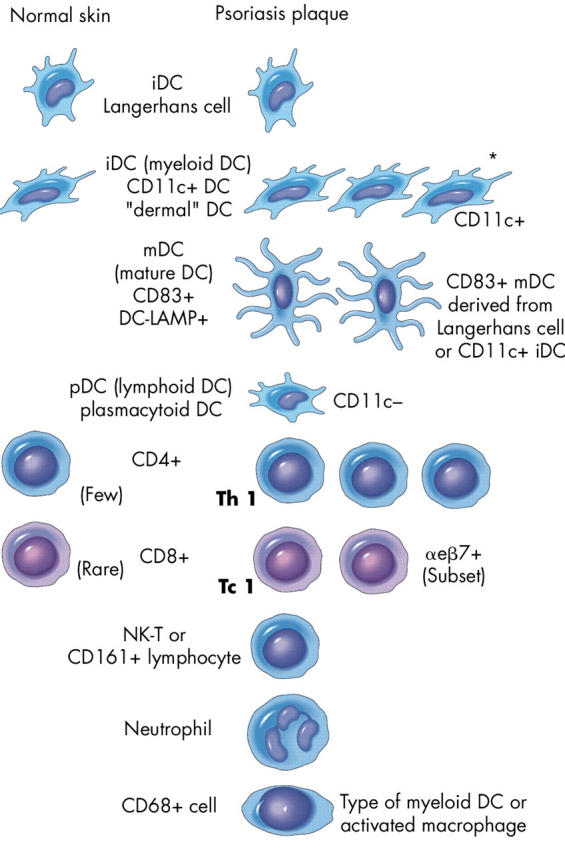
The array of leucocyte subsets that appear in psoriasis vulgaris lesions. iDC, immature dendritic cell; NK-T, natural killer T (cells).
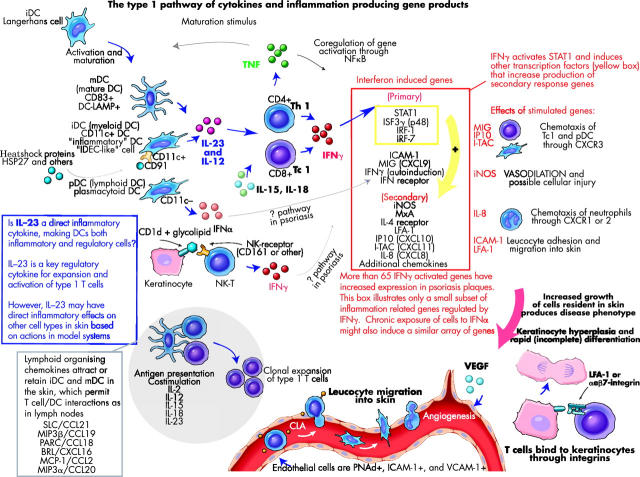
Figure 2.
