Influence of Slc11a1 on the Outcome of Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis Infection in Mice Is Associated with Th Polarization (original) (raw)
Abstract
Genetic analyses identified Ses1 as a significant quantitative trait locus influencing the carrier state of 129S6 mice following a sublethal challenge with Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis. Previous studies have determined that Slc11a1 was an excellent candidate gene for Ses1. Kinetics of infection in 129S6 mice and _Slc11a1_-deficient (129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg) mice demonstrated that the wild-type allele of Slc11a1 contributed to the S. enterica serovar Enteritidis carrier state as early as 7 days postinfection. Gene expression profiling demonstrated that 129S6 mice had a significant up-regulation of proinflammatory genes associated with macrophage activation at day 10 postinfection, followed by a gradual increase in immunoglobulin transcripts, whereas 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice had higher levels of immunoglobulins earlier in the infection. Quantitative reverse transcription-PCR revealed an increase in Th1 cytokine (Ifng and Il12) and Th1-specific transcription factor Tbx21 expression during infection in both the 129S6 and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg strains. However, the expression of Gata3, a transcription factor involved in Th2 polarization, Cd28, and Il4 was markedly increased in _Slc11a1_-deficient mice during infection, suggesting a predominant Th2 phenotype in 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg animals following S. enterica serovar Enteritidis infection. A strong immunoglobulin G2a response, reflecting Th1 activity, was observed only in 129S6 mice. All together, these results are consistent with an impact of Slc11a1 on Th cell differentiation during chronic S. enterica serovar Enteritidis infection. The presence of a Th2 bias in _Slc11a1_-deficient mice is associated with improved bacterial clearance.
Human infectious diseases are among the major causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Gram-negative bacteria of the genus Salmonella are ubiquitous in nature and inhabit the normal intestinal flora of multiple hosts. They can cause a variety of pathologies, including gastroenteritis, abortions, pneumonias, and lethal septicemias, in both humans and animals. Salmonella infections usually occur through ingestion of contaminated food or water and are responsible for two major disease patterns in humans, typhoid fever, a systemic disease, and salmonellosis, a self-containing gastrointestinal illness. Salmonella infection affects 1.4 million people annually in the United States alone, where Salmonella enterica serovars Enteritidis and Typhimurium account for more than half of the reported cases (16). Enteric fever is caused by the human pathogen S. enterica serovar Typhi and to a lesser extent by S. enterica serovar Paratyphi A and B. An estimated 21 million cases of typhoid fever are reported each year, with 200,000 associated fatalities (16). Approximately 5% of infected patients develop a chronic carrier state with active shedding of Salmonella for more than a year, whereas others become lifelong carriers (16). Chronic carriers are at an increased risk of undergoing relapses and developing other pathologies. They also become the new reservoir of the pathogen in the population, increasing the risks of infecting other people and thus playing a major role in the reemergence of epidemic-prone diseases.
In mice, S. enterica serovar Typhimurium causes a systemic disease resembling typhoid fever, and the outcome of infection relies on the activation of both the innate and adaptive immune responses of the host. Studies with mouse models of infection have identified several innate immune genes, including Slc11a1 (solute carrier family 11 member 1, also known as Nramp1), Tlr4 (Toll-like receptor 4), Nos2 (inducible nitric oxide synthase), and that for NADPH oxidase, that influence the early phase of S. enterica serovar Typhimurium infection (reviewed in reference 58). Clearance of the bacteria from the reticuloendothelial system during the late stage of infection involves T and B lymphocytes, costimulatory molecules (CD28), T-cell receptor (TCR), and the major histocompatibility complex class II genes (70).
We have developed a chronic model of Salmonella infection based on the inoculation of a sublethal dose of S. enterica serovar Enteritidis into C57BL/6J and 129S6/SvEvTac (129S6) mice (13). S. enterica serovar Enteritidis infection of C57BL/6J and 129S6 animals does not cause a clinical disease; however, persistence of the bacteria within the spleen and mesenteric lymph nodes is observed for a prolonged period of time in 129S6 compared to C57BL/6J mice (13, 14). Previous single-locus linkage analysis and a genome-wide search for interacting loci in a (C57BL/6J × 129S6)F2 segregating population have revealed that the genetic architecture of Salmonella persistence is different in females and males. In females, the genetic model included the individual effect of Ses3 on chromosome 15 and two significant interactions between Ses1 on chromosome 1 and D7Mit267 and between Ses1 and DXMit48, accounting for 47% of the total phenotypic variance. The model for males included the individual effect of Ses1.1 (proximal chromosome 1) and three interactions (_Ses1_-D9Mit218, _D2Mit197_-D4Mit2, and _D3Mit256_-D13Mit36) and explained 47% of the phenotypic variance (13, 14). These analyses have clearly demonstrated that Ses1, which was validated with congenic mice, is the locus having the greatest impact on the phenotypic variance in both females and males (14).
