Protein S-Nitrosylation: Determinants of Specificity and Enzymatic Regulation of S-Nitrosothiol-Based Signaling (original) (raw)
Abstract
Significance: Protein S-nitrosylation, the oxidative modification of cysteine by nitric oxide (NO) to form protein S-nitrosothiols (SNOs), mediates redox-based signaling that conveys, in large part, the ubiquitous influence of NO on cellular function. S-nitrosylation regulates protein activity, stability, localization, and protein–protein interactions across myriad physiological processes, and aberrant S-nitrosylation is associated with diverse pathophysiologies.
Recent Advances: It is recently recognized that S-nitrosylation endows S-nitroso-protein (SNO-proteins) with S-nitrosylase activity, that is, the potential to trans-S-nitrosylate additional proteins, thereby propagating SNO-based signals, analogous to kinase-mediated signaling cascades. In addition, it is increasingly appreciated that cellular S-nitrosylation is governed by dynamically coupled equilibria between SNO-proteins and low-molecular-weight SNOs, which are controlled by a growing set of enzymatic denitrosylases comprising two main classes (high and low molecular weight). S-nitrosylases and denitrosylases, which together control steady-state SNO levels, may be identified with distinct physiology and pathophysiology ranging from cardiovascular and respiratory disorders to neurodegeneration and cancer.
Critical Issues: The target specificity of protein S-nitrosylation and the stability and reactivity of protein SNOs are determined substantially by enzymatic machinery comprising highly conserved transnitrosylases and denitrosylases. Understanding the differential functionality of SNO-regulatory enzymes is essential, and is amenable to genetic and pharmacological analyses, read out as perturbation of specific equilibria within the SNO circuitry.
Future Directions: The emerging picture of NO biology entails equilibria among potentially thousands of different SNOs, governed by denitrosylases and nitrosylases. Thus, to elucidate the operation and consequences of S-nitrosylation in cellular contexts, studies should consider the roles of SNO-proteins as both targets and transducers of S-nitrosylation, functioning according to enzymatically governed equilibria.
Keywords: nitric oxide, S-nitrosylation, denitrosylation, redox signaling, S-nitrosylase
Introduction
Reversible post-translational protein modifications are essential regulators of cellular function. Oxidative modifications of cysteine (Cys) thiols provide a mechanism for redox-based control of protein activity. Generally, reversible Cys modifications subserve signaling functions whereas irreversible modifications result in loss of regulatory control (76, 173). Reversible Cys modifications include Cys sulfenylation (S-OH), S-glutathionylation (S-SG), and S-nitrosylation (S-NO). Chief among these modifications with respect to prevalence and demonstrated physiological signaling functions is S-nitrosylation, a covalent modification in which a nitric oxide (NO)-derived group is attached to a Cys thiol to generate an S-nitrosothiol (SNO), providing a ubiquitous mechanism for cellular signaling. NO was first identified as the endothelium-derived relaxing factor and was demonstrated to vasodilate blood vessels through activation of guanylyl cyclase to produce the second messenger cyclic GMP (cGMP) (82, 126, 141). However, it is now understood that NO exerts the majority of its biological influence through protein S-nitrosylation, affecting myriad cellular processes in physiology and pathophysiology, including the regulation of both activation and deactivation of guanylyl cyclase (3, 53, 58, 76, 117, 161). Thus, NO may be viewed as the prototypic redox-based signal.
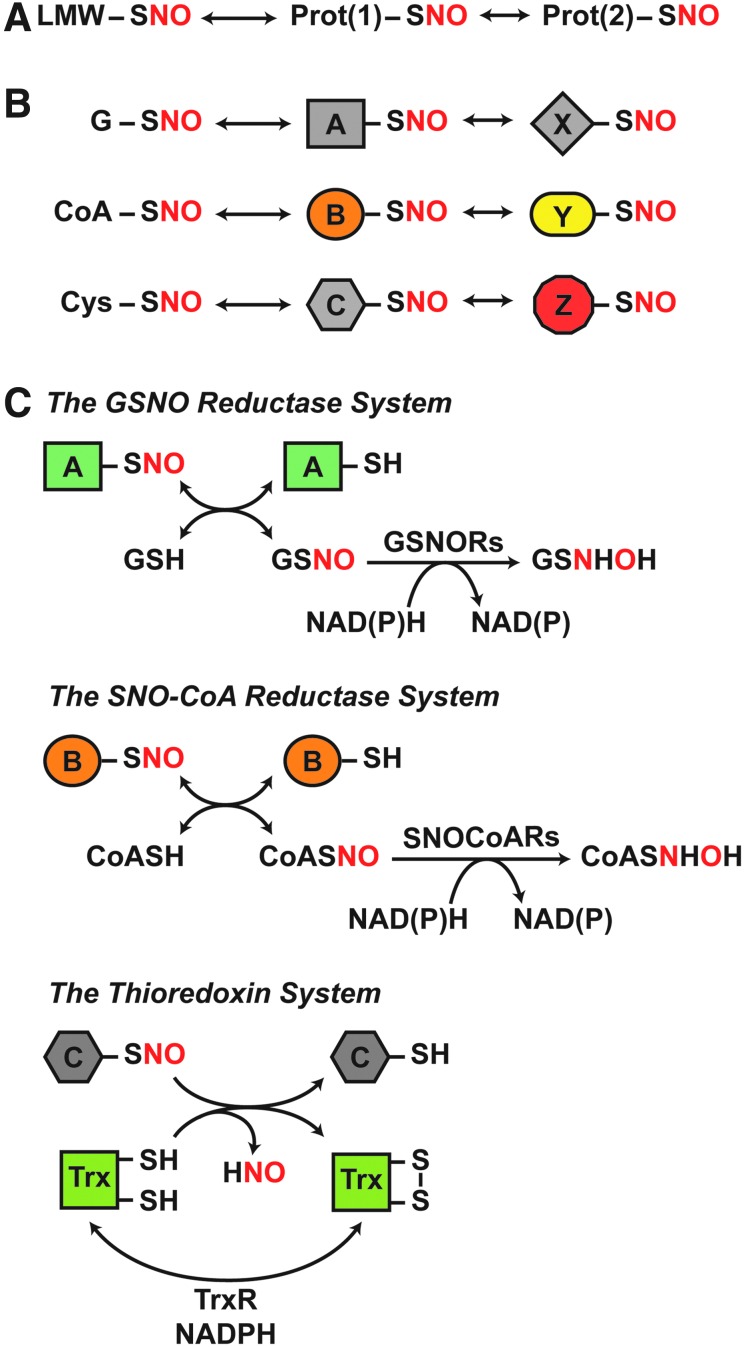
NO is predominantly generated by nitrate reductases in microbes and plants and by three isoforms of NO synthase (NOS) in mammalian cells: neuronal NOS (nNOS; NOS1), inducible NOS (iNOS; NOS2), and endothelial NOS (eNOS; NOS3). In principle, SNOs can initially form via multiple chemical routes that formally entail a one-electron oxidation, including reaction of NO with thiyl radical, transfer of the NO group from metal-NO complexes to Cys thiolate, or reaction of Cys thiolate with nitrosating species generated by NO auto-oxidation, exemplified by dinitrogen trioxide (N2O3) (60). However, the emerging evidence favors a primary role for metalloproteins in catalyzing de novo S-nitrosylation in situ (5, 26, 61, 119, 165), including under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions. The NO group can then transfer between donor and acceptor Cys thiols via trans-S-nitrosylation (198), which likely acts as a primary mechanism for S-nitrosylation in physiological settings. S-nitrosylation occurs both in proteins, producing S-nitroso-proteins (SNO-proteins), and in low-molecular-weight (LMW) thiols, including glutathione (GSH) and coenzyme A (CoA), generating S-nitrosoglutathione (GSNO) and S-nitroso-coenzyme A (SNO-CoA), respectively (2, 21). Protein and LMW-SNOs exist in thermodynamic equilibria, which are governed by the removal of SNO-proteins by SNO-protein denitrosylases (namely thioredoxin [Trx] 1/2 and thioredoxin-related protein of 14 kDa [Trp14]) or of LMW-SNOs by GSNO and SNO-CoA metabolizing activities (Fig. 1). In effect, NO-based signal transduction is represented by equilibria between LMW-SNOs and protein SNOs, and between SNO-proteins linked by transnitrosylation. Enzymatic governance of these equilibria, therefore, provides a basis for the regulation of NO-based signal transduction.
FIG. 1.
Coupled, dynamic equilibria that govern protein S-nitrosylation are regulated by enzymatic denitrosylases. (A) SNO-proteins are in equilibrium with LMW-SNOs and can further participate in protein-to-protein transfer of the NO group (trans-S-nitrosylation) to subserve NO-based signaling. (B) Transnitrosylation by both identified LMW-SNOs (G, glutathione; CoA, coenzyme A; Cys, cysteine) and SNO-proteins will result in distinct sets of SNO-proteins that mediate specific SNO signaling cascades. (C) Distinct enzymatic denitrosylases regulate the coupled equilibria that confer specificity to SNO-based signaling. These include GSNORs and SNO-CoA reductases, which regulate protein S-nitrosylation by GSNO and SNO-CoA, respectively. These LMW-SNOs are in equilibrium with cognate SNO-proteins. In contrast, Trxs directly denitrosylate SNO-proteins. The reaction schemes illustrated are detailed in the Enzymatic Denitrosylation section. GSNO, S-nitrosoglutathione; GSNORs, GSNO reductases; LMW-SNOs, low-molecular-weight S-nitrosothiol; NO, nitric oxide; SNO, S-nitrosothiol; SNO-CoA, S-nitroso-coenzyme A; SNO-protein, S-nitroso-protein; Trx, thioredoxin.
SNO Specificity
It is well established that protein S-nitrosylation exhibits remarkable spatiotemporal specificity in the targeting of protein Cys residues (44, 76, 97). Physiological amounts of NO typically target one or few Cys within a protein and this is sufficient to alter protein function and associated physiology or pathophysiology (39, 77, 166). It has emerged as a general rule that S-nitrosylation and alternative S-oxidative modifications, in particular those mediated by reactive oxygen species, most often target separate populations of Cys and, whether the same or different Cys are targeted, exert disparate functional effects (67, 165). Thus, proteomic analyses of Cys modifications have revealed that, under physiological conditions, there is little overlap between different redox-based Cys modifications (45, 67). Functional specificity is well illustrated in the case of the bacterial transcription factor OxyR, in which S-nitrosylation versus oxygen-based oxidative modification of a single, critical Cys activates distinct regulons (94, 165). Also, in the case of mammalian hemoglobin (Hb), S-nitrosylation versus oxidative modification of the same, single Cys mediate vasodilation and vasoconstriction, respectively (142). However, S-nitrosylation and alternative oxidative modifications may also target distinct Cys to exert coordinated effects as in the case of the ryanodine receptor/Ca2+-release channel (RyR) of mammalian skeletal muscle (RyR1), where S-nitrosylation of a single critical Cys and O2-based oxidation of a distinct set of Cys work in concert to activate Ca2+ release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) (49, 50, 179, 180, 205). There are a variety of mechanisms implicated in targeting S-nitrosylation of specific protein substrates and Cys residues within target proteins.
Acid-base and hydrophobic motifs
A role for an acid-base motif in determining the specificity of protein S-nitrosylation was first suggested by the analysis of S-nitrosylation of Cysβ93 of Hb (176). In this model, a histidine residue proximal to Cysβ93 in the oxygenated, R-state of Hb facilitates base-catalyzed S-nitrosylation whereas a proximal aspartic acid residue in the deoxygenated T-state facilitates acid-catalyzed denitrosylation, coupling oxygenation status of Hb to SNO formation and release in the respiratory cycle (72, 176). Thus, close proximity of charged acidic and basic side chains would regulate S-nitrosylation by influencing both thiol pKa (and, thus, reactivity) and SNO stability. Subsequent analysis suggested a more general acid-base motif, (K,R,H,D,E)C(D,E), where proximity of the acidic residue (D,E) is crucial (176). Acid-base motifs may also emerge from protein tertiary structure, as demonstrated for methionine adenosyltransferase (MAT) (143). S-nitrosylation of Cys121 of MAT is facilitated by distal primary sequence residues that are brought into proximity of Cys121 by tertiary protein structure: Arg357 and Arg363, which lower Cys121 pKa (143). Tertiary structure-derived acid-base motifs have also been shown to direct S-nitrosylation in caspase-3 and aquaporin-1 (77).
It is important to note that the mechanisms through which acidic and basic side chains direct protein S-nitrosylation are not restricted to control of target thiol pKa. In the case of MAT, Asp355 is proximate in tertiary structure to the target Cys121, and the acidic side chain of Asp355 promotes donation of an NO group from GSNO (143). Similarly, Savidge et al. (160) identified a conserved acid-base motif in the Cys protease domain of Clostridium difficile exotoxins TcdA and TcdB, in which tertiary structure brings Glu743 and His653 in proximity to catalytic Cys698 of TcdB. Mutation of Glu743 diminishes S-nitrosylation of Cys698, likely by altering the ability of GSNO to bind in a transnitrosylating orientation. A modified acid-base motif (that included hydrophobic elements) to predict GSNO-mediated protein S-nitrosylation was proposed for the bacterial transcription factor OxyR, based on oriented GSNO binding (76, 94). Docking analysis of multiple proteins has confirmed GSNO binding sites that likely mediate protein S-nitrosylation (76, 112). An expanded acid-base motif, representing acids and bases within 8 Å of sites of S-nitrosylation, has also been implicated in protein–protein interactions that may subserve transnitrosylation, as described later (112).
Hydrophobic environments, including membranes or those generated by protein structure and/or protein–protein interactions, can facilitate the formation of protein SNOs (77). Regions of hydrophobicity within a protein can provide sites of micellar catalysis by concentrating NO and O2, thereby promoting formation of nitrosating species, as was demonstrated for SNO-albumin, or may channel NO to target thiols, as was hypothesized for the transfer of NO from heme iron to Cys thiol in Hb (77, 107, 128, 151). Conceivably, interactions with transition metal (iron) nitrosyls within (or adjacent to) hydrophobic regions can also mediate protein S-nitrosylation, as in the cases of non-heme dinitrosyl iron complexes (26, 45, 76). Radical nitrosylating species may also be stabilized in hydrophobic compartments, promoting S-nitrosylation (60, 76). Hydrophobicity might play a role in S-nitrosylation of cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2), Src kinase, and tubulin at solvent-inaccessible Cys (3, 4, 44, 73, 93, 130). The importance of local hydrophobicity is exemplified by RyR1, in which one of fifty free Cys is targeted for S-nitrosylation and that Cys lies within a hydrophobic calmodulin-binding region (50, 179).
Proteomic analyses of S-nitrosylation sites have expanded our understanding of the role of motifs in targeting S-nitrosylation, in particular by pointing to the potential importance of residues that are more distal in primary sequence to the targeted SNO-Cys and therefore of trans-S-nitrosylative interactions between target proteins and both SNO-proteins and LMW-SNOs (Table 1). Probing of dbSNO 2.0 identified enrichment of charged amino acids in the primary sequence and tertiary structure near SNO-Cys (35). Greco et al. (70) found evidence of a primary sequence acid-base motif in SNO-proteins when the sequence was expanded to include residues −6 and +6 from the target Cys, and they identified SNO-Cys within hydrophobic regions of proteins. Analysis of the endogenous mouse liver proteome identified a linear acid-base motif around SNO-Cys and showed preferential location at accessible surfaces of α-helices and coils (45). The conformational flexibility of these secondary structures coupled with the presence of charged residues would aid in protein–protein interactions or protein–LMW thiol interactions to facilitate transnitrosylation. Marino and Gladyshev (112) analyzed 70 known SNO-Cys sites and provided a spatially expanded acid-base motif within 8 Å of the target Cys that might facilitate SNO-forming interactions. SNO site analysis of a dataset derived from treatment with S-nitrosylating agents (34) confirmed acid-base motifs while also emphasizing the importance of local hydrophobicity, and it correlated acid-base motifs with α-helices and hydrophobic motifs with β-sheets. It also identified a role for the +2 position in mediating protein–protein interactions, a position independently shown to facilitate the interaction of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) and sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) for transnitrosylation (96). Lee et al. (99) identified a linear hydrophobic motif and mutagenic analysis eliminated S-nitrosylation in some motif-containing proteins, validating its predictive power. Recently, Jia et al. (90) identified a mixed acid/base and hydrophobic motif that is recognized by the cognate transnitrosylase S100A9. Specifically, a complex of iNOS and S100A8/A9 targets proteins with the motif (I,L)XCXX(D,E) for transnitrosylation by S100A9. Introduction of the SNO motif into naive proteins conferred targeting by S100A8/9 (90).