Alternative pathways of leucocyte activation that converge to activate type 1 inflammatory genes which, in turn, regulate end stage inflammation in skin and the appearance of the psoriasis phenotype. BRL, Bonzo receptor ligand; DC, dendritic cell; ICAM, intercellular adhesion molecule; ITAC, interferon inducible T cell α chemoattractant; IL, interleukin; IFN, interferon; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; IP10, interferon inducible protein 10; IRF, interferon regulatory factor; ISF, interferon stimulated factor; LFA-1, leucocyte function associated antigen-1; MCP, monocyte chemoattractant protein; MIG, monokine induced by interferon γ; MIP, macrophage inflammatory protein; MxA, interferon induced cellular resistance mediator protein; NF, nuclear factor; NK, natural killer (cell); PARC, pulmonary and activation regulated chemokine; PNAd, peripheral node addressin; TNF tumour necrosis factor; SLC, secondary lymphoid tissue chemokine; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; VCAM, vascular cell adhesion molecule; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams J. R., Kelley S. L., Hayes E., Kikuchi T., Brown M. J., Kang S., Lebwohl M. G., Guzzo C. A., Jegasothy B. V., Linsley P. S. Blockade of T lymphocyte costimulation with cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4-immunoglobulin (CTLA4Ig) reverses the cellular pathology of psoriatic plaques, including the activation of keratinocytes, dendritic cells, and endothelial cells. J Exp Med. 2000 Sep 4;192(5):681–694. doi: 10.1084/jem.192.5.681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehm U., Klamp T., Groot M., Howard J. C. Cellular responses to interferon-gamma. Annu Rev Immunol. 1997;15:749–795. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.15.1.749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonish B., Jullien D., Dutronc Y., Huang B. B., Modlin R., Spada F. M., Porcelli S. A., Nickoloff B. J. Overexpression of CD1d by keratinocytes in psoriasis and CD1d-dependent IFN-gamma production by NK-T cells. J Immunol. 2000 Oct 1;165(7):4076–4085. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.7.4076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowcock Anne M., Cookson William O. C. M. The genetics of psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis and atopic dermatitis. Hum Mol Genet. 2004 Apr 1;13(SPEC):R43–R55. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddh094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyman Onur, Hefti Hans Peter, Conrad Curdin, Nickoloff Brian J., Suter Mark, Nestle Frank O. Spontaneous development of psoriasis in a new animal model shows an essential role for resident T cells and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Exp Med. 2004 Feb 23;199(5):731–736. doi: 10.1084/jem.20031482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunn G. J., Williams J., Sabers C., Wiederrecht G., Lawrence J. C., Jr, Abraham R. T. Direct inhibition of the signaling functions of the mammalian target of rapamycin by the phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitors, wortmannin and LY294002. EMBO J. 1996 Oct 1;15(19):5256–5267. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büchler Tomas, Hajek Roman, Bourkova Lida, Kovarova Lucie, Musilova Romana, Bulikova Alena, Doubek Michal, Svobodnik Adam, Mareschova Iveta, Vanova Pavlina. Generation of antigen-loaded dendritic cells in a serum-free medium using different cytokine combinations. Vaccine. 2003 Feb 14;21(9-10):877–882. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(02)00535-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry Jonathan L., Qin Jian-Zhong, Bonish Brian, Carrick Ryan, Bacon Patricia, Panella Jeffrey, Robinson June, Nickoloff Brian J. Innate immune-related receptors in normal and psoriatic skin. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2003 Feb;127(2):178–186. doi: 10.5858/2003-127-178-IIRRIN. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deguchi Masatoshi, Aiba Setsuya, Ohtani Haruo, Nagura Hiroshi, Tagami Hachiro. Comparison of the distribution and numbers of antigen-presenting cells among T-lymphocyte-mediated dermatoses: CD1a+, factor XIIIa+, and CD68+ cells in eczematous dermatitis, psoriasis, lichen planus and graft-versus-host disease. Arch Dermatol Res. 2002 Jul 27;294(7):297–302. doi: 10.1007/s00403-002-0334-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenczi K., Burack L., Pope M., Krueger J. G., Austin L. M. CD69, HLA-DR and the IL-2R identify persistently activated T cells in psoriasis vulgaris lesional skin: blood and skin comparisons by flow cytometry. J Autoimmun. 