We have previously reported that Slc11a1 is located at the maximum peak logarithm of the odds score of the Ses1 genetic interval, making this gene an excellent candidate based on its chromosomal position and its function (13). Slc11a1 has been shown in multiple studies to be of primordial importance in the outcome of infections with intracellular pathogens including S. enterica serovar Typhimurium in mice (67, 68). A role for SLC11A1 in the host defense against tuberculosis and leprosy was demonstrated in humans (6, 23, 24) and against salmonellosis and chronic Salmonella carriage in chickens (5, 31, 38). Slc11a1 is involved in the control of bacterial growth in the reticuloendothelial system during the early phase of Salmonella infection. In mice, Slc11a1 presents two allelic forms: a wild-type allele and a susceptible Slc11a1 allele (_Slc11a1_s) that has a nonconservative glycine-to-aspartic acid change at residue 169 which renders the mRNA too unstable to translate into a functional protein (42, 68). Slc11a1 is located in the late endosome-lysosome compartment of resting phagocytes (29, 59) and is recruited to the membrane of phagosomes containing live bacteria (29). During Salmonella infection, the bacteria are phagocytosed by macrophages and polymorphonuclear cells (PMNs), in which fusions of early endosomes with lysosomes decrease the internal phagosomal pH and confer bactericidal properties on these cells (18, 72). To circumvent bacterial killing, salmonellae generate a specialized compartment named the _Salmonella_-containing vacuole (SCV), in which the environment is favorable to the survival of the bacteria. Slc11a1 has been shown to have an impact on SCV maturation: SCVs formed in _Slc11a1_-deficient macrophages do not acquire M6PR (mannose 6-phosphate receptor), a protein known to regulate the delivery of a subset of lysosomal enzymes from the trans-Golgi network to the prelysosomal compartment (18, 29, 35, 72). In addition, Slc11a1 functions as a pH-dependent manganese (Mn2+) and iron (Fe2+) efflux pump (25, 33, 34) at the phagosomal membrane. Divalent cations like manganese and iron are critical for the survival of pathogens, and removal of these from the phagosome results in enhanced bacteriostatic and/or bactericidal activity. SCV maturation is restored in iron-depleted primary macrophages from _Slc11a1_-deficient mice, suggesting that Slc11a1 counteracts the ability of salmonellae to arrest phagosome maturation through depletion of iron and/or other cations (34).
The involvement of Slc11a1 in controlling S. enterica serovar Enteritidis clearance was initially demonstrated with mice carrying a null allele at Slc11a1 (129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg) (13). In the experimental model of S. enterica serovar Enteritidis infection, the wild-type allele at Slc11a1 contributes to Salmonella persistence in the spleens of 129S6 mice during the late phase of infection. The objective of the present study was to investigate this unexpected role of Slc11a1 in the outcome of a chronic Salmonella infection. These analyses provide evidence that functional polymorphisms at Slc11a1 are associated with T-helper cell polarization during a chronic S. enterica serovar Enteritidis infection, leading to either bacterial clearance (predominant Th2 response in 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice) or bacterial persistence (predominant Th1 response in 129S6 mice).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animals.
The inbred mouse strains 129S6/SvEvTac (129S6) and C57BL/6J were obtained from Taconic (Germantown, NY) and The Jackson Laboratories (Bar Harbor, ME), respectively. The 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice were provided by Philippe Gros (McGill University, Montreal, Québec, Canada). The 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice were generated by crossing chimeric offspring created with embryonic stem cells of 129S6/SvEvTac origin with 129S6/SvEvTac mice. Prior to infection, all mice were maintained in our animal facilities under conditions specified by the Canadian Council on Animal Care.
Salmonella infection.