Table 1.
S-Nitrosylation Motif Elements from S-Nitrosothiol-Proteome Analysis
| Source | Motif SNO sites/total SNO sites | Motif element | Proposed motif function | Identified linear motifa | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Curated list of NO-regulated proteins | 18/27 | Charged residues | Alter thiol reactivity | (K,R,H,D,E)C(D,E) | (176) |
| Curated list of SNO-proteins | 69/72 | Charged residues (at 8 Å) | Facilitate interactions | — | (112) |
| 45/72 | Solvent exposure | — | |||
| Endogenous mouse liver | ∼216/309 | Acidic residues | Facilitate interactions | DC CXXE | (45) |
| ∼57/142 | α-Helices | Facilitate interactions | |||
| 37/309 | GC couplet | — | GC | ||
| Solvent exposure | — | ||||
| Cys-SNO- or PAPANO-treated HASMCs | 16/18 | Charged residues | Alter thiol reactivity | (E,D)XXXC(E,D)XXC CX(K,H,R) | (70) |
| 3/18 | Hydrophobicity | — | |||
| SNO-Cys in peripheral blood monocytes | 5/19 | Charged residues | Transnitrosylation (by S100A8/A9) | (I,L)XCXX(D,E) | (90) |
| Hydrophobicity | |||||
| SNAP-treated MS-1 cells | 200/586 | Charged residues | — | (D,E)XXXC CX(K,R,H) (α-helix)CX(E) (α-helix) | (34) |
| 261/586 | Hydrophobicity | Facilitate interactions | CX(V,I,L) (β-sheet)CXXXIIXXXCVXXC CXA | ||
| Alter thiol reactivity | |||||
| 20/586 | CXG | ||||
| 60/586 | CXT | ||||
| GSNO-treated proteins | 80/138 | Hydrophobicity | — | (A,V,L,I)(A,V,L,I)XXXC | (99) |
| Cys-SNO or LPS treatment of BV-2 cells | Charged residues | — | KXXXXXC CXXXXXDKXC | (146) | |
| Hydrophobicity | — | AXC CXXXXXI | |||
| MXXC | |||||
| dbSNO 2.0 | 1079/1250 (Human) | Charged residues | — | Numerous motifs | (35) |
| 2315/2647 (Mouse) |
In sum, work identifying protein S-nitrosylation motifs demonstrates multiplex determination of the basis of specificity: Charged residues or local hydrophobicity may influence Cys reactivity or may facilitate protein–protein and protein–LMW thiol interactions to target Cys for S-nitrosylation/trans-S-nitrosylation, and these determinants can arise from primary, tertiary, or quaternary structure; whereas thiol pKa is not necessarily predictive of S-nitrosylation (45, 112). It is important to note that, in general, the emerging centrality of transnitrosylation implies an important role for protein tertiary structure that determines solvent accessibility/surface exposure of target thiols, which will not be captured by motifs based on primary sequence or secondary structure per se. The multiplex determination of S-nitrosylation, thus, underlies the specificity of SNO formation that allows it to act as a broad signaling mechanism. Indeed, computational analysis of the annotated protein data-bases using predicted SNO motifs indicates that ∼70% of the proteome may be targeted by S-nitrosylation, mainly at conserved Cys residues (1). However, proteomic analysis of endogenous SNO sites, rather than those from samples treated with RSNO donors (as has generally been the case) may provide a more physiological picture of predictive motifs, inasmuch as supra-physiological amounts of RSNO donors may S-nitrosylate Cys that would not be targeted physiologically or may catalyze higher oxidation states that would not occur in vivo.
Interaction with NOSs
Compartmentalization of substrates for S-nitrosylation with an NOS, which may entail their interaction with NOS either directly or through scaffolding proteins, provides a mechanism for specific targeting. High local concentrations of NO may promote the formation of nitrosating species (such as N2O3) (69). Intriguingly, each isoform of NOS is S-nitrosylated, potentially through metal auto-catalysis, and may therefore act as a transnitrosylating partner for scaffolded proteins, either directly or via formation of LMW-SNOs (47, 48, 120, 147, 153, 174). NOS expression is specific at the level of organs, cells, and subcellular compartments (191). In the heart, nNOS is localized to the SR whereas eNOS is localized to caveolae; consequently, nNOS regulates RyR2 S-nitrosylation, and eNOS regulates L-type Ca2+ channel S-nitrosylation to affect protein activity and myocyte contractility (9, 102). Localization of eNOS to the Golgi generates a local NO pool that is capable of targeting S-nitrosylation to compartmentalized proteins, and addition of a nuclear localization signal to eNOS increases nuclear S-nitrosylation (86). The finest grain of compartmentation is represented by the binding to separate regions of an individual target protein by different NOSs that results in the S-nitrosylation of different Cys (unpublished observations).
Numerous NOS–protein interactions have been demonstrated to target protein S-nitrosylation, either through direct interaction with the target protein or through a protein scaffold. nNOS scaffolds with the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) through postsynaptic density protein 95 (PSD-95); calcium flux through the NMDAR activates nNOS to target both NMDAR and PSD-95 for S-nitrosylation (27, 38, 78, 95). The scaffold protein carboxyl-terminal PDZ ligand of neuronal nitric oxide synthase protein (CAPON) mediates the interaction of nNOS and the G-protein Dexras1 to target Dexras1 S-nitrosylation (51). nNOS can bind directly and S-nitrosylate glucokinase in pancreatic β-cells, coupling insulin-stimulated NO production to glucokinase activity (155). After stimulation of the β2-adrenergic receptor, eNOS interacts with and S-nitrosylates β-arrestin 2 (β-arr2), G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2), and dynamin to regulate β2-adrenergic receptor trafficking (72, 136, 193, 197). iNOS directly binds and activates COX-2 via S-nitrosylation of a single Cys residue (93). Jia et al. (90) merged the concepts of NOS scaffolding and NO targeting. A complex including iNOS and S100A8/A9 provides both a source of NO and a mechanism for targeted transnitrosylation by S100A9 of multiple proteins with the motif I/L-X-C-X2-D/E. Interestingly, S100A9 expression is increased in mouse liver lacking a key denitrosylase, potentially identifying crosstalk between transnitrosylating and denitrosylating pathways (135). The co-localization of NOSs with target proteins, through either subcellular compartmentalization or protein–protein interactions, is thus an important mechanism in achieving S-nitrosylation specificity and, in some cases, may initiate transnitrosylation cascades to subserve NO signaling.
SNO Stability and Reactivity
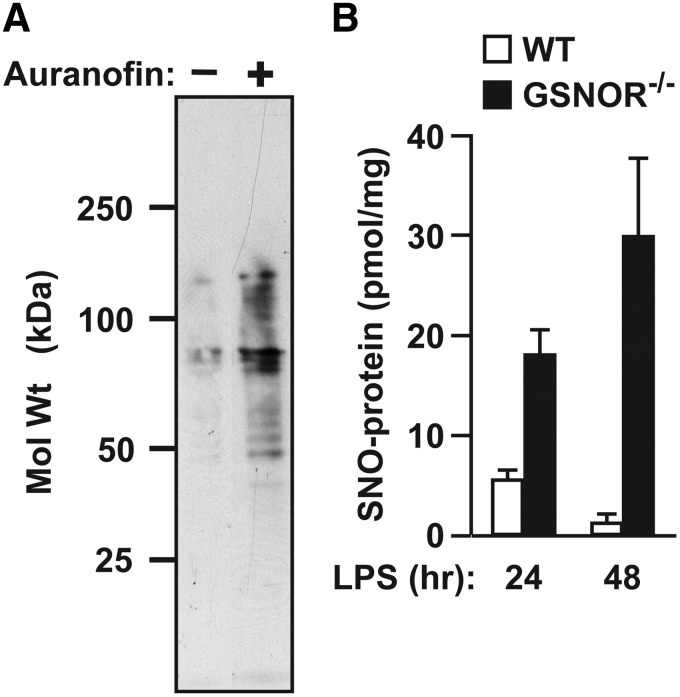
Cellular SNO-protein levels are governed by rates of both S-nitrosylation and denitrosylation. SNOs are readily detected in situ under basal conditions, and some protein SNOs are stable in the presence of NOS inhibitors; further, protein S-nitrosylation increases on inhibition of denitrosylases, indicating that steady-state S-nitrosylation is a function of denitrosylase activity (i.e., enzymatic breakdown) (2, 22, 56, 57, 68, 79, 87, 109, 111) (Fig. 2). Formally, RSNO decomposition may occur through a variety of mechanisms. Reducing agents, metal ions, heat, ultraviolet light, reactive oxygen species, and nucleophiles can mediate SNO decomposition through homolytic and heterolytic cleavage of the SNO bond to radical or ionic species (6, 175). Homolytic bond dissociation energies of RSNOs have been estimated between 20 and 32 kcal/mol, corresponding to spontaneous decomposition rates of seconds to years; since endogenous SNO probably trend toward the upper end of this range, homolysis is unlikely to be physiologically relevant (14, 175, 194). Although free metals, in particular Cu2+, can rapidly decompose RSNOs in vitro, metals are often sequestered in vivo and probably do not contribute appreciably to physiological denitrosylation (198). Thiols are abundant in cells and can react with SNOs to initiate NO transfer between thiols (primary reaction channel) or facilitate NO release and disulfide formation (in some cases). Both mechanisms are utilized by enzymatic denitrosylases to reduce SNO-proteins (Fig. 1 and vide infra), providing the principal physiological means of denitrosylation. This section discusses control of SNO stability and reactivity before considering enzymatic mechanisms for protein denitrosylation, which predominate in situ and are required for physiological signaling.
FIG. 2.
Steady-state protein S-nitrosylation reflects denitrosylase activity. (A) In cultured human embryonic kidney cells, suppression of Trx-mediated denitrosylation with the TrxR inhibitor auranofin results in greatly enhanced steady-state levels of SNO-proteins (as detected by the SNO-RAC method) (57). (B) After induction of iNOS by systemic administration of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS), steady-state levels of hepatic SNO-protein are greatly increased in the genetic absence of GSNOR [as assessed by photolysis-chemiluminescence; modified from Liu _et al._ (106)]. iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; TrxR, thioredoxin reductase.
RSNO bond chemistry
Initial studies on the stability of LMW RSNOs highlighted the importance of the R-group in RSNO stability. Electron-withdrawing R-groups (SNO-destabilizing) inhibited Bacillus cereus spore outgrowth compared with electron-donating R-groups (SNO-stabilizing) (125, 173). Primary and secondary RSNOs decomposed rapidly whereas tertiary RSNOs, such as S-nitroso-N-acetyl-penacillamine (SNAP), were stable almost indefinitely and could be isolated for storage (175). Roy et al. (159) proposed a model in which tertiary RSNOs prefer a resonance structure with S = N double-bond character, increasing the strength of the S-N bond and reducing NO lability. However, a kinetic (rather than thermodynamic) basis for “stability” of tertiary RSNOs is likely: The bulky R-group of tertiary RSNOs sterically hinders reactivity (7, 13, 14, 132). Indeed, primary and tertiary SNOs adopt planar cis or trans conformations, respectively, with the cis conformation slightly favored thermodynamically over trans (13). A large energy barrier to interconversion between conformers is consistent with the S = N double bond character (7), but such conformational restraints, which limit bond flexibility (to increase stability), may apply to either primary or tertiary RSNOs. By contrast, non-planar orientations of RSNO are intrinsically less stable. Hydrogen bonding and other interactions, as may occur in proteins, may also influence SNO stability. Thus, the protein R-group might affect protein SNO stability and reactivity through a variety of mechanisms.
Recently, Paige et al. (138) demonstrated that a subset of proteins S-nitrosylated by GSNO in cell lysates were relatively resistant to denitrosylation by GSH, pointing to changes in protein conformation that altered target Cys-SNO accessibility or SNO bond chemistry. Similarly, treatment of spinal cord explants with GSNO resulted in the formation of SNO-proteins and individual SNO-proteins were denitrosylated at substantially different rates after subsequent addition of GSH (158). The crystal structure of S-nitroso-hemoglobin (SNO-Hb) (32) has provided important structural insights into SNO stability. Within the R-state of Hb, Cysβ93-SNO is buried in a hydrophobic pocket that is inaccessible to solvent, thereby promoting stability; subsequent de-oxygenation of Hb and transition to the T-state expose SNO to the aqueous environment, facilitating liberation of the NO group for vascular bioactivity (91, 118). More generally, S-nitrosylation of proteins may alter charge distribution surrounding the target Cys, which may modulate protein–protein or protein–LMW thiol interactions to affect SNO stability and reactivity (112, 152).
SNOs may accept electrons and participate in various interactions with the protein backbone (32, 76). The protein R-group may thus influence the nature of the SNO moiety, including the S-N bond itself. Despite demonstrated planarity of the SNO group in crystal structures of small-molecule RSNOs (which suggests S-N double bond character), the S-N bond in most RSNOs (1.75–1.80 Å) is longer than usual (7, 43, 63), consistent with the propensity for transnitrosylative reactions (Fig. 3). Various interactions with atoms of the SNO group may alter transnitrosylation kinetics. Metal or Lewis acid coordination with sulfur destabilizes RSNOs and promotes decomposition; coordination with nitrogen or oxygen stabilizes RSNOs (8, 144). Timerghazin et al. (188) proposed a resonance model of the RSNO bond that predicts three structures: the putative RSNO resonance structure with an S-N single-bond, a zwitterionic structure with an S = N double-bond, and a novel ionic structure in which the RSNO is represented as a non-bonded ion pair. This model provides a framework for understanding SNO-thiol reactions, chiefly the propensity for trans-S-nitrosylating or S-thiolating reactions to occur: Interactions favoring electrophilicity at the nitrogen atom would promote transnitrosylation reactions, likely through nitroxyl disulfide (SNO2) formation (80); conversely, interactions favoring sulfur atom electrophilicity would preference S-thiolation (disulfide forming) reactions (Fig. 3). Proteins, therefore, could exert a high degree of control over SNO-thiol reactions through the interaction of charged residues with the SNO bond or by modulating the local chemical environment (183). In this sense, the reactive fate of the SNO-Cys is dictated by the local environment, with protein structure and characteristics of the aqueous milieu determining whether the SNO-protein–thiol reaction will be trans-S-nitrosylative or S-thiolative. Empirically and thermodynamically, the general case strongly favors trans-S-nitrosylation, as discussed in the following section.
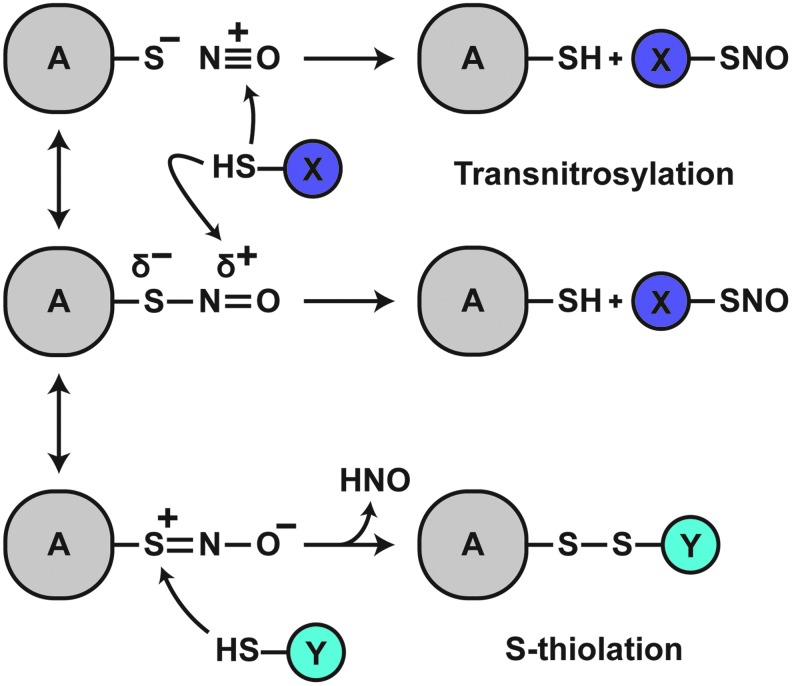
FIG. 3.