2000 Feb;14(1):63–78. doi: 10.1006/jaut.1999.0343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhlbrigge R. C., Kieffer J. D., Armerding D., Kupper T. S. Cutaneous lymphocyte antigen is a specialized form of PSGL-1 expressed on skin-homing T cells. Nature. 1997 Oct 30;389(6654):978–981. doi: 10.1038/40166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon Kenneth B., Papp Kim A., Hamilton Tiffani K., Walicke Patricia A., Dummer Wolfgang, Li Nicole, Bresnahan Brian W., Menter Alan, Efalizumab Study Group Efalizumab for patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2003 Dec 17;290(23):3073–3080. doi: 10.1001/jama.290.23.3073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb Alice B., Chaudhari Umesh, Mulcahy Lisa D., Li Shu, Dooley Lisa T., Baker Daniel G. Infliximab monotherapy provides rapid and sustained benefit for plaque-type psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003 Jun;48(6):829–835. doi: 10.1067/mjd.2003.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb S. L., Gilleaudeau P., Johnson R., Estes L., Woodworth T. G., Gottlieb A. B., Krueger J. G. Response of psoriasis to a lymphocyte-selective toxin (DAB389IL-2) suggests a primary immune, but not keratinocyte, pathogenic basis. Nat Med. 1995 May;1(5):442–447. doi: 10.1038/nm0595-442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helms Cynthia, Cao Li, Krueger James G., Wijsman Ellen M., Chamian Francesca, Gordon Derek, Heffernan Michael, Daw Jil A. Wright, Robarge Jason, Ott Jurg. A putative RUNX1 binding site variant between SLC9A3R1 and NAT9 is associated with susceptibility to psoriasis. Nat Genet. 2003 Nov 9;35(4):349–356. doi: 10.1038/ng1268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewett Duncan, Samuelsson Lena, Polding Joanne, Enlund Fredrik, Smart Devi, Cantone Kathryn, See Chee Gee, Chadha Sapna, Inerot Annica, Enerback Charlotta. Identification of a psoriasis susceptibility candidate gene by linkage disequilibrium mapping with a localized single nucleotide polymorphism map. Genomics. 2002 Mar;79(3):305–314. doi: 10.1006/geno.2002.6720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh Katsuhiko, Sakakibara Masahiro, Yamasaki Sho, Takeuchi Arata, Arase Hisashi, Miyazaki Masaru, Nakajima Nobuyuki, Okada Masato, Saito Takashi. Cutting edge: negative regulation of immune synapse formation by anchoring lipid raft to cytoskeleton through Cbp-EBP50-ERM assembly. J Immunol. 2002 Jan 15;168(2):541–544. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.2.541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karason Ari, Gudjonsson Johann E., Upmanyu Ruchi, Antonsdottir Arna A., Hauksson Valdimar B., Runasdottir E. Hjaltey, Jonsson Hjortur H., Gudbjartsson Daniel F., Frigge Michael L., Kong Augustine. A susceptibility gene for psoriatic arthritis maps to chromosome 16q: evidence for imprinting. Am J Hum Genet. 2002 Dec 9;72(1):125–131. doi: 10.1086/345646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga Tetsuya, Duan Hong, Urabe Kazunori, Furue Masutaka. In situ localization of CD83-positive dendritic cells in psoriatic lesions. Dermatology. 2002;204(2):100–103. doi: 10.1159/000051825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopp T., Kieffer J. D., Rot A., Strommer S., Stingl G., Kupper T. S. Inflammatory skin disease in K14/p40 transgenic mice: evidence for interleukin-12-like activities of p40. J Invest Dermatol. 2001 Sep;117(3):618–626. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.2001.01441.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopp Tamara, Lenz Petra, Bello-Fernandez Concha, Kastelein Robert A., Kupper Thomas S., Stingl Georg. IL-23 production by cosecretion of endogenous p19 and transgenic p40 in keratin 14/p40 transgenic mice: evidence for enhanced cutaneous immunity. J Immunol. 2003 Jun 1;170(11):5438–5444. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.11.5438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger Gerald G., Callis Kristina P. Development and use of alefacept to treat psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003 Aug;49(2 Suppl):S87–S97. doi: 10.1016/mjd.2003.552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger James G. The immunologic basis for the treatment of psoriasis with new biologic agents. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002 Jan;46(1):1–26. doi: 10.1067/mjd.2002.120568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebwohl Mark. Psoriasis. Lancet. 2003 Apr 5;361(9364):1197–1204. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)12954-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebwohl Mark, Tyring Stephen K., Hamilton Tiffani K., Toth Darryl, Glazer Scott, Tawfik Naji H., Walicke Patricia, Dummer Wolfgang, Wang Xiaolin, Garovoy Marvin R. A novel targeted T-cell modulator, efalizumab, for plaque psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2003 Nov 20;349(21):2004–2013. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa030002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Edmund, Trepicchio William L., Oestreicher Judith L., Pittman Debra, Wang Frank, Chamian Francesca, Dhodapkar Madhav, Krueger James G. Increased expression of interleukin 23 p19 and p40 in lesional skin of patients with psoriasis vulgaris. J Exp Med. 2004 Jan 5;199(1):125–130. doi: 10.1084/jem.20030451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonardi Craig L., Powers Jerold L., Matheson Robert T., Goffe Bernard S., Zitnik Ralph, Wang Andrea, Gottlieb Alice B., Etanercept Psoriasis Study Group Etanercept as monotherapy in patients with psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2003 Nov 20;349(21):2014–2022. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa030409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor J. M., Barker J. N., Ross E. L., MacDonald D. M. Epidermal dendritic cells in psoriasis possess a phenotype associated with antigen presentation: in situ expression of beta 2-integrins. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992 Sep;27(3):383–388. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(92)70203-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestle F. O., Turka L. A., Nickoloff B. J. Characterization of dermal dendritic cells in psoriasis. Autostimulation of T lymphocytes and induction of Th1 type cytokines. J Clin Invest. 1994 Jul;94(1):202–209. doi: 10.1172/JCI117308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestle F. O., Zheng X. G., Thompson C. B., Turka L. A., Nickoloff B. J. Characterization of dermal dendritic cells obtained from normal human skin reveals phenotypic and functionally distinctive subsets. J Immunol. 1993 Dec 1;151(11):6535–6545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson Peter, Holmberg Jens, Tordsson Jesper, Lu Shemin, Akerström Bo, Holmdahl Rikard. Positional identification of Ncf1 as a gene that regulates arthritis severity in rats. Nat Genet. 2002 Dec 2;33(1):25–32. doi: 10.1038/ng1058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppmann B., Lesley R., Blom B., Timans J. C., Xu Y., Hunte B., Vega F., Yu N., Wang J., Singh K. Novel p19 protein engages IL-12p40 to form a cytokine, IL-23, with biological activities similar as well as distinct from IL-12. Immunity. 2000 Nov;13(5):715–725. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)00070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine R. Convergence of TNFalpha and IFNgamma signalling pathways through synergistic induction of IRF-1/ISGF-2 is mediated by a composite GAS/kappaB promoter element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997 Nov 1;25(21):4346–4354. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.21.4346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prokunina Ludmila, Castillejo-López Casimiro, Oberg Fredrik, Gunnarsson Iva, Berg Louise, Magnusson Veronica, Brookes Anthony J., Tentler Dmitry, Kristjansdóttir Helga, Gröndal Gerdur. A regulatory polymorphism in PDCD1 is associated with susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus in humans. Nat Genet. 2002 Oct 28;32(4):666–669. doi: 10.1038/ng1020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahman P., Bartlett S., Siannis F., Pellett F. J., Farewell V. T., Peddle L., Schentag C. T., Alderdice C. A., Hamilton S., Khraishi M. CARD15: a pleiotropic autoimmune gene that confers susceptibility to psoriatic arthritis. Am J Hum Genet. 2003 Jul 23;73(3):677–681. doi: 10.1086/378076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahman P., Elder J. T. Genetic epidemiology of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005 Mar;64 (Suppl 2):ii37–ii41. doi: 10.1136/ard.2004.030775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottman J. B., Smith T. L., Ganley K. G., Kikuchi T., Krueger J. G. Potential role of the chemokine receptors CXCR3, CCR4, and the integrin alphaEbeta7 in the pathogenesis of psoriasis vulgaris. Lab Invest. 2001 Mar;81(3):335–347. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.3780242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi Noriko, Takahashi Takeshi, Hata Hiroshi, Nomura Takashi, Tagami Tomoyuki, Yamazaki Sayuri, Sakihama Toshiko, Matsutani Takaji, Negishi Izumi, Nakatsuru Syuichi. Altered thymic T-cell selection due to a mutation of the ZAP-70 gene causes autoimmune arthritis in mice. Nature. 