The Salmonella stock and infectious dose were prepared as previously described (60). Briefly, mice were infected intravenously with 1,000 CFU of S. enterica serovar Enteritidis strain 3b (William Kay, University of Victoria, Victoria, British Columbia, Canada) and sacrificed 1, 3, 5, 7, 10, or 42 days postinoculation by carbon dioxide asphyxiation. The spleens were removed aseptically and used for CFU counts, RNA extraction, or splenocyte purification. The Salmonella loads in the spleens were obtained, counted, and analyzed as described by us previously (13). The spleen index was determined as the root square of the spleen weight (×100) divided by the body weight (26).
Hematology.
Blood samples were obtained by cardiac puncture from control animals and infected mice at 10 and 42 days postinoculation. The collected blood was diluted 1:200 in 1× phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) or 1:10 in 3% acetic acid to enumerate the erythrocytes (RBC) and leukocytes (WBC), respectively, and the numbers of cells were determined microscopically with a hemocytometer. The percentages of macrophages, lymphocytes, and polymorphonuclear cells were determined by differential counts of 400 cells on blood smears stained with Diff-Quick (Dade Behring, Zurich, Switzerland).
Tissue sample collection and histological evaluation.
Mice were anesthetized with a mixture of ketamine and xylazine in saline. Anesthetized mice were perfused through cardiac puncture with 0.9% saline, followed by 4% paraformaldehyde in 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.4). The tissues were collected and kept in 20% sucrose-PBS for further histopathologic examination. Fixed tissue samples were processed, embedded in paraffin, sectioned at 5 μm, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin.
Flow cytometry.
Spleens were aseptically removed from control and infected 129S6 and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice. The red pulp was removed through gentle homogenization of the spleen between the frosted ends of two sterile glass slides, red blood cells were lysed, and splenocytes were extracted with Lympholyte M (Cedarlane Laboratories Limited, Hornby, Ontario, Canada). Splenocytes were counted and adjusted to the desired concentration in RPMI medium (Invitrogen Life Technologies, Burlington, Ontario, Canada). The cells were stained with 2 μg of monoclonal antibody (MAb) suspended in PBS supplemented with 1% bovine serum albumin and 0.1% sodium azide for 30 min at 4°C. After washes, the cells were suspended in PBS with 1% fetal calf serum (HyClone, Logan, Utah) and 0.1% sodium azide. These cells were immediately analyzed by FACScan (BD Biosciences, Mississauga, Ontario, Canada). Data analysis was performed with the CellQuest software (BD Biosciences, Mississauga, Ontario, Canada). The different splenic cell populations were determined by single-color staining of surface markers. Fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated MAbs were all purchased from PharMingen (BD Biosciences, Mississauga, Ontario, Canada). The MAbs used were against mouse CD3 (clone 145-2C11, hamster immunoglobulin G [IgG]), CD4 (clone RM4-5, rat IgG2a), CD8 (clone 53-6.7, rat IgG2a), B220 (clone RA3-6B2, rat IgG2a), MAC-1 (clone M1/70, rat IgG2b), F4/80 [clone 6F12, rat IgG2a(κ)], Gr-1 (clone RB6-8C5, rat IgG2b), αβ TCR [clone H57-597, Armenian hamster IgG2(λ1)], γδ TCR [clone GL3, Armenian hamster IgG2(κ)], and PanNK/CD49b [clone DX5, rat IgM(κ)].
RNA extraction.
RNA was extracted from the spleens of control and infected animals with TRIZOL reagent according to the manufacturer's instructions (Invitrogen Life Technologies, Burlington, Ontario, Canada). Briefly, 30 to 50 μg of the spleen was homogenized and placed in TRIZOL solution to extract the RNA. The RNA was purified with chloroform and precipitated in isopropanol. The RNeasy total RNA cleanup kit was used as an extra RNA-purifying step (QIAGEN, Mississauga, Ontario, Canada). The RNA was suspended in RNase-free diethyl pyrocarbonate water (Invitrogen Life Technologies, Burlington, Ontario, Canada) and quantitated by spectrophotometry, and its quality was observed by gel electrophoresis with morpholinepropanesulfonic acid (MOPS) buffer, as well as with the RNA 6000 Nano LabChip with the 2100 bioanalyzer (Agilent, Palo Alto, CA).
Microarray analysis.