Differential RSNO reactivity. By default (middle scheme), a partial negative charge exists on the S atom of the SNO bond; a partial positive charge exists on the N atom. This intrinsically favors transnitrosylative reactions. Positive charge coordination with the S atom or negative charge coordination with the N or O atom would further increase electrophilicity of the N atom, enhancing the propensity for transnitrosylation (top). In contrast, negative charge coordination with the S atom or positive charge coordination with the N or O atom would increase electrophilicity of the S atom, preferencing S-thiolation reactions (bottom).
Protein SNO–thiol reaction bias
The identification of an increasing number of Cys-to-Cys transnitrosylases has established a critical role for transnitrosylation in NO-based signaling (3, 37, 90, 96, 142). Enzymatically targeted S-nitrosylation may rationalize empirical evidence that transnitrosylation reactions of RSNO predominate under physiological conditions. Mechanistically, activation barriers for thiolate attack at the N atom (in SNO) are reportedly lower than barriers for attack at the S atom, and transnitrosylation products are predicted to be more thermodynamically favorable (55). Reaction of thiolate with the S atom of RSNO generates the nitroxyl anion (NO−) leaving group, which is a spin-forbidden reaction; conditions conducive to nitroxyl (HNO) generation, which would be required to make this energetically favorable (12, 85, 181, 186), may be disfavored by physiologically relevant proteins. By contrast, the model reaction of GSNO with GSH in vitro supposes both N- and S-directed thiolate attack to rationalize myriad observed products; however, the control exerted by protein R-groups on SNO-generating thiol reactions is absent in this model, and low-yield S-directed reactions are observed because of high reactant concentrations (167, 200). Reaction of GSNO with an engineered protein nanopore primarily resulted in transnitrosylation reactions at physiological pH (36). In addition, SNAP does not participate in S-thiolation reactions, likely due to R-group steric hindrance (36).
SNO sites do not overlap S-oxidation sites
Examination of the endogenous SNO-proteome has provided information regarding the overlap between S-nitrosylation and other S-oxidative modifications at a given Cys. Doulias et al. (45) identified 328 SNO-Cys, none of which overlapped with Cys that participate in disulfide-bond formation or were S-glutathionylated. Gould et al. (67) also found minimal overlap between SNO-Cys and annotated disulfide bonds, consistent with predictions based on structural analysis that SNO-Cys were highly unlikely to undergo disulfide formation. Although S-nitrosylation might, in principle, promote S-glutathionylation, eNOS-deficient mice exhibited little change in the S-glutathionylation proteome (67, 116). The case of RyR1 is illustrative. It possesses ∼100 Cys residues, many of which are subject to oxidation in vivo. However, only one is modified by S-nitrosylation and that Cys is not included among those oxidized to either disulfide or sulfenic acid (180). Vicinality may provide a unique context in which S-thiolation reactions are preferred due to high localized thiol molarity (6), and, indeed, disulfide bond formation within some proteins can be catalyzed by S-nitrosylation (6, 62, 110). Nonetheless, it should be noted that examples of NO-catalyzed disulfide formation by endogenous NO (i.e., physiological amounts as opposed to high concentrations of NO donors) have, to the best of our knowledge, not been reported. Moreover, current methods of detection are unable to distinguish between disulfide bonds and SNO2, and, thus, some putative S-nitrosylation-catalyzed disulfides could instead represent SNO2s. Taken together, current data suggest that physiological SNOs exist primarily as a distinct population, and a confluence of protein-mediated interactions and protein-driven influence on SNO (versus thiol) reactivity, exemplified in protein transnitrosylation reactions, achieves specificity for SNO-based modifications (among the different oxidative Cys modifications) and determines SNO reactivity. As an illustrative example of multiple determination, the interaction between the anion exchange protein 1 (AE1) and SNO-Hb, which results usually in transnitrosylation of AE1 (N-directed attack), leads instead to disulfide formation (S-directed attack) after disruption of the native orientation between SNO in Hb and thiol in AE1 (142).
Enzymatic Denitrosylation
Because protein S-nitrosylation is a ubiquitous post-translational modification that operates across cell types and phylogeny to convey the influence of NO, the requirement for enzymatic machinery governing SNO-protein denitrosylation is evident. Presently, two major classes of denitrosylating enzymes comprising seven proteins have been identified: SNO-protein denitrosylases, typified by the Trx system, and LMW-SNO denitrosylases, including the GSNO reductase (GSNOR) and SNO-CoA reductase (SNO-CoAR) systems (Table 2). Additional denitrosylase activities have been reported (21), which remain to be validated under physiological conditions.
Table 2.
Targets of Enzymatic Denitrosylation
| Denitrosylase | Target |
|---|---|
| High-molecular-weight denitrosylases | |
| Trx1 | Caspase-3 (20), Caspase-8 (163), Caspase-9 (20), PTP1B (20), NF-κB (92), NSF (84), iNOS (17), nNOS (147), MEK1 (17), STAT3 (17), PRMT1 (17), PA28β (17) GAPDH (31), Actin (187), Annexin-1 (22), 14-3-3θ (22), ∼50 proteins (22), >400 proteins (17), >500 proteins (18) |
| Trx2 | Caspase-3 (20) |
| Trp14 | Caspase-3 (137), Cathepsin B (137) |
| Low-molecular-weight denitrosylases | |
| GSNO reductases | |
| GSNOR | GRK2 (197), β-arrestin 2 (136), RyR1 (123), RyR2 (16), PLN (83), NCX (83), Actin (83), TPM (144), cTnC (144), cTnI (144), LTCC (144), SERCA2a (144), MYBPC3 (144), HIF-1α (103), PPARγ (30), Cx43 (178), AGT (195), Apaf-1 (29), c-Jun (29), HSF1 (29), CNA (29), CUGBP1 (29), NF-M (29), Ras (115), TRAP1 (154), Stip1 (207), GAPDH (206), Caspase-6 (206), VDAC1 (206), ∼85 unique proteins (206), ∼76 unique proteins (39) |
| CBR1 | No identified targets |
| SNO-CoA reductases | |
| SNO-CoAR | GAPDH (2) |
| Adh6 | Erg10 (2), ∼15 proteins (2) |
The Trx system
The Trx system was initially identified as a major component of cellular redox homeostasis through its role as a disulfide reductase (40). The Trx system consists of Trx-1/2, thioredoxin reductase (TrxR), and NADPH. Using a dithiol active site (C-X-X-C), Trx1 reduces target protein disulfide bonds with concomitant oxidation of Cys32 and Cys35 of Trx1. Subsequent reduction of Trx1 by TrxR is coupled to NADPH consumption, regenerating reduced Trx1. In addition to its role in disulfide reduction, the Trx system plays a major role in SNO-protein denitrosylation (20, 164, 177). Trx-dependent denitrosylation likely proceeds through: (i) mixed disulfide formation via attack of the more nucleophilic active site Cys (Cys32 in Trx1) on the sulfur of the SNO bond, with release of nitroxyl anion (as HNO); (ii) resolution of the mixed disulfide by the second active site Cys to form oxidized Trx, and iii. reduction of Trx disulfide by TrxR (20) (Fig. 4A). Support for this mechanism was found in studies where Trx modified by mutation of the resolving Cys was employed to “trap” target SNO-proteins (17, 19). This analysis showed enhanced interaction of Trx with target proteins under conditions of elevated NO or SNO, whereas treatment with H2O2 (meant to oxidize proteins and form disulfide bonds) resulted in comparatively little protein trapping (17). These results indicate that SNO-proteins are a critical cellular substrate for Trx. A proposed, alternative initial step in Trx-mediated denitrosylation is transnitrosylation from the target protein to the active site Cys of Trx and subsequent release of nitroxyl anion (or HNO) (164, 177). Trx primarily exists in its reduced form due to TrxR activity, which may facilitate its role as a denitrosylase. Trx has also been reported to metabolize GSNO, but inefficiently, and a physiological role for this activity has not been demonstrated (129, 177). The thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) inhibits Trx denitrosylating activity; endogenous NO relieves this inhibition by repressing TXNIP, providing a mechanism to dynamically regulate Trx-mediated protein denitrosylation in response to NO (56).
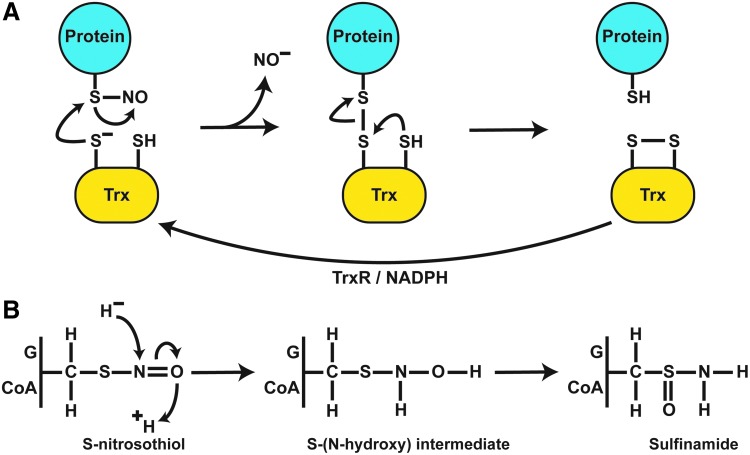
FIG. 4.
Enzymatic mechanisms of protein denitrosylation. (A) Denitrosylation by Trx requires a direct interaction with target SNO-proteins. Nucleophilic attack by an active Cys leads to mixed disulfide formation between Trx and target proteins with liberation of NO as a nitroxyl anion (likely as HNO). The mixed disulfide is resolved by the second active site Cys of Trx, generating oxidized Trx and reduced target protein thiol. Trx is subsequently reduced by TrxR and NADPH to regenerate denitrosylating activity. (B) A common reaction scheme exists for the reduction of GSNO and SNO-CoA by their cognate denitrosylases (GSNOR and SNO-CoA reductase). Hydride transfer from NAD(P)H to the N atom and protonation of the O atom lead to an S-(N-hydroxy) intermediate that rearranges to sulfinamide. HNO, nitroxyl.
Numerous substrates for Trx-mediated denitrosylation have been identified (Table 2). Constitutive and Fas-induced SNO-caspase-3 denitrosylation in the cytosol and mitochondria was ascribed to cytosolic Trx1 and mitochondrial Trx2, respectively (20, 111, 177). Trx also denitrosylates nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) after cytokine stimulation, further illustrating the importance of stimulus-coupled denitrosylation in activation of immune signaling (92). Trx likely mediates denitrosylation of insulin signaling components in adipocytes, a finding of particular importance since iNOS is induced in obesity (134, 145). Proteomic analyses have identified numerous proteins with a wide variety of cellular functions as targets of Trx-mediated denitrosylation, aiding in the elucidation of new roles for endogenous Trx-mediated denitrosylation (17, 18, 22, 185, 203). Further, analysis of targets of denitrosylation by Trx identified the motifs C-X5-K and C-X6-K within targeted SNO-proteins (202).
In addition to its role as a denitrosylase, Trx1 has been identified as a trans-S-nitrosylase (121). Trx1 in the oxidized state is S-nitrosylated at Cys73, which mediates the S-nitrosylation of caspase-3 and other targets, and uncouples Trx1 transnitrosylase and denitrosylase activities (120, 122, 201). The stability of SNO-Trx is regulated by both Trx- and GSH-mediated denitrosylation (164). Interestingly, charged residues proximal to Cys73 are required for Trx transnitrosylase activity, consistent with identified motif elements facilitating transnitrosylation reactions (122). Additional Trx1 transnitrosylation motifs have been proposed that involve proximal alanine residues (201). Of note, quantitative mass spectrometry allows for the distinction between targets of Trx-mediated S-nitrosylation and denitrosylation, and it may aid in delineating their roles (203).
Trp14 was recently identified as having denitrosylating activity toward GSNO and SNO-proteins, including caspase-3 and cathespsin B, and this activity was dependent on both TrxR1 and NADPH (137). Future work will be necessary to identify a role for Trp14 denitrosylating activity in vivo. Similarly, protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) has been reported to catalyze the denitrosylation of GSNO and SNO-PDI (169), though an in vivo role for this activity has not been established.
LMW-SNO denitrosylases
Two of the most abundant LMW cellular thiols are GSH and CoA. GSH is present in cells up to 10 m_M_ and is concentrated in airway lining fluid, where endogenous GSNO was first discovered (65); CoA levels significantly vary by cellular compartment, with concentrations near 2.5 m_M_ in mitochondria and 0.05 m_M_ in the cytosol (199). Both GSH and CoA can interact with and denitrosylate target proteins via transnitrosylation, generating GSNO and SNO-CoA, respectively (Fig. 1). Metabolism of GSNO and SNO-CoA by cognate denitrosylases (GSNOR; SNOCoAR) prevents further transnitrosylating activity of these RSNOs, which are in equilibrium with SNO-proteins. To date, GSNOR and carbonyl reductase 1 (CBR1) have been identified as mammalian GSNORs (15, 89, 105), and GSNOR is conserved from bacteria to humans; alcohol dehydrogenase 6 (Adh6) and aldo-keto reductase 1A1 (AKR1A1) have been identified as SNOCoARs in yeast and mammals, respectively (2). SNO-Cys (162) and S-nitroso-homocysteine (33, 88) have also been described as LMW-SNOs that may exist in equilibrium with SNO-proteins to regulate protein S-nitrosylation, although dedicated enzymatic mechanisms addressing these LMW-SNOs have yet to be identified and their physiological roles remain to be established.
The GSNOR system
Purification of NADH-dependent GSNO-metabolizing activity identified alcohol dehydrogenase class III (ADH5 in humans) as a phylogenetically conserved GSNOR (89, 105). ADH5 is found in most tissues, with highest activity in the liver (106). GSNO, the only SNO substrate for ADH5, represents the most efficient substrate for ADH5, and the enzyme was re-designated as GSNOR (89, 105, 106). GSNO has been detected in human airways, but not in cells (65, 105), pointing to efficient metabolism by GSNOR. Reduction of GSNO proceeds via hydride transfer from the NADH cofactor to the nitrogen of the SNO bond with subsequent solvent-derived protonation of the SNO oxygen atom to generate an S-(N-hydroxy) intermediate that resolves to GSH sulfinamide (89, 171) (Fig. 4B). Further, in the presence of GSNOR, treatment of SNO-proteins with GSH in vitro diminishes SNO levels, and addition of NADH causes a sharp decline in the levels of both SNO-proteins and LMW-SNOs (GSNO) (22). Genetic deficiency of GSNOR increased GSNO and SNO-protein levels in situ, indicating GSNO as a physiological target of GSNOR in vivo. These findings demonstrate that LMW-SNOs and SNO-proteins are in a cellular equilibrium that is governed by GSNOR (39, 59, 105, 106, 206).
Regulation of GSNOR expression and activity is multifaceted and likely context dependent. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) induces GSNOR messenger RNA (mRNA) expression in lungs, which is reversed by NOS inhibition (23). Treatment of hepatocytes with Cys-SNO increased GSNOR activity by induction of GSNOR mRNA, which might be transcriptionally mediated by Sp1 (108, 109). Interleukin-13 (IL-13) increased GSNOR expression in bronchoalveolar lavage cells from asthmatic patients and in A549 human lung carcinoma cells (114). GSNOR is also regulated by miR-342-3p, which downregulates GSNOR expression (150). S-nitrosylation of GSNOR might regulate enzymatic activity allosterically: Increased S-nitrosylation of GSNOR has been observed in mouse lungs and brain, corresponding with an increase in GSNOR activity (28, 140). In contrast, treatment of purified Arabidopsis, human, and yeast GSNOR with Cys-SNO inhibited GSNOR activity through S-nitrosylation of an allosteric Cys, and this inhibition was reversed by mutating Cys to alanine (71). The site(s) of endogenous GSNOR S-nitrosylation have yet to be identified, and the effect of in situ S-nitrosylation on GSNOR enzymatic activity remains uncertain.