2003 Nov 27;426(6965):454–460. doi: 10.1038/nature02119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson L., Enlund F., Torinsson A., Yhr M., Inerot A., Enerbäck C., Wahlström J., Swanbeck G., Martinsson T. A genome-wide search for genes predisposing to familial psoriasis by using a stratification approach. Hum Genet. 1999 Dec;105(6):523–529. doi: 10.1007/s004399900182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenolikar S., Weinman E. J. NHERF: targeting and trafficking membrane proteins. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2001 Mar;280(3):F389–F395. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.2001.280.3.F389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortman Ken, Liu Yong-Jun. Mouse and human dendritic cell subtypes. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002 Mar;2(3):151–161. doi: 10.1038/nri746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuhiro Shinya, Yamada Ryo, Chang Xiaotian, Suzuki Akari, Kochi Yuta, Sawada Tetsuji, Suzuki Masakatsu, Nagasaki Miyuki, Ohtsuki Masahiko, Ono Mitsuru. An intronic SNP in a RUNX1 binding site of SLC22A4, encoding an organic cation transporter, is associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Genet. 2003 Nov 9;35(4):341–348. doi: 10.1038/ng1267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomfohrde J., Silverman A., Barnes R., Fernandez-Vina M. A., Young M., Lory D., Morris L., Wuepper K. D., Stastny P., Menter A. Gene for familial psoriasis susceptibility mapped to the distal end of human chromosome 17q. Science. 1994 May 20;264(5162):1141–1145. doi: 10.1126/science.8178173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tominaga K., Yoshimoto T., Torigoe K., Kurimoto M., Matsui K., Hada T., Okamura H., Nakanishi K. IL-12 synergizes with IL-18 or IL-1beta for IFN-gamma production from human T cells. Int Immunol. 2000 Feb;12(2):151–160. doi: 10.1093/intimm/12.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Victor Frank C., Gottlieb Alice B. TNF-alpha and apoptosis: implications for the pathogenesis and treatment of psoriasis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2002 Dec;1(3):264–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villadsen Louise S., Schuurman Janine, Beurskens Frank, Dam Tomas N., Dagnaes-Hansen Frederik, Skov Lone, Rygaard Jorgen, Voorhorst-Ogink Marleen M., Gerritsen Arnout F., van Dijk Marc A. Resolution of psoriasis upon blockade of IL-15 biological activity in a xenograft mouse model. J Clin Invest. 2003 Nov;112(10):1571–1580. doi: 10.1172/JCI18986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voltz J. W., Weinman E. J., Shenolikar S. Expanding the role of NHERF, a PDZ-domain containing protein adapter, to growth regulation. Oncogene. 2001 Oct 1;20(44):6309–6314. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinman E. J. New functions for the NHERF family of proteins. J Clin Invest. 2001 Jul;108(2):185–186. doi: 10.1172/JCI13518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollenberg A., Kraft S., Hanau D., Bieber T. Immunomorphological and ultrastructural characterization of Langerhans cells and a novel, inflammatory dendritic epidermal cell (IDEC) population in lesional skin of atopic eczema. J Invest Dermatol. 1996 Mar;106(3):446–453. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12343596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollenberg Andreas, Wagner Moritz, Günther Sandra, Towarowski Andreas, Tuma Evelyn, Moderer Martina, Rothenfusser Simon, Wetzel Stefanie, Endres Stefan, Hartmann Gunther. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells: a new cutaneous dendritic cell subset with distinct role in inflammatory skin diseases. J Invest Dermatol. 2002 Nov;119(5):1096–1102. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.2002.19515.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia Yu-Ping, Li Baosheng, Hylton Donna, Detmar Michael, Yancopoulos George D., Rudge John S. Transgenic delivery of VEGF to mouse skin leads to an inflammatory condition resembling human psoriasis. Blood. 2003 Mar 20;102(1):161–168. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-12-3793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Xianghong, Krueger James G., Kao Ming-Chih J., Lee Ed, Du Fenghe, Menter Alan, Wong Wing Hung, Bowcock Anne M. Novel mechanisms of T-cell and dendritic cell activation revealed by profiling of psoriasis on the 63,100-element oligonucleotide array. Physiol Genomics. 2003 Mar 18;13(1):69–78. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00157.2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]