Total spleen RNAs of 129S6 and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg female mice were extracted from control and _Salmonella-_infected animals sacrificed at days 10 and 42 postchallenge and were pooled to account for all possible intrastrain variation. These RNA pools were used to prepare biotinylated targets as previously described (65). Preparation of fluorescent cRNA, hybridization, and scanning of the arrays were done according to the manufacturer's instructions (Affymetrix, Santa Clara, CA). Briefly, 10 μg of RNA was reversed transcribed to double-stranded cDNA with an oligo(dT) primer containing a T7 RNA polymerase binding site. The cDNA was transcribed in vitro to cRNA with biotinylated dUTP and dCTP. Microarray hybridizations were performed with 10 μg of target cRNA on the Affymetrix U74Av2 GeneChip (Affymetrix, Santa Clara, CA). These microarrays contain probe sets for 12,000 mouse genes (6,000 known genes and 6,000 expressed sequence tags). Hybridized microarrays were scanned with a GeneArray scanner (Hewlett-Packard, Palo Alto, CA). Transcript expression levels were calculated from a single average difference ratio across 16 probe pairs, as well as a reliability score (ambiguous or absent [A], marginal [M], or present [P], based on the hybridization variability within each probe set) following scanning of the hybridized microarrays with the Affymetrix GeneChip Mas 4 software (Affymetrix, Santa Clara, CA).
The raw expression values were analyzed with the GeneSpring software package v7.0 (Silicon Genetics, Redwood City, CA). The data were normalized per chip to the 50th percentile and per gene by using the median. All values below 0.1 were reassigned a threshold value of 0.1. The probe sets showing an A reliability score at all of the time points were discarded. Once the normalization steps were done, we considered the genes with an expression change of twofold or more between the 129S6 and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mouse strains at any time point for further analysis. GeneSpring allowed the regular retrieval of newly annotated expressed sequence tags from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (www.ncbi.nih.gov/). The selected genes were then organized in functional clusters. The genes that were scrutinized in more detail were the ones with known functions or those involved in pathways implicated in inflammation.
Quantification of the expression of genes influencing Th cell development.
A set of genes known to be involved in the differentiation process of Th cells were selected for quantification and include the cytokine genes Ifng, Il12, and Il4; the transcription factor genes Tbx21 and Gata3; and the costimulatory molecule genes Cd28, Cd80, and Cd86. Reverse transcription was performed with 5 μg of total RNA and Moloney murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase (Invitrogen Life Technologies, Burlington, Ontario, Canada). Real-time PCR was performed in duplicate on each transcript with Brilliant SYBR green QPCR master mix according to the manufacturer's (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA) instructions. The primers used were designed from the coding sequences of the genes as obtained from the Affymetrix identification number and the Ensembl mouse genome server (www.ensembl.org/Mus_musculus/). The relative expression of the genes was normalized to the amount of TATA box-binding protein (Tbp) (endogenous reference) and compared to a calibrator (gene mRNA expression in naive animals) by using the 2−ΔΔCT method (40).
Measurements of cytokines in serum during infection.
Interleukin-12 (IL-12), gamma interferon (IFN-γ), and IL-4 levels in serum were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) at days 1, 3, 5, 7, 10, and 42 postinfection with paired MAbs and recombinant mouse cytokines as standards according to the manufacturer's (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN) instructions.
Antibody response to Salmonella infection.
Serum was obtained from the blood of control and _Salmonella-_infected mice. Total serum IgG, IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b, IgG3, and IgM levels were measured with commercial ELISA kits (Bethyl Laboratories, Montgomery, TX). The anti-Salmonella IgG, IgG1, and IgG2a responses to S. enterica serovar Enteritidis were determined by ELISA with sonicated-killed S. enterica serovar Enteritidis as previously described (4).
Statistical analysis.
Data were analyzed by analysis of variance and the Wilcoxon rank-sum test, where appropriate. Two-tailed P values of <0.05 were considered statistically significant. Where appropriate, P value adjustments for multiple testing were done by a Bonferroni method (69). All analyses were conducted with SAS 9.1 (69).
RESULTS
_Slc11a1_-deficient mice clear S. enterica serovar Enteritidis more efficiently.