CBR1 is a member of a class of NADPH-dependent enzymes that mediate carbonyl reduction of both physiological substrates and xenobiotics (133). CBR1 is a cytosolic protein that metabolizes endogenous substrates, including prostaglandins, steroids, and lipid aldehydes, and plays a role in detoxification of aldehydes during oxidative stress (15, 133). The crystal structure of CBR1 confirmed the existence of a GSH binding site, and CBR1 mediated as much as 30% of NADPH-dependent GSNO reduction in lung cells (15). Importantly, the NADPH:NADP+ ratio is usually >1, whereas the ratio of NADH:NAD+ is <1 (15). Thus, NADPH-dependent GSNO reduction by CBR1 and the remaining NADPH-dependent GSNOR(s) should play an important role in steady-state denitrosylation. Further, GSNO might regulate the activity of CBR1 (74, 172). GSNO was shown to reduce CBR1 activity, possibly by catalyzing S-glutathionylation at C227 (172). Treatment with GSNO also promoted formation of a disulfide between vicinal thiols C226 and C227 in CBR1, which altered substrate efficiency (74). Whether these modifications occur in vivo with physiological levels of GSNO remains to be seen.
GSNOR in physiology and pathophysiology
The physiological role of GSNOR-dependent S-nitrosylation/denitrosylation is best characterized in the cardiovascular system. GSNOR-deficient (GSNOR knock-out [GSNOR-KO]) mice have low systemic vascular resistance, consistent with systemic vasodilation (16). Although blood pressure may be maintained by increased cardiac output under some conditions, GSNOR-KO mice are highly susceptible to hypotension, including that induced by anesthesia (16, 106). Thus, GSNO is an endothelium-derived relaxation factor (EDRF) in the classic use of the term.
Part of the cardiovascular influence of GSNOR is exerted through the control by GSNOR of SNO-Hb levels within red blood cells (RBCs). GSNOR-KO mice have elevated levels of SNO-Hb within RBCs, which may contribute to cardioprotection (104, 142). These findings are consistent with the demonstration by Zhang et al. (208) of an essential role for SNO-Hb (SNO-βCys93) in hypoxic vasodilation, a critically important mechanism to couple oxygen delivery to local tissue oxygen demand. Mutant βCys93Ala mice are ischemic at baseline and highly susceptible to cardiac injury and mortality (209). In addition to enhanced levels of SNO-Hb, GSNOR-KO mice are protected from cardiac injury by virtue of increased capillary density (103). Increased S-nitrosylation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1α) in GSNOR-KO mice stabilizes HIF-1α under normoxia by preventing its degradation by von-Hippel Lindau tumor suppressor (pVHL); this drives cardiac angiogenesis through VEGF induction (103). Thus, GSNOR may protect from myocardial ischemia through a variety of mechanisms.
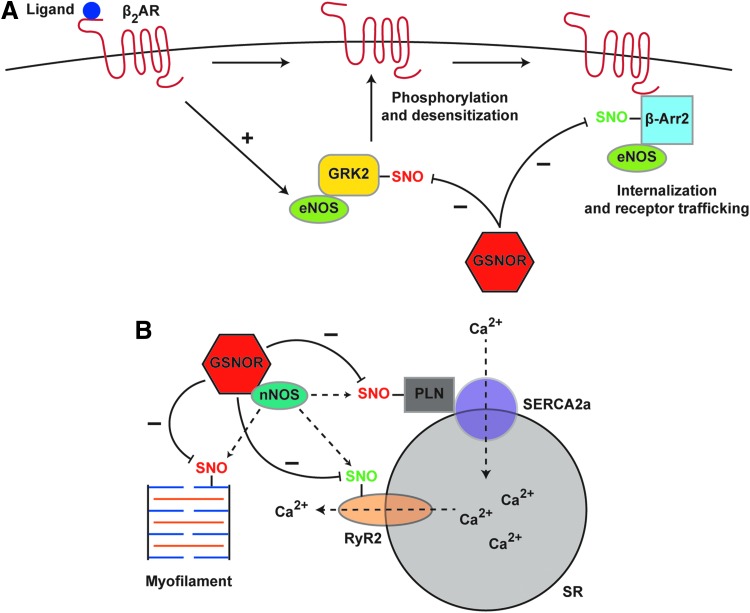
GSNOR also influences cardiac (and pulmonary) function by regulating S-nitrosylation of multiple elements contributing to trafficking of the beta-2 adrenergic receptor (β2-AR) (72). GSNOR-KO mice demonstrate increased β2-AR expression in heart and lungs, and enhanced S-nitrosylation of two key proteins involved in receptor desensitization, internalization, and degradation: GRK2 and β-arr2 (136, 197). GRK2 phosphorylates the β2-AR on receptor activation, leading to receptor desensitization by recruitment of β-arr2. Stimulus-coupled, eNOS-mediated S-nitrosylation of GRK2 inhibits receptor phosphorylation, preventing receptor internalization and desensitization (197). β-arr2 also undergoes a cycle of S-nitrosylation and denitrosylation dependent on eNOS, which promotes receptor internalization and recycling (136). eNOS-derived S-nitrosylation of dynamin, a protein involved in regulation of endocytic budding for β2-AR internalization, is also coupled to β2-AR activation; however, it is unclear whether GSNOR mediates its denitrosylation (193).
The role of GSNOR in the heart includes regulation of calcium-handling machinery. GSNOR-KO mice exhibit an impaired inotropic response to isoproterenol that is due, in part, to impaired stimulus-coupled denitrosylation of RyR2, leading to pathological calcium leak (16). By contrast, cardiomyocytes from GSNOR-transgenic (GSNOR-TG) mice increase contractility in response to isoproterenol without increasing calcium flux (and accordingly, GSNOR-TG mice are resistant to pathological hypertrophy) (83). S-nitrosylation was shown to affect the activity of multiple calcium-handling proteins, including phospholamban and cardiac troponin C (83). Stimulus-coupled S-nitrosylation was required for phospholamban multimerization to relieve inhibition of sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 2 (SERCA2a), whereas S-nitrosylation of cardiac troponin C reduced its sensitivity to calcium. In addition, diminished cardiac contractility in sepsis is worsened in GSNOR-KO mice and improved in GSNOR-TG mice (168). Improvements in GSNOR-TG mice versus GSNOR-KO mice were attributed to restoration of calcium sensitivity of calcium-handling proteins. Taken together, these data indicate that GSNOR regulates cardiac β2-AR function, calcium flux, and myofilament calcium sensitivity (Fig. 5).
FIG. 5.
Stimulus-coupled S-nitrosylation and denitrosylation: cardiomyocytes as an exemplary case. (A) Ligand-induced activation of the β2-AR in cardiomyocytes stimulates eNOS activity. eNOS-dependent S-nitrosylation of GRK2 suppresses GRK2 activity, whereas S-nitrosylation of β-arr2 facilitates β-arr2 activity, thereby regulating receptor desensitization and internalization. GSNOR negatively regulates the S-nitrosylation status of both GRK2 and β-arr2. (B) nNOS and GSNOR interact directly at the SR in cardiomyocytes. β2-AR activation stimulates nNOS-dependent S-nitrosylation of components of calcium handling (PLN, SERCA2a, RyR2) and of cardiac myofilaments, which is regulated by GSNOR-dependent denitrosylation. (A, B) SNO depicted in red indicates inhibition of normal function by S-nitrosylation; SNO depicted in green indicates activation of normal function by S-nitrosylation. Additional details are provided in the subsection “GSNOR in physiology and pathophysiology.” β-arr2, β-arrestin 2; β2-AR, beta-2 adrenergic receptor; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; GRK2, G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 2; nNOS, neuronal nitric oxide synthase; PLN, phospholamban; RyR2, ryanodine receptor 2; SERCA2a, sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 2; SR, sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Accumulating evidence suggests that aberrant GSNOR-dependent denitrosylation may be relevant to human disease. GSNOR-KO mice display multi-organ dysfunction and mortality in models of sepsis, with particularly notable histological derangement in the liver and thymus (106). These effects as well as enhanced SNO-protein levels, as seen in humans, were reversed by iNOS inhibition (106). Deletion of GSNOR also leads to spontaneous hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and carcinogen-induced HCC by downregulation of O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyl transferase (AGT), a DNA repair enzyme (195). Carcinogen challenge by diethylnitrosamine stimulates iNOS-dependent S-nitrosylation and degradation of AGT, causing increased mutagenesis (101, 184, 195, 196). A further role for GSNOR in HCC was demonstrated by Rizza et al. (154), who reported that downregulation of GSNOR increases S-nitrosylation and degradation of mitochondrial chaperone tumor necrosis factor type 1 receptor-associated protein (TRAP1), leading to an increase in succinate dehydrogenase (complex II) activity. Inhibition of succinate dehydrogenase in this setting caused necrosis and apoptosis of tumor cells. Interestingly, GSNOR is downregulated in HCC patients and is located in a chromosomal region that is frequently deleted in patients with HCC, strongly implicating loss of GSNOR in human HCC (154, 195). GSNOR is also downregulated in breast cancers (29) and lung cancer, the latter associated with activating Ras S-nitrosylation (115).
GSNOR activity may also play a significant role in airway disease. In a murine model of asthma, wild-type mice treated with ovalbumin displayed increased airway GSNOR, reduced SNO levels, and increased airway hyper-responsiveness compared with GSNOR-KO mice (148). Inhibition of iNOS restored airway sensitivity to methacholine, confirming the role of SNO in mediating asthma protection. Inhibitors of GSNOR recapitulate the protective phenotype demonstrated in GSNOR-KO mice (24, 54). Increased GSNOR activity and diminished SNO levels are observed in bronchoalveolar lavage samples from human asthma patients, strongly linking GSNOR to asthma in humans (114, 149). Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in GSNOR predict asthmatic phenotype in patients as well as response to β2-AR agonists (124, 204). Mechanistically, GSNO may prevent tachyphylaxis to β2-AR agonists by preventing receptor desensitization (148, 197).
In addition, GSNOR plays a role in the maturation of CF transmembrane conductance regulator protein (CFTR) (207). GSNOR regulates S-nitrosylation of Stip1, a co-chaperone in CFTR folding and maturation, leading to Stip1 stabilization and reduced CFTR maturation. Bronchial epithelial cells displaying a cystic fibrosis phenotype as a result of the common F508del-CFTR mutant display increased GSNOR activity and reduced CFTR maturation, and genetic or pharmacological inhibition of GSNOR rescues CFTR maturation by increasing Stip1 S-nitrosylation and degradation (207). Further, restoration of GSNO by inhibition of GSNOR may alleviate cigarette smoke-induced dysfunction of CFTR (25).
GSNOR has also been implicated broadly in cell maturation and fate. GSNOR-KO mice display lymphopenia, with reduced peripheral T cell and B cell counts (206). Inhibition of iNOS reverses the lymphopenia by reducing apoptosis in the thymus. GSNOR has also been shown to play a role in stem cell maturation. Lima et al. (103) observed increased numbers of bone marrow-derived hematopoietic stem cells in GSNOR-KO mice, indicating a potential role for S-nitrosylation in stem cell biology (103). Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) derived from GSNOR-KO mice showed reduced capacity for vasculogenesis associated with downregulation of the VEGF receptor platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRα) (66). NOS inhibitors restored vasculogenesis in GSNOR-KO MSCs, whereas NO donors reduced vasculogenesis in wild-type or human MSCs. In addition, MSCs from GSNOR-KO mice have reduced adipogenesis with a coordinate increase in osteoblastogenesis (30). In this model, increased S-nitrosylation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) prevents transcriptional activation of PPARγ target genes. This biases MSC differentiation and may help explain the observed reduction in body fat mass in GSNOR-KO mice.
GSNOR has been implicated in tissue recovery from diverse insults. GSNOR inhibition protected zebrafish from acetaminophen-induced liver toxicity through activation of Nrf2, a key stress response protein (41). Protection against liver injury was also observed in GSNOR-KO mice, whereas pharmacological inhibition of GSNOR aided in liver recovery. Notably, cardiac regeneration after myocardial infarction is enhanced in GSNOR-KO mice (75). Cardiac injury in GSNOR-KO mice was associated with increased proliferation of differentiated cardiomyocytes, expansion of cardiac stem cells, and neovascularization by endothelial cells (75). GSNOR may, therefore, provide a novel target for regenerative therapy.
Thus, in sum, genetic or pharmacological suppression of GSNOR (and other denitrosylases) provides a means to study the specific roles of endogenous SNO-proteins, and it has provided important insights into the role of GSNO and SNO-proteins in both physiology and pathophysiology across multiple tissue types and diseases. Inhibition of endogenous denitrosylation supports physiologically relevant conclusions that are not accessible by other, for example, pharmacological, means of SNO enhancement.
The SNO-CoAR system
CoA, one of the most abundant LMW cellular thiols, plays a central role in cellular metabolism as a carrier molecule for myriad metabolic intermediates in catabolic energy production and anabolic biosynthesis of lipids, sterols, ketone bodies, neurotransmitters, and amino acids (42, 100). SNO-CoA had been synthesized in vitro, and it was hypothesized that S-nitrosylation of CoA might adversely affect cellular function by limiting the availability of CoA (156, 157, 189). However, NO is not available physiologically in sufficient amounts to modify the CoA pool by mass action. The existence of endogenous SNO-CoA and the establishment of its role in regulating protein S-nitrosylation was provided by the identification of yeast Adh6 and mammalian AKR1A1 as dedicated SNO-CoARs (2).
Yeast Adh6 is a zinc-containing enzyme with obligate specificity for NADPH as a cofactor (190), originally identified as an NADPH-dependent, medium-chain cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase with broad activity against alcohol substrates (98, 170). Crystallization of Adh6 revealed an active site structure that is capable of accepting a wide variety of large or hydrophobic substrates (170, 190), but its physiological substrate(s) and function remained unclear. More recently, Adh6 was shown to account for ∼80% of NADPH-dependent SNO-CoAR activity in yeast lysates (2). Adh6 likely catalyzes SNO-CoA reduction via hydride transfer from NADPH and protonation from the aqueous environment to produce CoA-sulfinamide, similar to GSNOR (Fig. 4B). Enzymatic efficiency (Km ∼180 μ_M_) toward SNO-CoA is roughly equivalent to efficiency for other known substrates (2, 98).
Knock-out of Adh6 in yeast led to an SNO-CoA-dependent increase in both endogenous protein S-nitrosylation and S-nitrosylation induced by treatment with exogenous S-nitrosylating agents (2). Cytosolic thiolase (yeast: ergosterol biosynthesis protein 10 [Erg10]; mammal: ACAT2) showed increased S-nitrosylation in Adh6-mutant yeast, and Erg10 was S-nitrosylated by SNO-CoA but not other LMW-SNOs, which inhibited thiolase activity, leading to a decrease in the downstream metabolite mevalonate, a key intermediate in sterol biosynthesis. Interestingly, both CoA and acetyl-CoA levels were altered in Adh6-mutant yeast, implicating SNO-CoA in control of additional metabolic processes.
In mammalian tissues, AKR1A1 (henceforth SNO-CoAR) was shown to mediate NADPH-dependent SNO-CoA reduction (2). SNO-CoAR is a member of the aldo-keto reductase (AKR) superfamily of enzymes that catalyze a variety of oxidative or reductive reactions (11). AKRs are characterized by a conserved (β/α)8 barrel and exist as monomers, dimers, or tetramers (11). SNO-CoAR is cytosolic and monomeric, and has a role in the reduction of a variety of endogenous and exogenous substrates, including dl-glyceraldehyde and d-glucuronate as well as SNO-CoA (11, 133). However, SNO-CoA is the preferred endogenous substrate for SNO-CoAR (with a Km of ∼20 μ_M_, compared with 1.7 and 4.2 m_M_ for dl-glyceraldehyde and d-glucuronate, respectively) and the only known substrate for human SNO-CoAR (see the following paragraph). AKRs are characterized by an active site tetrad consisting of tyrosine, aspartate, histidine, and lysine, and catalytic tyrosine residues are conserved throughout AKRs (10, 11). Reduction of SNO-CoA (as for aldehydes) proceeds via hydride transfer with subsequent protonation of the oxygen atom by the active site tyrosine; aspartate and lysine might lower tyrosine pKa through a hydrogen bonding network, whereas histidine serves to orient the substrate (10). Reduction of SNO-CoA by SNO-CoAR produces CoA-sulfinamide, similar to yeast Adh6 (2) (Fig. 4B).