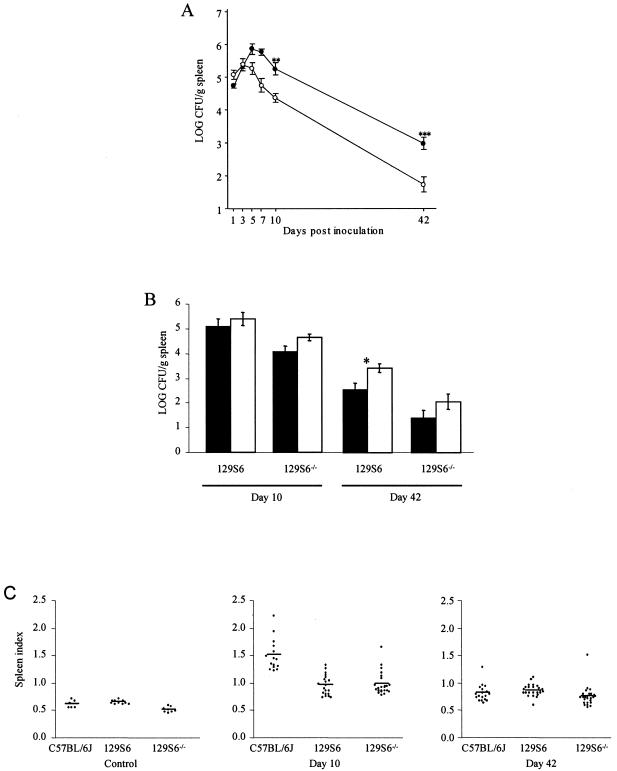
We investigated the candidacy of Slc11a1 as the gene underlying Ses1 with mice carrying a null allele at Slc11a1 (129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg). Initial data have shown that 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice have a significantly lower spleen S. enterica serovar Enteritidis load compared to that of wild-type 129S6 mice at day 42 postinfection (13). To characterize the course of S. enterica serovar Enteritidis infection in mice carrying a null allele at Slc11a1, we infected 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg knockout mice with ∼103 CFU of salmonellae and compared the bacterial loads in the spleens of these animals to those of their wild-type 129S6 counterparts on days 1, 3, 5, 7, 10, and 42 postinfection (Fig. 1A). Bacterial loads in the spleen were consistently lower in 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice in both the early (days 5, 7, and 10) and the late (day 42) phases of infection (Fig. 1A). The early difference in bacterial load observed at day 3 between the C57BL/6J and 129S6 mice (13) was not reproduced in this study, suggesting that the higher S. enterica serovar Enteritidis load observed in C57BL/6J mice is not explained by Slc11a1 but rather by a C57BL/6J background effect. We observed an impact of gender on the spleen bacterial loads in both wild-type and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice. Female mice had lower bacterial loads than the males at day 42 postinfection, consistent with our genetic models (Fig. 1B). _Slc11a1_-deficient mice present a phenotype very similar to that observed in 129S6.B6-Ses1 congenic mice with respect to bacterial load and sex effect, providing further evidence that Slc11a1 is the likely gene underlying Ses1 (14).
FIG. 1.
(A) Kinetics of infection in inbred mice following administration of a sublethal inoculum of S. enterica serovar Enteritidis. Black and white circles represent groups of four to six 129S6 and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice, respectively, that were sacrificed at different time points following intravenous infection with 1,000 CFU of S. enterica serovar Enteritidis strain 3b. The experiments were done in triplicate. The data are the average log CFU per gram of spleen ± the standard error of the mean. Asterisks represent the significance levels of the difference in the numbers of Salmonella CFU between the two strains of mice (**, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001). (B) Graphic representation of Salmonella carriage in female (black columns) and male (white columns) 129S6 and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg (129S6−/−) mice at days 10 and 42 following a challenge with S. enterica serovar Enteritidis. The asterisk represents the significance levels of the differences in Salmonella carriage between the female and male mice (P < 0.05). (C) Scatterplots demonstrating the spleen indexes of C57BL/6J, 129S6, and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg (129S6−/−) control mice and mice infected for 10 and 42 days with S. enterica serovar Enteritidis. The experiments were done in triplicate, and each dot represents an animal.
Slc11a1-deficient mice develop a marked leukocytosis during infection which correlates with bacterial clearance.
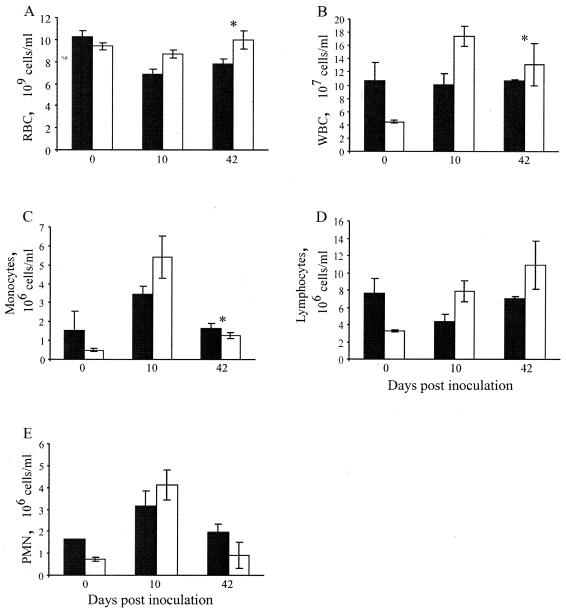
Hematological parameters of 129S6 and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice were measured during infection with S. enterica serovar Enteritidis. As expected, all control mice had levels of RBC and WBC within the accepted norms (Fig. 2A and B). The proportions of monocytes, lymphocytes, and PMNs within the WBC compartment were also normal (Fig. 2C, D, and E). Following infection, only the 129S6 mice developed moderate anemia, as demonstrated by the lower erythrocyte levels at day 42 postinoculation compared to those of the noninfected mice (Fig. 2A). Decreases of 38% (day 10) and 17% (day 42) in the numbers of RBC were noted in the peripheral blood from 129S6 mice compared to that from 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg animals after infection. In 129S6 mice, total WBC were found to be at constant levels throughout the infection, compared to 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice, which showed an increase in total WBC at day 10 postinfection (Fig. 2B). The leukocytosis of 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice is explained by a sharp increase in monocyte and PMN levels at day 10 postinfection (Fig. 2C and E). In addition, 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice showed an increase in circulating lymphocyte counts throughout infection, whereas 129S6 mice developed a transient lymphopenia following Salmonella challenge characteristic of a more acute disease condition (Fig. 2D). Taken together, these results suggest that the hematological parameters reflect the progression of the infection in 129S6 and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice and suggest that 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg animals are in a recovery phase of the Salmonella infection compared to 129S6 mice.
FIG. 2.
Hematological analysis of 129S6 (black columns) and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg (white columns) mice following an intravenous challenge with 1,000 CFU of S. enterica serovar Enteritidis. The total numbers of RBC (A) and WBC (B), as well as the levels of circulating monocytes (C), lymphocytes (D), and PMNs (E) were evaluated in naive (day 0) and infected (days 10 and 42) animals. The data are expressed as the mean of the total number of cells per milliliter ± the standard error of the mean for groups of two to six control and infected animals, respectively. An asterisk indicates a significant difference in a hematological parameter between the two strains of mice (P < 0.05).
Slc11a1 has no impact on the macroscopic and histopathologic phenotypes and cellularity of the spleen during S. enterica serovar Enteritidis infection.
The finding that the wild-type allele at Slc11a1 influences the outcome of a persistent S. enterica serovar Enteritidis infection was unexpected since it has been shown in several studies to be protective against highly virulent S. enterica serovar Typhimurium infections. We hypothesized that the absence of a functional Slc11a1 protein may cause increased recruitment of inflammatory cells at the site of infection, which in turn, by secreting specific cytokines or other inflammatory mediators, are able to more efficiently eliminate the bacteria later during infection. To investigate this hypothesis, we measured the spleen index, performed a histopathologic analysis of the spleen, and analyzed spleen cell types by fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS) in control and infected 129S6 and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice.
The spleen index was measured in 129S6 and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice and compared to that of the C57BL/6J (Slc11a1 Asp169) strain. All mice presented a transient splenomegaly following infection with S. enterica serovar Enteritidis (Fig. 1C). Control 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg animals had a significantly lower spleen index average (0.52 ± 0.02; P < 0.0001) than the spleen index average of the 129S6 (0.63 ± 0.01) mice (Fig. 1C), although they were both within normal limits. The C57BL/6J mice presented the highest spleen index (1.50 ± 0.30) at day 10 postinfection. The 129S6 and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg strains had a significant and comparable increase in their spleen indexes 10 days postinfection (∼0.95 to 1.13). By day 42 postinfection, the spleen index decreased in all mouse strains, with the 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice having significantly lower values than their wild-type counterparts (P = 0.0342) (Fig. 1C). These data showed that _Slc11a1_-deficient mice behave similarly to 129S6.B6-Ses1 mice (not shown) with respect to splenomegaly and that Slc11a1 has little or no effect on the development of this phenotype during infection with S. enterica serovar Enteritidis.