SNO-CoAR is expressed in most or all mammalian tissues with the highest activity in kidney and liver, and SNO-CoAR is responsible for the majority of NADPH-dependent SNO-CoA reduction (2, 131, 139). Before its identification as a SNO-CoAR, the only physiological role described for AKR1A1 involved the reduction of d-glucuronic acid in ascorbate synthesis (64, 182). However, for humans and many other mammals, ascorbate intake is required due to genetic mutations preventing endogenous ascorbate synthesis (46). Thus, SNO-CoA reduction is likely the predominant endogenous role of SNO-CoAR in humans and mammals generally. Although SNO-CoAR-deficient mice display increased S-nitrosylation of SNO-proteins, the physiological roles of SNO-CoA-dependent S-nitrosylation remain largely unexplored.
Specificity in Denitrosylation
The steady-state level of protein S-nitrosylation is governed by multiple factors: (i) production of NO and cellular nitrosating equivalents, (ii) transnitrosylating reactions with LMW-SNOs and other SNO-proteins, and (iii) SNO removal by denitrosylases. An illustrative example of the multi-factorial governance of protein S-nitrosylation is provided by GAPDH. The function of GAPDH is regulated by S-nitrosylation, but GAPDH is also a prototypical transnitrosylase, and the denitrosylation of GAPDH is subserved by Trx, GSNOR, and SNO-CoAR (2, 31, 96, 206). Our emphasis on enzymatic denitrosylation highlights its critical role in modulating the dynamic equilibria that govern transnitrosylation of target proteins by LMW-SNOs and by SNO-proteins, thereby regulating SNO-based signaling under basal conditions and in response to altered levels of NO production.
Subcellular localization
Subcellular compartmentalization of denitrosylases was first demonstrated for the Trx system. Trx1/TrxR1 and Trx2/TrxR2 localize to the cytosol and mitochondria, respectively, and thus regulate denitrosylation within these compartments (20). Fas-induced denitrosylation of mitochondrial caspase-3 is mediated by mitochondrial-specific Trx2, and specific inhibition of Trx2 diminishes Fas-dependent signaling in lymphocytes (20).
Early analyses of GSNOR demonstrated localization in both the cytosol and the nucleus, and subcellular localization has been shown to play a role in directing GSNOR activity (52, 81). Localization of GSNOR to myoendothelial junctions (gap junctions between smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells) facilitates stimulus-coupled denitrosylation of connexin-43 (178). S-nitrosylation of connexin-43 is mediated by co-localized eNOS, and stimulation with phenylephrine activates GSNOR-dependent denitrosylation of connexin-43 (178). GSNOR was also shown to localize to the SR in the heart where it interacted directly with nNOS and acted to facilitate stimulus-coupled denitrosylation of RyR2 (9, 16). These examples illustrate co-localization of the enzymatic machinery for stimulus-coupled S-nitrosylation/denitrosylation, also likely the case for β-arr2, which interacts with eNOS and undergoes a cycle of dynamic S-nitrosylation and GSNOR-dependent denitrosylation after β2-AR activation (136). GSNOR localization may also be regulated in physiological contexts and dysregulated in pathology. GSNOR is typically localized in puncta distributed throughout the cytosol, but it associates with mitotic spindles during cell division in normal lung cells; in contrast, GSNOR redistributes in a perinuclear fashion in lung carcinoma cells (113).
Interaction of denitrosylases with substrates
In addition to subcellular localization of denitrosylases, specificity in denitrosylation can result from protein–protein or protein–LMW thiol interactions of denitrosylases. The requirement for protein–protein interaction is inherent for Trx because the catalytic mechanism of Trx most likely involves formation of a mixed disulfide between Trx and target substrate (19). Thus, structural motifs predicting protein–protein interactions with Trx that mediate denitrosylation may correspond with motifs that predict S-nitrosylation (17, 18, 22).
Protein denitrosylation by transnitrosylation of GSH or CoA requires binding of SNO-protein and LMW partner in a reactive orientation. As described earlier, thiolase S-nitrosylation is mediated selectively by SNO-CoA; SNO-CoA inhibits thiolase activity, whereas GSNO does not (2). Thus, it is likely that SNO-CoA has preferential access to the regulatory Cys in Erg10 (thiolase). In addition, direct interaction of GSNO or SNO-CoARs with target proteins may aid in denitrosylation by rapidly metabolizing newly formed GSNO or SNO-CoA. To date, limited examples of direct interaction of LMW denitrosylases with target proteins exist. GSNOR was demonstrated to directly bind Stip1, leading to denitrosylation and stabilization of this co-chaperone involved in CFTR maturation (207). GAPDH is a target of SNO-CoAR-mediated denitrosylation and is also predicted to exist in a macromolecular protein complex with SNO-CoAR (2, 192). Such protein complexes, and other proteins that co-immunoprecipitate with GSNOR and SNO-CoAR, may represent facile targets of denitrosylation by these enzymes.
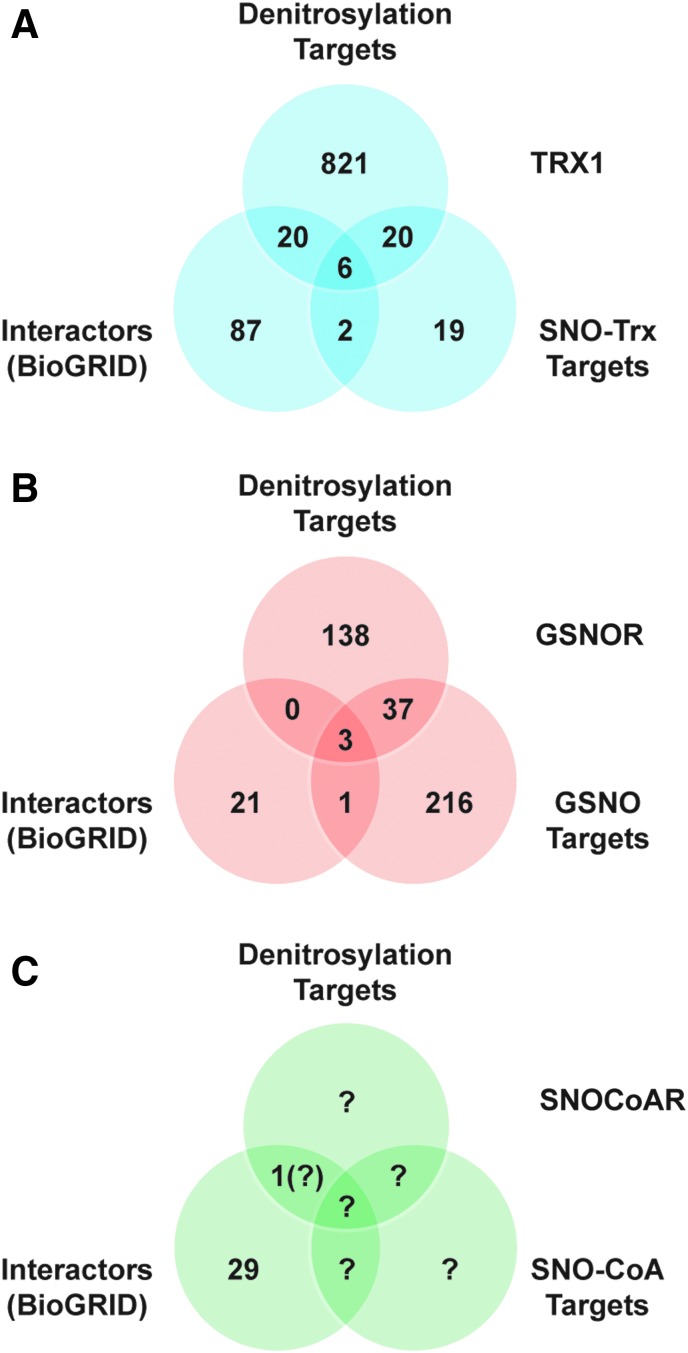
To highlight the role of protein–protein interactions, we examined the overlap for Trx1 between the set of all interacting proteins (identified in BioGRID), targets of denitrosylation by Trx1 (identified in trapping studies), and targets of trans-S-nitrosylation by Trx1 (Fig. 6A). Strikingly, we observed ∼55% overlap between targets of transnitrosylation by Trx1 and of denitrosylation by Trx1 (17, 18, 201). These likely represent proteins whose S-nitrosylation status is regulated by both functions of Trx1, dependent on cellular redox status. It is also of note that 22% of all Trx1-interacting proteins (via BioGRID) were identified SNO-proteins whose denitrosylation was regulated by Trx1. However, the set of substrates of Trx1-mediated denitrosylation as assessed by functional “trapping” greatly exceeds the set of interactors identified in the BioGRID data set, emphasizing the importance of stabilization of transient interactions between SNO-proteins and Trx1 in assessing protein–protein interactions mediating regulation of protein S-nitrosylation.
FIG. 6.
Protein–protein interactions mediate enzymatic S-nitrosylation/denitrosylation. (A) For the Trx1 system, a Venn diagram shows overlap between the sets of interacting proteins, targets of denitrosylation, and targets of trans-S-nitrosylation. Interacting proteins were retrieved from BioGRID. Targets of Trx1 denitrosylation were obtained from Ben-Lulu et al. (17, 18). Targets of transnitrosylation by SNO-Trx1 are from Wu et al. (201). (B) A similar analysis for GSNOR also reveals overlap between interactors and targets of GSNOR-regulated denitrosylation, although the data sets are substantially smaller than in the case of Trx1. Targets of GSNOR-regulated denitrosylation are unique proteins from references in Table 2. Targets of GSNO-mediated S-nitrosylation are from Murray et al. (127) and Paige et al. (138). (C) Relatively few mammalian substrates of S-nitrosylation by SNO-CoA or of denitrosylation by SNO-CoAR have been identified to date, as indicated by question marks. SNO-CoAR, S-nitroso-coenzyme A reductase.
At present, relatively few interacting proteins are known for GSNOR and SNO-CoAR, although overlap between sets of proteins interacting with GSNOR and known to be denitrosylated by GSNOR is evident (Fig. 6B, C). Note that the influence of protein–protein interactions of GSNOR (or SNO-CoAR) with SNO-proteins that would subserve regulation of protein denitrosylation would be based on the indirect effect of GSNOR/SNO-CoAR on protein S-nitrosylation via regulation of LMW-SNOs. This regulatory mechanism may be facilitated by the interaction of SNO-proteins with GSNOR/SNO-CoARs that would control local concentrations of LMW-SNOs. In the absence of a “trapping” strategy, as applied for Trx1, substrates whose denitrosylation is regulated by GSNOR (or SNO-CoAR) dependent on transient protein–protein interaction will be underestimated. Also, in the case of SNO-CoA-mediated S-nitrosylation and denitrosylation in mammalian systems, the set of targets remains largely unexplored, and the importance of protein–protein interactions cannot yet be assessed (Fig. 6C). Future examinations of targets of denitrosylation regulated by both GSNOR and SNO-CoARs should strive to include interaction data.
It is also worth considering that, in general, localization of targets of denitrosylation to particular signaling pathways or functional mechanisms may be identified with specific denitrosylases. Gene ontology analysis of Trx1 targets from substrate trapping experiments in monocytes (THP-1 or RAW264.7 cells) identified targets across multiple cellular processes, including translation, cell cycle and division, stress response, and apoptosis (17). Similar analysis of Trx1 targets in A549 lung carcinoma cells identified targets that are important for cell cycle, inflammatory signaling, transcriptional regulation, and RNA processing (18). Analysis of sites of protein S-nitrosylation in hearts from GSNOR-deficient mice found clustering within oxidoreductases, kinase binding proteins, and transferases (39). Further, the majority of SNO-CoA-dependent targets of S-nitrosylation identified in Adh6-null yeast were clustered among metabolic enzymes (2).
Concluding Remarks
Precisely targeted protein S-nitrosylation has emerged as a key mediator of NO-based redox signaling across classes of protein, cell type, and phylogeny. The emerging perspective presented here incorporates a central role for nitrosylases and denitrosylases in conferring specificity on S-nitrosylation-based cellular signaling. From this perspective, denitrosylases govern the dynamic equilibria among SNOs, created by S-nitrosylases, which mediate the cellular functions of NO. Thus, the identification of protein denitrosylases and the genetic manipulation of these enzymes has greatly facilitated our understanding of the in situ role of protein S-nitrosylation in both physiology and pathophysiology. Further study of dysregulated S-nitrosylation/denitrosylation that is associated with the many pathophysiologies in which S-nitrosylation goes awry should provide a promising focus of efforts to devise novel therapeutic approaches.
Abbreviations Used
β2-AR
beta-2 adrenergic receptor
β-arr2
β-arrestin 2
Adh6
alcohol dehydrogenase 6
AE1
anion exchange protein 1
AGT
O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyl transferase
AKR
aldo-keto reductase
AKR1A1
aldo-keto reductase 1A1
CBR1
carbonyl reductase 1
CFTR
CF transmembrane conductance regulator protein
CoA
coenzyme A
COX-2
cyclooxygenase 2
Cys
cysteine
eNOS
endothelial nitric oxide synthase
Erg10
ergosterol biosynthesis protein 10
GAPDH
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
GRK2
G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 2
GSH
glutathione
GSNO
S-nitrosoglutathione
GSNOR
S-nitrosoglutathione reductase
GSNOR-KO
GSNOR knock-out
GSNOR-TG
GSNOR transgenic
Hb
hemoglobin
HCC
hepatocellular carcinoma
HIF-1α
hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha
HNO
nitroxyl
iNOS
inducible nitric oxide synthase
LMW
low molecular weight
MAT
methionine adenosyltransferase
mRNA
messenger RNA
MSC
mesenchymal stem cell
N2O3
dinitrogen trioxide
NMDAR
N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor
NO
nitric oxide
NOS
nitric oxide synthase
nNOS
neuronal nitric oxide synthase
PDI
protein disulfide isomerase
PPARγ
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma
PSD-95
postsynaptic density protein 95
RBCs
red blood cells
RyR
ryanodine receptor/Ca2+-release channel
SERCA2a
sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 2
SNAP
S-nitroso-N-acetyl-penacillamine
SNO
S-nitrosothiol
SNO2
nitroxyl disulfide
SNO-CoA
S-nitroso-coenzyme A
SNO-CoAR
SNO-CoA reductase
SNO-Hb
S-nitroso-hemoglobin
SNO-protein
S-nitroso-protein
SR
sarcoplasmic reticulum
Trx
thioredoxin
TrxR
thioredoxin reductase
TXNIP
thioredoxin-interacting protein
VEGF
vascular endothelial growth factor
References
- 1.Abunimer A, Smith K, Wu TJ, Lam P, Simonyan V, and Mazumder R. Single-nucleotide variations in cardiac arrhythmias: prospects for genomics and proteomics based biomarker discovery and diagnostics. Genes (Basel) 5: 254–269, 2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Anand P, Hausladen A, Wang Y, Zhang G, Stomberski C, Brunengraber H, Hess DT, and Stamler JS. Identification of S-nitroso-CoA reductases that regulate protein S-nitrosylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111: 18572–18577, 2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Anand P. and Stamler JS. Enzymatic mechanisms regulating protein S-nitrosylation: implications in health and disease. J Mol Med 90: 233–244, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Andre FR, dos Santos PF, and Rando DG. Theoretical studies of the role of C-terminal cysteines in the process of S-nitrosylation of human Src kinases. J Mol Model 22: 23, 2016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Angelo M, Singel DJ, and Stamler JS. An S-nitrosothiol (SNO) synthase function of hemoglobin that utilizes nitrite as a substrate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103: 8366–8371, 2006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Arnelle DR. and Stamler JS. NO+, NO, and NO− donation by S-nitrosothiols: implications for regulation of physiological functions by S-nitrosylation and acceleration of disulfide formation. Arch Biochem Biophys 318: 279–285, 1995 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Arulsamy N, Bohle DS, Butt JA, Irvine GJ, Jordan PA, and Sagan E. Interrelationships between conformational dynamics and the redox chemistry of S-nitroso thiols. J Am Chem Soc 121: 7115–7123, 1999 [Google Scholar]
- 8.Baciu C, Cho KB, and Gauld JW. Influence of Cu+ on the RS-NO bond dissociation energy of S-nitrosothiols. J Phys Chem B 109: 1334–1336, 2005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Barouch LA, Harrison RW, Skaf MW, Rosas GO, Cappola TP, Kobeissi ZA, Hobai IA, Lemmon CA, Burnett AL, O'Rourke B, Rodriguez ER, Huang PL, Lima JAC, Berkowitz DE, and Hare JM. Nitric oxide regulates the heart by spatial confinement of nitric oxide synthase isoforms. Nature 416: 337–339, 2002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Barski OA, Gabbay KH, Grimshaw CE, and Bohren KM. Mechanism of human aldehyde reductase: characterization of the active site pocket. Biochemistry 34: 11264–11275, 1995 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Barski OA, Tipparaju SM, and Bhatnagar A. The aldo-keto reductase superfamily and its role in drug metabolism and detoxification. Drug Metab Rev 40: 553–624, 2008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bartberger MD, Fukuto JM, and Houk KN. On the acidity and reactivity of HNO in aqueous solution and biological systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98: 2194–2198, 2001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bartberger MD, Houk KN, Powell SC, Mannion JD, Lo KY, Stamler JS, and Toone EJ. Theory, spectroscopy, and crystallographic analysis of S-nitrosothiols: conformational distribution dictates spectroscopic behavior. J Am Chem Soc 122: 5889–5890, 2000 [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bartberger MD, Mannion JD, Powell SC, Stamler JS, Houk KN, and Toone EJ. S-N dissociation energies of S-nitrosothiols: on the origins of nitrosothiol decomposition rates. J Am Chem Soc 123: 8868–8869, 2001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bateman RL, Rauh D, Tavshanjian B, and Shokat KM. Human carbonyl reductase 1 is an S-nitrosoglutathione reductase. J Biol Chem 283: 35756–35762, 2008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Beigi F, Gonzalez DR, Minhas KM, Sun QA, Foster MW, Khan SA, Treuer A V, Dulce RA, Harrison RW, Saraiva RM, Premer C, Schulman IH, Stamler JS, and Hare JM. Dynamic denitrosylation via S-nitrosoglutathione reductase regulates cardiovascular function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109: 4314–4319, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ben-Lulu S, Ziv T, Admon A, Weisman-Shomer P, and Benhar M. A substrate trapping approach identifies proteins regulated by reversible S-nitrosylation. Mol Cell Proteomics 13: 2573–2583, 2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ben-Lulu S, Ziv T, Weisman-Shomer P, and Benhar M. Nitrosothiol-trapping-based proteomic analysis of S-nitrosylation in human lung carcinoma cells. PLoS One 12: e0169862, 2017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Benhar M. Nitric oxide and the thioredoxin system: a complex interplay in redox regulation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1850: 2476–2484, 2015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Benhar M, Forrester MT, Hess DT, and Stamler JS. Regulated protein denitrosylation by cytosolic and mitochondrial thioredoxins. Science 320: 1050–1054, 2008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Benhar M, Forrester MT, and Stamler JS. Protein denitrosylation: enzymatic mechanisms and cellular functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10: 721–732, 2009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Benhar M, Thompson JW, Moseley MA, and Stamler JS. Identification of S-nitrosylated targets of thioredoxin using a quantitative proteomic approach. Biochemistry 49: 6963–6969, 2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bhandari V, Choo-Wing R, Chapoval SP, Lee CG, Tang C, Kim YK, Ma B, Baluk P, Lin MI, McDonald DM, Homer RJ, Sessa WC, and Elias JA. Essential role of nitric oxide in VEGF-induced, asthma-like angiogenic, inflammatory, mucus, and physiologic responses in the lung. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103: 11021–11026, 2006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Blonder JP, Mutka SC, Sun X, Qiu J, Green LH, Mehra NK, Boyanapalli R, Suniga M, Look K, Delany C, Richards JP, Looker D, Scoggin C, and Rosenthal GJ. Pharmacologic inhibition of S-nitrosoglutathione reductase protects against experimental asthma in BALB/c mice through attenuation of both bronchoconstriction and inflammation. BMC Pulm Med 14: 3, 2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bodas M, Silverberg D, Walworth K, Brucia K, and Vij N. Augmentation of S-nitrosoglutathione controls cigarette smoke-induced inflammatory-oxidative stress and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease-emphysema pathogenesis by restoring cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator function. Antioxid Redox Signal 27: 433–451, 2017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bosworth CA, Toledo JC, Zmijewski JW, Li Q, and Lancaster JR. Dinitrosyliron complexes and the mechanism(s) of cellular protein nitrosothiol formation from nitric oxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106: 4671–4676, 2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Brenman JE, Chao DS, Gee SH, McGee AW, Craven SE, Santillano DR, Wu Z, Huang F, Xia H, Peters MF, Froehner SC, and Bredt DS. Interaction of nitric oxide synthase with the postsynaptic density protein PSD-95 and alpha1-syntrophin mediated by PDZ domains. Cell 84: 757–767, 1996 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Brown-Steinke K, DeRonde K, Yemen S, and Palmer LA. Gender differences in S-nitrosoglutathione reductase activity in the lung. PLoS One 5: e14007, 2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Cañas A, López-Sánchez LM, Peñarando J, Valverde A, Conde F, Hernández V, Fuentes E, López-Pedrera C, de la Haba-Rodríguez JR, Aranda E, and Rodríguez-Ariza A. Altered S-nitrosothiol homeostasis provides a survival advantage to breast cancer cells in HER2 tumors and reduces their sensitivity to trastuzumab. Biochim Biophys Acta 1862: 601–610, 2016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Cao Y, Gomes SA, Rangel EB, Paulino EC, Fonseca TL, Li J, Teixeira MB, Gouveia CH, Bianco AC, Kapiloff MS, Balkan W, and Hare JM. S-nitrosoglutathione reductase-dependent PPARγ denitrosylation participates in MSC-derived adipogenesis and osteogenesis. J Clin Invest 125: 1679–1691, 2015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Chakravarti R. and Stuehr DJ. Thioredoxin-1 regulates cellular heme insertion by controlling S-nitrosation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem 287: 16179–16186, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Chan NL, Rogers PH, and Arnone A. Crystal structure of the S-nitroso form of liganded human hemoglobin. Biochemistry 37: 16459–16464, 1998 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Chen Y, Zhao S, Wang Y, Li Y, Bai L, Liu R, Fan J, and Liu E. Homocysteine reduces protein S-nitrosylation in endothelium. Int J Mol Med 34: 1277–1285, 2014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Chen YJ, Ku WC, Lin PY, Chou HC, Khoo KH, and Chen YJ. S-alkylating labeling strategy for site-specific identification of the s-nitrosoproteome. J Proteome Res 9: 6417–6439, 2010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Chen YJ, Lu CT, Su MG, Huang KY, Ching WC, Yang HH, Liao YC, Chen YJ, and Lee TY. dbSNO 2.0: a resource for exploring structural environment, functional and disease association and regulatory network of protein S-nitrosylation. Nucleic Acids Res 43: D503–D511, 2015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Choi LS. and Bayley H. S-nitrosothiol chemistry at the single-molecule level. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 51: 7972–7976, 2012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Choi MS, Nakamura T, Cho SJ, Han X, Holland EA, Qu J, Petsko GA, Yates JR, Liddington RC, and Lipton SA. Transnitrosylation from DJ-1 to PTEN attenuates neuronal cell death in Parkinson's disease models. J Neurosci 34: 15123–15131, 2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Choi YB, Tenneti L, Le DA, Ortiz J, Bai G, Chen HS, and Lipton SA. Molecular basis of NMDA receptor-coupled ion channel modulation by S-nitrosylation. Nat Neurosci 3: 15–21, 2000 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Chung HS, Murray CI, Venkatraman V, Crowgey EL, Rainer PP, Cole RN, Bomgarden RD, Rogers JC, Balkan W, Hare JM, Kass DA, and Van Eyk JE. Dual labeling biotin switch assay to reduce bias derived from different cysteine subpopulations: a method to maximize S-nitrosylation detection. Circ Res 117: 846–857, 2015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Collet JF. and Messens J. Structure, function, and mechanism of thioredoxin proteins. Antioxid Redox Signal 13: 1205–1216, 2010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Cox AG, Saunders DC, Kelsey PB, Conway AA, Tesmenitsky Y, Marchini JF, Brown KK, Stamler JS, Colagiovanni DB, Rosenthal GJ, Croce KJ, North TE, and Goessling W. S-nitrosothiol signaling regulates liver development and improves outcome following toxic liver injury. Cell Rep 6: 56–69, 2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Davaapil H, Tsuchiya Y, and Gout I. Signalling functions of coenzyme A and its derivatives in mammalian cells. Biochem Soc Trans 42: 1056–1062, 2014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Denis PA, Ventura ON, Mai HT, and Nguyen MT. Ab initio and density functional study of thionitroso XNS and thiazyl isomers XSN, X = H, F, Cl, Br, OH, SH, NH2, CH3, CF3, and SiF3. J Phys Chem A 108: 5073–5080, 2004 [Google Scholar]
- 44.Derakhshan B, Hao G, and Gross SS. Balancing reactivity against selectivity: the evolution of protein S-nitrosylation as an effector of cell signaling by nitric oxide. Cardiovasc Res 75: 210–219, 2007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Doulias PT, Greene JL, Greco TM, Tenopoulou M, Seeholzer SH, Dunbrack RL, and Ischiropoulos H. Structural profiling of endogenous S-nitrosocysteine residues reveals unique features that accommodate diverse mechanisms for protein S-nitrosylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107: 16958–16963, 2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Drouin G, Godin JR, and Pagé B. The genetics of vitamin C loss in vertebrates. Curr Genomics 12: 371–378, 2011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Erwin PA, Lin AJ, Golan DE, and Michel T. Receptor-regulated dynamic S-nitrosylation of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase in vascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 280: 19888–19894, 2005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Erwin PA, Mitchell DA, Sartoretto J, Marletta MA, and Michel T. Subcellular targeting and differential S-nitrosylation of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase. J Biol Chem 281: 151–157, 2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Eu JP, Hare JM, Hess DT, Skaf M, Sun J, Cardenas-Navina I, Sun QA, Dewhirst M, Meissner G, and Stamler JS. Concerted regulation of skeletal muscle contractility by oxygen tension and endogenous nitric oxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100: 15229–15234, 2003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Eu JP, Sun J, Xu L, Stamler JS, and Meissner G. The skeletal muscle calcium release channel: coupled O2 sensor and NO signaling functions. Cell 102: 499–509, 2000 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Fang M, Jaffrey SR, Sawa A, Ye K, Luo X, and Snyder SH. Dexras1: a G protein specifically coupled to neuronal nitric oxide synthase via CAPON. Neuron 28: 183–193, 2000 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Fernández MR, Biosca JA, and Parés X. S-nitrosoglutathione reductase activity of human and yeast glutathione-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase and its nuclear and cytoplasmic localisation. Cell Mol Life Sci 60: 1013–1018, 2003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Fernhoff NB, Derbyshire ER, and Marletta MA. A nitric oxide/cysteine interaction mediates the activation of soluble guanylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106: 21602–21607, 2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Ferrini ME, Simons BJ, Bassett DJP, Bradley MO, Roberts K, and Jaffar Z. S-nitrosoglutathione reductase inhibition regulates allergen-induced lung inflammation and airway hyperreactivity. PLoS One 8: e70351, 2013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Filipovic MR, Miljkovic JL, Nauser T, Royzen M, Klos K, Shubina T, Koppenol WH, Lippard SJ, and Ivanović-Burmazović I. Chemical characterization of the smallest S-nitrosothiol, HSNO; cellular cross-talk of H2S and S-nitrosothiols. J Am Chem Soc 134: 12016–12027, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Forrester MT, Seth D, Hausladen A, Eyler CE, Foster MW, Matsumoto A, Benhar M, Marshall HE, and Stamler JS. Thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) is a feedback regulator of S-nitrosylation. J Biol Chem 284: 36160–36166, 2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Forrester MT, Thompson JW, Foster MW, Nogueira L, Moseley MA, and Stamler JS. Proteomic analysis of S-nitrosylation and denitrosylation by resin-assisted capture. Nat Biotechnol 27: 557–559, 2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Foster MW, Hess DT, and Stamler JS. Protein S-nitrosylation in health and disease: a current perspective. Trends Mol Med 15: 391–404, 2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Foster MW, Liu L, Zeng M, Hess DT, and Stamler JS. A genetic analysis of nitrosative stress. Biochemistry 48: 792–799, 2009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Foster MW, McMahon TJ, and Stamler JS. S-nitrosylation in health and disease. Trends Mol Med 9: 160–168, 2003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Foster MW. and Stamler JS. New insights into protein S-nitrosylation. Mitochondria as a model system. J Biol Chem 279: 25891–25897, 2004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Fourquet S, Guerois R, Biard D, and Toledano MB. Activation of NRF2 by nitrosative agents and H2O2 involves KEAP1 disulfide formation. J Biol Chem 285: 8463–8471, 2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Fu Y, Mou Y, Lin BL, Liu L, and Guo QX. Structures of the X−Y−NO molecules and homolytic dissociation energies of the Y−NO bonds (Y = C, N, O, S). J Phys Chem A 106: 12386–12392, 2002 [Google Scholar]