We next examined the consequence of infection with S. enterica serovar Enteritidis for the spleens of the C57BL/6J, 129S6, congenic 129.B6-Ses1, and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mouse strains at day 10 and day 42 postinfection. Microscopic examination of histological sections of the spleens showed similar lesions in all mice, consisting of mild lymphoid atrophy of the periarteriolar lymphoid sheaths at day 10. Splenic thrombosis was also noted in 129S6, 129S6.B6-Ses1, and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice. At day 42, there were no significant histological changes in the spleen sections from any of the strains analyzed (data not shown).
We further investigated the recruitment of immune cells to the spleen by FACS analysis in 129S6 and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg naive and infected mice. Single-cell suspensions were prepared from the spleen and analyzed for surface markers expressed on mononuclear phagocytes (Mac1 and F4/80), granulocytes (Gr-1), T lymphocytes (CD3, CD4, CD8, and αβ and γδ TCRs), B lymphocytes (B220), and NK cells (PanNK). The total cellularity and the different cellular compartments were comparable in uninfected 129S6 and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice (Table 1). Both strains showed significant increases in the total number of spleen cells at day 10 postinfection, although the increase was more pronounced in 129S6 mice (Table 1). This increase affected all cellular compartments but was not significantly different between the 129S6 and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mouse spleens. The number of positively stained cells returned to uninfected levels in both strains at 42 days postinfection (Table 1).
TABLE 1.
Distribution of cell types in the spleens of 129S6 and 129S6-Slc11a1tm1Mcg mice
| Strain | No. of days p.i.c | Total no. of cellsa | Total no. of stained cells/spleen (106)a | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD3 | CD4 | CD8 | B220 | MAC | F4/80 | αβ | γδ | Gr1 | Pan-NK | |||
| 129S6 | 0 | 20.0 ± 0.0 | 7.1 ± 0.5 | 5.2 ± 0.2 | 1.8 ± 0.2 | 12.3 ± 0.7 | 1.2 ± 0.2 | 1.5 ± 0.8 | 6.6 ± 0.3 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 1.5 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.1 |
| 129S6 | 10 | 170.0 ± 19.3 | 70.8 ± 10.0 | 46.1 ± 6.7 | 19.6 ± 3.0 | 59.1 ± 6.0 | 27.2 ± 3.9 | 20.9 ± 2.9 | 76.3 ± 10.8 | 37.1 ± 4.1 | 20.1 ± 3.0 | 10.4 ± 1.6 |
| 129S6 | 42 | 16.3 ± 1.8 | 7.5 ± 0.9 | 5.9 ± 1.4 | 1.7 ± 0.2 | 9.3 ± 1.0 | 1.2 ± 0.2 | 1.9 ± 0.3 | 7.8 ± 1.2 | 1.7 ± 0.4 | 2.1 ± 0.4 | 0.4 ± 0.1 |
| 129S6−/−b | 0 | 13.9 ± 6.1 | 5.1 ± 2.6 | 3.9 ± 2.2 | 1.2 ± 0.5 | 8.9 ± 3.3 | 0.6 ± 0.3 | 0.5 ± 0.2 | 4.4 ± 3.4 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.4 | 0.2 ± 0.1 |
| 129S6−/−b | 10 | 149.0 ± 22.5 | 53.7 ± 4.5 | 38.1 ± 3.3 | 14.4 ± 1.4 | 52.4 ± 8.3 | 22.5 ± 4.1 | 16.8 ± 3.4 | 60.2 ± 6.3 | 33.2 ± 6.7 | 18.5 ± 3.1 | 9.4 ± 1.8 |
| 129S6−/−b | 42 | 17.3 ± 2.7 | 6.7 ± 1.2 | 4.9 ± 4.7 | 1.8 ± 0.3 | 8.9 ± 1.6 | 1.8 ± 0.7 | 1.3 ± 0.2 | 7.4 ± 1.2 | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 2.7 ± 0.7 | 0.3 ± 0.0 |
Overall, the histopathologic changes in the spleen and the cell types involved in splenomegaly were very similar in 129S6 and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice following S. enterica serovar Enteritidis infection. These results did not suggest a difference in the type and extent of cellular inflammation in the spleens of 129S6 and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice that could explain the difference in bacterial clearance between the two strains.
Impact of Slc11a1 on gene expression profiles in the spleen during infection with S. enterica serovar Enteritidis.