- 64.Gabbay KH, Bohren KM, Morello R, Bertin T, Liu J, and Vogel P. Ascorbate synthesis pathway: dual role of ascorbate in bone homeostasis. J Biol Chem 285: 19510–19520, 2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Gaston B, Reilly J, Drazen JM, Fackler J, Ramdev P, Arnelle D, Mullins ME, Sugarbaker DJ, Chee C, and Singel DJ. Endogenous nitrogen oxides and bronchodilator S-nitrosothiols in human airways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90: 10957–10961, 1993 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Gomes SA, Rangel EB, Premer C, Dulce RA, Cao Y, Florea V, Balkan W, Rodrigues CO, Schally AV, and Hare JM. S-nitrosoglutathione reductase (GSNOR) enhances vasculogenesis by mesenchymal stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110: 2834–2839, 2013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Gould NS, Evans P, Martínez-Acedo P, Marino SM, Gladyshev VN, Carroll KS, and Ischiropoulos H. Site-specific proteomic mapping identifies selectively modified regulatory cysteine residues in functionally distinct protein networks. Chem Biol 22: 965–975, 2015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Gow AJ, Chen Q, Hess DT, Day BJ, Ischiropoulos H, and Stamler JS. Basal and stimulated protein S-nitrosylation in multiple cell types and tissues. J Biol Chem 277: 9637–9640, 2002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Gow AJ. and Ischiropoulos H. Nitric oxide chemistry and cellular signaling. J Cell Physiol 187: 277–282, 2001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Greco TM, Hodara R, Parastatidis I, Heijnen HFG, Dennehy MK, Liebler DC, and Ischiropoulos H. Identification of S-nitrosylation motifs by site-specific mapping of the S-nitrosocysteine proteome in human vascular smooth muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103: 7420–7425, 2006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Guerra D, Ballard K, Truebridge I, and Vierling E. S-nitrosation of conserved cysteines modulates activity and stability of S-nitrosoglutathione reductase (GSNOR). Biochemistry 55: 2452–2464, 2016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Haldar SM. and Stamler JS. S-nitrosylation: integrator of cardiovascular performance and oxygen delivery. J Clin Invest 123: 101–110, 2013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Hao G, Derakhshan B, Shi L, Campagne F, and Gross SS. SNOSID, a proteomic method for identification of cysteine S-nitrosylation sites in complex protein mixtures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103: 1012–1017, 2006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Hartmanová T, Tambor V, Lenčo J, Staab-Weijnitz CA, Maser E, and Wsól V. S-nitrosoglutathione covalently modifies cysteine residues of human carbonyl reductase 1 and affects its activity. Chem Biol Interact 202: 136–145, 2013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Hatzistergos KE, Paulino EC, Dulce RA, Takeuchi LM, Bellio MA, Kulandavelu S, Cao Y, Balkan W, Kanashiro-Takeuchi RM, and Hare JM. S-nitrosoglutathione reductase deficiency enhances the proliferative expansion of adult heart progenitors and myocytes post myocardial infarction. J Am Heart Assoc 4: e001974, 2015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Hess DT, Matsumoto A, Kim SO, Marshall HE, and Stamler JS. Protein S-nitrosylation: purview and parameters. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6: 150–166, 2005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Hess DT, Matsumoto A, Nudelman R, and Stamler JS. S-nitrosylation: spectrum and specificity. Nat Cell Biol 3: E46–E49, 2001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Ho GPH, Selvakumar B, Mukai J, Hester LD, Wang Y, Gogos JA, and Snyder SH. S-nitrosylation and S-palmitoylation reciprocally regulate synaptic targeting of PSD-95. Neuron 71: 131–141, 2011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Hoffmann J, Haendeler J, Zeiher AM, and Dimmeler S. TNFalpha and oxLDL reduce protein S-nitrosylation in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 276: 41383–41387, 2001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Houk KN, Hietbrink BN, Bartberger MD, McCarren PR, Choi BY, Voyksner RD, Stamler JS, and Toone EJ. Nitroxyl disulfides, novel intermediates in transnitrosation reactions. J Am Chem Soc 125: 6972–6976, 2003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Iborra FJ, Renau-Piqueras J, Portoles M, Boleda MD, Guerri C, and Pares X. Immunocytochemical and biochemical demonstration of formaldhyde dehydrogenase (class III alcohol dehydrogenase) in the nucleus. J Histochem Cytochem 40: 1865–1878, 1992 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Ignarro LJ, Buga GM, Wood KS, Byrns RE, and Chaudhuri G. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor produced and released from artery and vein is nitric oxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 84: 9265–9269, 1987 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Irie T, Sips PY, Kai S, Kida K, Ikeda K, Hirai S, Moazzami K, Jiramongkolchai P, Bloch DB, Doulias PT, Armoundas AA, Kaneki M, Ischiropoulos H, Kranias E, Bloch KD, Stamler JS, and Ichinose F. S-nitrosylation of calcium-handling proteins in cardiac adrenergic signaling and hypertrophy. Circ Res 117: 793–803, 2015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Ito T, Yamakuchi M, and Lowenstein CJ. Thioredoxin increases exocytosis by denitrosylating N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor. J Biol Chem 286: 11179–11184, 2011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Ivanova LV, Cibich D, Deye G, Talipov MR, and Timerghazin QK. Modeling of S-nitrosothiol-thiol reactions of biological significance: HNO production by S-thiolation requires a proton shuttle and stabilization of polar intermediates. Chembiochem 18: 726–738, 2017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Iwakiri Y, Satoh A, Chatterjee S, Toomre DK, Chalouni CM, Fulton D, Groszmann RJ, Shah VH, and Sessa WC. Nitric oxide synthase generates nitric oxide locally to regulate compartmentalized protein S-nitrosylation and protein trafficking. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103: 19777–19782, 2006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Jaffrey SR, Erdjument-Bromage H, Ferris CD, Tempst P, and Snyder SH. Protein S-nitrosylation: a physiological signal for neuronal nitric oxide. Nat Cell Biol 3: 193–197, 2001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Jakubowski H. Homocysteine-thiolactone and S-nitroso-homocysteine mediate incorporation of homocysteine into protein in humans. Clin Chem Lab Med 41: 1462–1466, 2003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Jensen DE, Belka GK, and Du Bois GC. S-Nitrosoglutathione is a substrate for rat alcohol dehydrogenase class III isoenzyme. Biochem J 331: 659–668, 1998 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Jia J, Arif A, Terenzi F, Willard B, Plow EF, Hazen SL, and Fox PL. Target-selective protein S-nitrosylation by sequence motif recognition. Cell 159: 623–634, 2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Jia L, Bonaventura C, Bonaventura J, and Stamler JS. S-nitrosohaemoglobin: a dynamic activity of blood involved in vascular control. Nature 380: 221–226, 1996 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Kelleher ZT, Sha Y, Foster MW, Foster WM, Forrester MT, and Marshall HE. Thioredoxin-mediated denitrosylation regulates cytokine-induced nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) activation. J Biol Chem 289: 3066–3072, 2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Kim SF, Huri DA, and Snyder SH. Inducible nitric oxide synthase binds, S-nitrosylates, and activates cyclooxygenase-2. Science 310: 1966–1970, 2005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Kim SO, Merchant K, Nudelman R, Beyer WF, Keng T, DeAngelo J, Hausladen A, and Stamler JS. OxyR: a molecular code for redox-related signaling. Cell 109: 383–396, 2002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Kornau HC, Schenker LT, Kennedy MB, and Seeburg PH. Domain interaction between NMDA receptor subunits and the postsynaptic density protein PSD-95. Science 269: 1737–1740, 1995 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Kornberg MD, Sen N, Hara MR, Juluri KR, Nguyen JVK, Snowman AM, Law L, Hester LD, and Snyder SH. GAPDH mediates nitrosylation of nuclear proteins. Nat Cell Biol 12: 1094–1100, 2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Kovacs I. and Lindermayr C. Nitric oxide-based protein modification: formation and site-specificity of protein S-nitrosylation. Front Plant Sci 4: 137, 2013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Larroy C, Fernández MR, González E, Parés X, and Biosca JA. Characterization of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae YMR318C (ADH6) gene product as a broad specificity NADPH-dependent alcohol dehydrogenase: relevance in aldehyde reduction. Biochem J 361: 163–172, 2002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Lee YI, Giovinazzo D, Kang HC, Lee Y, Jeong JS, Doulias PT, Xie Z, Hu J, Ghasemi M, Ischiropoulos H, Qian J, Zhu H, Blackshaw S, Dawson VL, and Dawson TM. Protein microarray characterization of the S-nitrosoproteome. Mol Cell Proteomics 13: 63–72, 2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Leonardi R, Zhang YM, Rock CO, and Jackowski S. Coenzyme A: back in action. Prog Lipid Res 44: 125–153, 2005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Leung J, Wei W, and Liu L. S-nitrosoglutathione reductase deficiency increases mutagenesis from alkylation in mouse liver. Carcinogenesis 34: 984–989, 2013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Lima B, Forrester MT, Hess DT, and Stamler JS. S-nitrosylation in cardiovascular signaling. Circ Res 106: 633–646, 2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Lima B, Lam GKW, Xie L, Diesen DL, Villamizar N, Nienaber J, Messina E, Bowles D, Kontos CD, Hare JM, Stamler JS, and Rockman HA. Endogenous S-nitrosothiols protect against myocardial injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106: 6297–6302, 2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Lipton AJ, Johnson MA, Macdonald T, Lieberman MW, Gozal D, and Gaston B. S-nitrosothiols signal the ventilatory response to hypoxia. Nature 413: 171–174, 2001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Liu L, Hausladen A, Zeng M, Que L, Heitman J, and Stamler JS. A metabolic enzyme for S-nitrosothiol conserved from bacteria to humans. Nature 410: 490–494, 2001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Liu L, Yan Y, Zeng M, Zhang J, Hanes MA, Ahearn G, McMahon TJ, Dickfeld T, Marshall HE, Que LG, and Stamler JS. Essential roles of S-nitrosothiols in vascular homeostasis and endotoxic shock. Cell 116: 617–628, 2004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Liu X, Miller MJS, Joshi MS, Thomas DD, and Lancaster JR. Accelerated reaction of nitric oxide with O2 within the hydrophobic interior of biological membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95: 2175–2179, 1998 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.López-Sánchez LM, Corrales FJ, González R, Ferrín G, Muñoz-Castañeda JR, Ranchal I, Hidalgo AB, Briceño J, López-Cillero P, Gómez MA, De La Mata M, Muntané J, and Rodríguez-Ariza A. Alteration of S-nitrosothiol homeostasis and targets for protein S-nitrosation in human hepatocytes. Proteomics 8: 4709–4720, 2008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.López-Sánchez LM, Corrales FJ, López-Pedrera C, Aranda E, and Rodríguez-Ariza A. Pharmacological impairment of s-nitrosoglutathione or thioredoxin reductases augments protein S-nitrosation in human hepatocarcinoma cells. Anticancer Res 30: 415–421, 2010 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Mahoney CW, Pak JH, and Huang KP. Nitric oxide modification of rat brain neurogranin. Identification of the cysteine residues involved in intramolecular disulfide bridge formation using site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem 271: 28798–28804, 1996 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Mannick JB, Hausladen A, Liu L, Hess DT, Zeng M, Miao QX, Kane LS, Gow AJ, and Stamler JS. Fas-induced caspase denitrosylation. Science 284: 651–654, 1999 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Marino SM. and Gladyshev VN. Structural analysis of cysteine S-nitrosylation: a modified acid-based motif and the emerging role of trans-nitrosylation. J Mol Biol 395: 844–859, 2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Marozkina NV. and Gaston B. S-nitrosylation signaling regulates cellular protein interactions. Biochim Biophys Acta 1820: 722–729, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Marozkina NV, Wang XQ, Stsiapura V, Fitzpatrick A, Carraro S, Hawkins GA, Bleecker E, Meyers D, Jarjour N, Fain SB, Wenzel S, Busse W, Castro M, Panettieri RA, Moore W, Lewis SJ, Palmer LA, Altes T, de Lange EE, Erzurum S, Teague WG, and Gaston B. Phenotype of asthmatics with increased airway S-nitrosoglutathione reductase activity. Eur Respir J 45: 87–97, 2015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Marozkina NV, Wei C, Yemen S, Wallrabe H, Nagji AS, Liu L, Morozkina T, Jones DR, and Gaston B. S-nitrosoglutathione reductase in human lung cancer. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 46: 63–70, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Martínez-Ruiz A. and Lamas S. Signalling by NO-induced protein S-nitrosylation and S-glutathionylation: convergences and divergences. Cardiovasc Res 75: 220–228, 2007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Mayer B, Kleschyov AL, Stessel H, Russwurm M, Munzel T, Koesling D, and Schmidt K. Inactivation of soluble guanylate cyclase by stoichiometric S-nitrosation. Mol Pharmacol 75: 886–891, 2009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.McMahon TJ, Exton Stone A, Bonaventura J, Singel DJ, and Stamler JS. Functional coupling of oxygen binding and vasoactivity in S-nitrosohemoglobin. J Biol Chem 275: 16738–16745, 2000 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Minning DM, Gow AJ, Bonaventura J, Braun R, Dewhirst M, Goldberg DE, and Stamler JS. Ascaris haemoglobin is a nitric oxide-activated “deoxygenase.” Nature 401: 497–502, 1999 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Mitchell DA, Erwin PA, Michel T, and Marletta MA. S-nitrosation and regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Biochemistry 44: 4636–4647, 2005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Mitchell DA. and Marletta MA. Thioredoxin catalyzes the S-nitrosation of the caspase-3 active site cysteine. Nat Chem Biol 1: 154–158, 2005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Mitchell DA, Morton SU, Fernhoff NB, and Marletta MA. Thioredoxin is required for S-nitrosation of procaspase-3 and the inhibition of apoptosis in Jurkat cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104: 11609–11614, 2007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Moon Y, Cao Y, Zhu J, Xu Y, Balkan W, Buys ES, Diaz F, Kerrick WG, Hare JM, and Percival JM. GSNOR deficiency enhances in situ skeletal muscle strength, fatigue resistance, and RyR1 S-nitrosylation without impacting mitochondrial content and activity. Antioxid Redox Signal 26: 165–181, 2017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Moore PE, Ryckman KK, Williams SM, Patel N, Summar ML, and Sheller JR. Genetic variants of GSNOR and ADRB2 influence response to albuterol in African-American children with severe asthma. Pediatr Pulmonol 44: 649–654, 2009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Morris S. and Hansen JN. Inhibition of Bacillus cereus spore outgrowth by covalent modification of a sulfhydryl group by nitrosothiol and iodoacetate. J Bacteriol 148: 465–471, 1981 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Murad F. Cyclic guanosine monophosphate as a mediator of vasodilation. J Clin Invest 78: 1–5, 1986 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Murray CI, Uhrigshardt H, O'Meally RN, Cole RN, and Van Eyk JE. Identification and quantification of S-nitrosylation by cysteine reactive tandem mass tag switch assay. Mol Cell Proteomics 11: M111.013441, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Nedospasov A, Rafikov R, Beda N, and Nudler E. An autocatalytic mechanism of protein nitrosylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97: 13543–13548, 2000 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Nikitovic D. and Holmgren A. S-nitrosoglutathione is cleaved by the thioredoxin system with liberation of glutathione and redox regulating nitric oxide. J Biol Chem 271: 19180–19185, 1996 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Nogales E, Whittaker M, Milligan RA, and Downing KH. High-resolution model of the microtubule. Cell 96: 79–88, 1999 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.O'Connor T, Ireland LS, Harrison DJ, and Hayes JD. Major differences exist in the function and tissue-specific expression of human aflatoxin B1 aldehyde reductase and the principal human aldo-keto reductase AKR1 family members. Biochem J 343: 487–504, 1999 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.de Oliveira MG, Shishido SM, Seabra AB, and Morgon NH. Thermal stability of primary S-nitrosothiols: roles of autocatalysis and structural effects on the rate of nitric oxide release. J Phys Chem A 106: 8963–8970, 2002 [Google Scholar]
- 133.Oppermann U. Carbonyl reductases: the complex relationships of mammalian carbonyl- and quinone-reducing enzymes and their role in physiology. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 47: 293–322, 2007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Ovadia H, Haim Y, Nov O, Almog O, Kovsan J, Bashan N, Benhar M, and Rudich A. Increased adipocyte S-nitrosylation targets anti-lipolytic action of insulin: relevance to adipose tissue dysfunction in obesity. J Biol Chem 286: 30433–30443, 2011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Ozawa K, Tsumoto H, Wei W, Tang C-H, Komatsubara AT, Kawafune H, Shimizu K, Liu L, and Tsujimoto G. Proteomic analysis of the role of S-nitrosoglutathione reductase in lipopolysaccharide-challenged mice. Proteomics 12: 2024–2035, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Ozawa K, Whalen EJ, Nelson CD, Mu Y, Hess DT, Lefkowitz RJ, and Stamler JS. S-nitrosylation of beta-arrestin regulates beta-adrenergic receptor trafficking. Mol Cell 31: 395–405, 2008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Pader I, Sengupta R, Cebula M, Xu J, Lundberg JO, Holmgren A, Johansson K, and Arnér ESJ. Thioredoxin-related protein of 14 kDa is an efficient l-cystine reductase and S-denitrosylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111: 6964–6969, 2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Paige JS, Xu G, Stancevic B, and Jaffrey SR. Nitrosothiol reactivity profiling identifies S-nitrosylated proteins with unexpected stability. Chem Biol 15: 1307–1316, 2008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Palackal NT, Burczynski ME, Harvey RG, and Penning TM. The ubiquitous aldehyde reductase (AKR1A1) oxidizes proximate carcinogen trans-dihydrodiols to o-quinones: potential role in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon activation. Biochemistry 40: 10901–10910, 2001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Palmer LA, Kimberly deRonde , Brown-Steinke K, Gunter S, Jyothikumar V, Forbes MS, and Lewis SJ. Hypoxia-induced changes in protein S-nitrosylation in female mouse brainstem. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 52: 37–45, 2015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Palmer RM, Ferrige AG, and Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature 327: 524–526, 1987 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Pawloski JR, Hess DT, and Stamler JS. Export by red blood cells of nitric oxide bioactivity. Nature 409: 622–626, 2001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Perez-Mato I, Castro C, Ruiz FA, Corrales FJ, and Mato JM. Methionine adenosyltransferase S-nitrosylation is regulated by the basic and acidic amino acids surrounding the target thiol. J Biol Chem 274: 17075–17079, 1999 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Perissinotti LL, Leitus G, Shimon L, Estrin D, and Doctorovich F. A unique family of stable and water-soluble S-nitrosothiol complexes. Inorg Chem 47: 4723–4733, 2008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Perreault M. and Marette A. Targeted disruption of inducible nitric oxide synthase protects against obesity-linked insulin resistance in muscle. Nat Med 7: 1138–1143, 2001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Qu Z, Meng F, Bomgarden RD, Viner RI, Li J, Rogers JC, Cheng J, Greenlief CM, Cui J, Lubahn DB, Sun GY, and Gu Z. Proteomic quantification and site-mapping of S-nitrosylated proteins using isobaric iodoTMT reagents. J Proteome Res 13: 3200–3211, 2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Qu ZW, Miao WY, Hu SQ, Li C, Zhuo XL, Zong YY, Wu YP, and Zhang G-Y. N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor-dependent denitrosylation of neuronal nitric oxide synthase increase the enzyme activity. PLoS One 7: e52788, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Que LG, Liu L, Yan Y, Whitehead GS, Gavett SH, Schwartz DA, and Stamler JS. Protection from experimental asthma by an endogenous bronchodilator. Science 308: 1618–1621, 2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Que LG, Yang Z, Stamler JS, Lugogo NL, and Kraft M. S-nitrosoglutathione reductase: an important regulator in human asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 180: 226–231, 2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Raffay TM, Dylag AM, Di Fiore JM, Smith LA, Einisman HJ, Li Y, Lakner MM, Khalil AM, MacFarlane PM, Martin RJ, and Gaston B. S-nitrosoglutathione attenuates airway hyperresponsiveness in murine bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Mol Pharmacol 90: 418–426, 2016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Rafikova O, Rafikov R, and Nudler E. Catalysis of S-nitrosothiols formation by serum albumin: the mechanism and implication in vascular control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99: 5913–5918, 2002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Raju K, Doulias PT, Evans P, Krizman EN, Jackson JG, Horyn O, Daikhin Y, Nissim I, Yudkoff M, Nissim I, Sharp KA, Robinson MB, and Ischiropoulos H. Regulation of brain glutamate metabolism by nitric oxide and S-nitrosylation. Sci Signal 8: ra68, 2015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Ravi K, Brennan LA, Levic S, Ross PA, and Black SM. S-nitrosylation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase is associated with monomerization and decreased enzyme activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101: 2619–2624, 2004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Rizza S, Montagna C, Cardaci S, Maiani E, Di Giacomo G, Sanchez-Quiles V, Blagoev B, Rasola A, De Zio D, Stamler JS, Cecconi F, and Filomeni G. S-nitrosylation of the mitochondrial chaperone TRAP1 sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to inhibitors of succinate dehydrogenase. Cancer Res 76: 4170–4182, 2016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Rizzo MA. and Piston DW. Regulation of beta cell glucokinase by S-nitrosylation and association with nitric oxide synthase. J Cell Biol 161: 243–248, 2003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Roediger WE. Nitric oxide-dependent nitrosation of cellular CoA: a proposal for tissue responses. Nitric Oxide 5: 83–87, 2001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Roediger WE, Hems R, Wiggins D, and Gibbons GF. Inhibition of hepatocyte lipogenesis by nitric oxide donor: could nitric oxide regulate lipid synthesis? IUBMB Life 56: 35–40, 2004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Romero JM. and Bizzozero OA. Intracellular glutathione mediates the denitrosylation of protein nitrosothiols in the rat spinal cord. J Neurosci Res 87: 701–709, 2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Roy B, du Moulinet d'Hardemare A, and Fontecave M. New thionitrites: synthesis, stability, and nitric oxide generation. J Org Chem 59: 7019–7026, 1994 [Google Scholar]
- 160.Savidge TC, Urvil P, Oezguen N, Ali K, Choudhury A, Acharya V, Pinchuk I, Torres AG, English RD, Wiktorowicz JE, Loeffelholz M, Kumar R, Shi L, Nie W, Braun W, Herman B, Hausladen A, Feng H, Stamler JS, and Pothoulakis C. Host S-nitrosylation inhibits clostridial small molecule-activated glucosylating toxins. Nat Med 17: 1136–1141, 2011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Sayed N, Baskaran P, Ma X, van den Akker F, and Beuve A. Desensitization of soluble guanylyl cyclase, the NO receptor, by S-nitrosylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104: 12312–12317, 2007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Scharfstein JS, Keaney JF, Slivka A, Welch GN, Vita JA, Stamler JS, and Loscalzo J. In vivo transfer of nitric oxide between a plasma protein-bound reservoir and low molecular weight thiols. J Clin Invest 94: 1432–1439, 1994 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Sengupta R, Billiar TR, Kagan VE, and Stoyanovsky DA. Nitric oxide and thioredoxin type 1 modulate the activity of caspase 8 in HepG2 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 391: 1127–1130, 2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Sengupta R, Ryter SW, Zuckerbraun BS, Tzeng E, Billiar TR, and Stoyanovsky DA. Thioredoxin catalyzes the denitrosation of low-molecular mass and protein S-nitrosothiols. Biochemistry 46: 8472–8483, 2007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Seth D, Hausladen A, Wang YJ, and Stamler JS. Endogenous protein S-nitrosylation in E. coli: regulation by OxyR. Science 336: 470–473, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Seth D. and Stamler JS. The SNO-proteome: causation and classifications. Curr Opin Chem Biol 15: 129–136, 2011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Singh SP, Wishnok JS, Keshive M, Deen WM, and Tannenbaum SR. The chemistry of the S-nitrosoglutathione/glutathione system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93: 14428–14433, 1996 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Sips PY, Irie T, Zou L, Shinozaki S, Sakai M, Shimizu N, Nguyen R, Stamler JS, Chao W, Kaneki M, and Ichinose F. Reduction of cardiomyocyte S-nitrosylation by S-nitrosoglutathione reductase protects against sepsis-induced myocardial depression. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 304: H1134–H1146, 2013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Sliskovic I, Raturi A, and Mutus B. Characterization of the S-denitrosation activity of protein disulfide isomerase. J Biol Chem 280: 8733–8741, 2005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.de Smidt O, du Preez JC, and Albertyn J. The alcohol dehydrogenases of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a comprehensive review. FEMS Yeast Res 8: 967–978, 2008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Staab CA, Alander J, Brandt M, Lengqvist J, Morgenstern R, Grafström RC, and Höög J-O. Reduction of S-nitrosoglutathione by alcohol dehydrogenase 3 is facilitated by substrate alcohols via direct cofactor recycling and leads to GSH-controlled formation of glutathione transferase inhibitors. Biochem J 413: 493–504, 2008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Staab CA, Hartmanová T, El-Hawari Y, Ebert B, Kisiela M, Wsol V, Martin HJ, and Maser E. Studies on reduction of S-nitrosoglutathione by human carbonyl reductases 1 and 3. Chem Biol Interact 191: 95–103, 2011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Stamler JS. and Hausladen A. Oxidative modifications in nitrosative stress. Nat Struct Biol 5: 247–249, 1998 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Stamler JS, Singel DJ, and Loscalzo J. Biochemistry of nitric oxide and its redox-activated forms. Science 258: 1898–1902, 1992 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Stamler JS. and Toone EJ. The decomposition of thionitrites. Curr Opin Chem Biol 6: 779–785, 2002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Stamler JS, Toone EJ, Lipton SA, and Sucher NJ. (S)NO signals: translocation, regulation, and a consensus motif. Neuron 18: 691–696, 1997 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Stoyanovsky DA, Tyurina YY, Tyurin VA, Anand D, Mandavia DN, Gius D, Ivanova J, Pitt B, Billiar TR, and Kagan VE. Thioredoxin and lipoic acid catalyze the denitrosation of low molecular weight and protein S-nitrosothiols. J Am Chem Soc 127: 15815–15823, 2005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Straub AC, Billaud M, Johnstone SR, Best AK, Yemen S, Dwyer ST, Looft-Wilson R, Lysiak JJ, Gaston B, Palmer L, and Isakson BE. Compartmentalized connexin 43 S-nitrosylation/denitrosylation regulates heterocellular communication in the vessel wall. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 31: 399–407, 2011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Sun J, Xin C, Eu JP, Stamler JS, and Meissner G. Cysteine-3635 is responsible for skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor modulation by NO. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98: 11158–11162, 2001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Sun QA, Hess DT, Nogueira L, Yong S, Bowles DE, Eu J, Laurita KR, Meissner G, and Stamler JS. Oxygen-coupled redox regulation of the skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor-Ca2+ release channel by NADPH oxidase 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108: 16098–16103, 2011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Szmytkowski C. and Maciag K. Total cross section for electron impact on nitrogen monoxide. J Phys B At Mol Opt Phys 24: 4273–4279, 1991 [Google Scholar]
- 182.Takahashi M, Miyata S, Fujii J, Inai Y, Ueyama S, Araki M, Soga T, Fujinawa R, Nishitani C, Ariki S, Shimizu T, Abe T, Ihara Y, Nishikimi M, Kozutsumi Y, Taniguchi N, and Kuroki Y. In vivo role of aldehyde reductase. Biochim Biophys Acta 1820: 1787–1796, 2012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Talipov MR. and Timerghazin QK. Protein control of S-nitrosothiol reactivity: interplay of antagonistic resonance structures. J Phys Chem B 117: 1827–1837, 2013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Tang CH, Wei W, Hanes MA, and Liu L. Hepatocarcinogenesis driven by GSNOR deficiency is prevented by iNOS inhibition. Cancer Res 73: 2897–2904, 2013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Tello D, Tarín C, Ahicart P, Bretón-Romero R, Lamas S, and Martínez-Ruiz A. A “fluorescence switch” technique increases the sensitivity of proteomic detection and identification of S-nitrosylated proteins. Proteomics 9: 5359–5370, 2009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Tennyson J. and Noble CJ. Low-energy electron scattering by the NO molecule. J Phys B At Mol Phys 19: 4025–4033, 1986 [Google Scholar]
- 187.Thom SR, Bhopale VM, Milovanova TN, Yang M, and Bogush M. Thioredoxin reductase linked to cytoskeleton by focal adhesion kinase reverses actin S-nitrosylation and restores neutrophil β(2) integrin function. J Biol Chem 287: 30346–30357, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Timerghazin QK, Peslherbe GH, and English AM. Resonance description of S-nitrosothiols: insights into reactivity. Org Lett 9: 3049–3052, 2007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Tu SI, Byler DM, and Cavanaugh JR. Nitrite inhibition of acyl transfer by coenzyme A via the formation of an S-nitrosothiol derivative. J Agric Food Chem 32: 1057–1060, 1984 [Google Scholar]
- 190.Valencia E, Larroy C, Ochoa WF, Parés X, Fita I, and Biosca JA. Apo and Holo structures of an NADPH-dependent cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Biol 341: 1049–1062, 2004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Villanueva C. and Giulivi C. Subcellular and cellular locations of nitric oxide synthase isoforms as determinants of health and disease. Free Radic Biol Med 49: 307–316, 2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Wan C, Borgeson B, Phanse S, Tu F, Drew K, Clark G, Xiong X, Kagan O, Kwan J, Bezginov A, Chessman K, Pal S, Cromar G, Papoulas O, Ni Z, Boutz DR, Stoilova S, Havugimana PC, Guo X, Malty RH, Sarov M, Greenblatt J, Babu M, Derry WB, Tillier ER, Wallingford JB, Parkinson J, Marcotte EM, and Emili A. Panorama of ancient metazoan macromolecular complexes. Nature 525: 339–344, 2015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Wang G, Moniri NH, Ozawa K, Stamler JS, and Daaka Y. Nitric oxide regulates endocytosis by S-nitrosylation of dynamin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103: 1295–1300, 2006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Wang PG, Xian M, Tang X, Wu X, Wen Z, Cai T, and Janczuk AJ. Nitric oxide donors: chemical activities and biological applications. Chem Rev 102: 1091–1134, 2002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Wei W, Li B, Hanes MA, Kakar S, Chen X, and Liu L. S-nitrosylation from GSNOR deficiency impairs DNA repair and promotes hepatocarcinogenesis. Sci Transl Med 2: 19ra13, 2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Wei W, Yang Z, Tang CH, and Liu L. Targeted deletion of GSNOR in hepatocytes of mice causes nitrosative inactivation of O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase and increased sensitivity to genotoxic diethylnitrosamine. Carcinogenesis 32: 973–977, 2011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Whalen EJ, Foster MW, Matsumoto A, Ozawa K, Violin JD, Que LG, Nelson CD, Benhar M, Keys JR, Rockman HA, Koch WJ, Daaka Y, Lefkowitz RJ, and Stamler JS. Regulation of beta-adrenergic receptor signaling by S-nitrosylation of G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 2. Cell 129: 511–522, 2007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Williams DLH. The chemistry of S-nitrosothiols. Acc Chem Res 32: 869–876, 1999 [Google Scholar]
- 199.Williamson JR. and Corkey BE. Assay of citric acid cycle intermediates and related compounds—update with tissue metabolite levels and intracellular distribution. In: Biomembranes, Part F: Bioenergetics-Oxidative Phosphorylation, edited by Fleischer S. and Packer L. New York, NY: Academic Press, 1979, pp. 200–222 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Wong PS, Hyun J, Fukuto JM, Shirota FN, DeMaster EG, Shoeman DW, and Nagasawa HT. Reaction between S-nitrosothiols and thiols: generation of nitroxyl (HNO) and subsequent chemistry. Biochemistry 37: 5362–5371, 1998 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.Wu C, Liu T, Chen W, Oka S, Fu C, Jain MR, Parrott AM, Baykal AT, Sadoshima J, and Li H. Redox regulatory mechanism of transnitrosylation by thioredoxin. Mol Cell Proteomics 9: 2262–2275, 2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Wu C, Parrott AM, Fu C, Liu T, Marino SM, Gladyshev VN, Jain MR, Baykal AT, Li Q, Oka S, Sadoshima J, Beuve A, Simmons WJ, and Li H. Thioredoxin 1-mediated post-translational modifications: reduction, transnitrosylation, denitrosylation, and related proteomics methodologies. Antioxid Redox Signal 15: 2565–2604, 2011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Wu C, Parrott AM, Liu T, Jain MR, Yang Y, Sadoshima J, and Li H. Distinction of thioredoxin transnitrosylation and denitrosylation target proteins by the ICAT quantitative approach. J Proteomics 74: 2498–2509, 2011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204.Wu H, Romieu I, Sienra-Monge JJ, Estela Del Rio-Navarro B, Anderson DM, Jenchura CA, Li H, Ramirez-Aguilar M, Del Carmen Lara-Sanchez I, and London SJ. Genetic variation in S-nitrosoglutathione reductase (GSNOR) and childhood asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 120: 322–328, 2007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.Xu L, Eu JP, Meissner G, and Stamler JS. Activation of the cardiac calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor) by poly-S-nitrosylation. Science 279: 234–237, 1998 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206.Yang Z, Wang ZE, Doulias PT, Wei W, Ischiropoulos H, Locksley RM, and Liu L. Lymphocyte development requires S-nitrosoglutathione reductase. J Immunol 185: 6664–6669, 2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 207.Zaman K, Sawczak V, Zaidi A, Butler M, Bennett D, Getsy P, Zeinomar M, Greenberg Z, Forbes M, Rehman S, Jyothikumar V, DeRonde K, Sattar A, Smith L, Corey D, Straub A, Sun F, Palmer L, Periasamy A, Randell S, Kelley TJ, Lewis SJ, and Gaston B. Augmentation of CFTR maturation by S-nitrosoglutathione reductase. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 310: L263–L270, 2016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 208.Zhang R, Hess DT, Qian Z, Hausladen A, Fonseca F, Chaube R, Reynolds JD, and Stamler JS. Hemoglobin βCys93 is essential for cardiovascular function and integrated response to hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112: 6425–6430, 2015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 209.Zhang R, Hess DT, Reynolds JD, and Stamler JS. Hemoglobin S-nitrosylation plays an essential role in cardioprotection. J Clin Invest 126: 4654–4658, 2016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]