To further investigate the specific activation of inflammatory cells involved in the ability of 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice to clear an S. enterica serovar Enteritidis infection, we performed gene expression profiling with commercial Affymetrix DNA chips. Because the spleen is the key tissue for S. enterica serovar Enteritidis persistence and since bacterial clearance is more efficient in females compared to males (13, 14), we used spleen RNAs prepared from female 129S6 and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice to study the effect of Slc11a1 on the expression profile of genes influencing the adaptive and cellular immune responses. In this analysis, we selected the genes that had a minimum 2.0-fold change in their expression levels between the control and infected mice, as well as between the 129S6 and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice, at any one of the time points studied. As expected from the histopathology and FACS analyses, the majority of up- and down-regulated genes in the spleen during a Salmonella infection were found at day 10 postinoculation (Table 2). The numbers of genes transcriptionally altered at day 10 and day 42 postinfection were 149 and 74, respectively. A large proportion of these genes (about 30%) have been shown to be involved in immunity to infection. At day 10 postinfection, the 129S6 mice had higher expression of the type 1 cytokine gene Ifng associated with cell-mediated immunity genes and of additional genes involved in the early response to infection, including those for acute-phase proteins (Saa3 and Irg1); proinflammatory molecules (Il1a and Tnfa); T-cell-, monocyte-, and granulocyte-tropic chemokines or receptors (Ccl2, Cxcl5, Ccl7, Ccl8, and Fpr1); and macrophage receptors (Marco, Msr1, and Cd14) (Table 2). At day 10 postinfection, the _Slc11a1_-deficient mice presented higher Ig levels and showed an increase in the expression in inflammatory genes, although not as strong as the response mounted by their wild-type counterparts (Table 2). Other host response genes, including the cell surface lymphocyte antigens (Cd8b and Klra7) and the cell adhesion molecule Icam1, were up-regulated in _Slc11a1_-deficient mice.
TABLE 2.
Genes differentially expressed in 129S6 versus 129S6-Slc11a1tm1Mcg mice at day 10 following an S. enterica serotype Enteritidis challengea
| Group and designation | Gene name or productb | Identifierc | Function | Fold change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immune response | ||||
| Saa3 | Serum amyloid A3 | Mm.14277 | Acute immune response | 5.51 |
| Irg1 | Immunoresponsive gene 1 | Mm.4662 | Inflammation | 4.83 |
| Ccl8 | Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 8 | Mm.42029 | Inflammation | 4.20 |
| Marco | Macrophage receptor | Mm.1856 | Scavenger receptor | 3.88 |
| Cxcl5 | Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 5 | Mm.4660 | Inflammation | 3.45 |
| Msr1 | Macrophage scavenger receptor 1 | Mm.239291 | Endocytosis | 3.19 |
| Tnfa | Tumor necrosis factor alpha | Mm.1293 | Inflammation | 2.88 |
| Il1a | IL-1α | Mm.15534 | Cytokine | 2.85 |
| Ifng | IFN-γ | Mm.240327 | Inflammation | 2.84 |
| Chia pending | Chitinase (pending) | NA | Eosinophil chemotactic cytokine | 2.77 |
| Fpr1 | _N_-Formyl peptide chemotactic receptor | Mm.56951 | Chemotaxis | 2.48 |
| Aif1 | Allograft inflammatory factor 1 | Mm.10742 | Inflammation | 2.37 |
| Ccl2 | Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 | Mm.290320 | Inflammation | 2.33 |
| Lilrb4 | Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor B4 | Mm.34408 | Immune response | 2.22 |
| Ier3 | Immediate-early response 3 | Mm.25613 | Acute immune response | 2.20 |
| Ccr5 | Chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 5 | Mm.14302 | Chemokine receptor | 2.17 |
| Cd14 | CD14 antigen | Mm.3460 | Inflammation | 2.16 |
| Bnip3 | BCL2/adenovirus E1B-interacting protein 1, NIP3 | Mm.2159 | Apoptosis | 2.04 |
| Ccl7 | Cytokine gene | Mm.341574 | Chemotaxis | 2.03 |
| Ccl21a | Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 21a (leucine) | Mm.348219 | Chemokine | −2.01 |
| Bcl2a1a | B-cell leukemia/lymphoma 2-related protein A1a | Mm.196770 | Apoptosis | −2.03 |
| Ifrd1 | IFN-related developmental regulator 1 | Mm.168 | Cell differentiation | −2.07 |
| Icam1 | Intercellular adhesion molecule | Mm.90364 | Defense response | −2.23 |
| Klra13 | Killer cell lectin-like receptor A, member 13 | Mm.333431 | Defense response | −2.29 |
| Cd8b | CD8 antigen, beta chain | Mm.333148 | Immune response | −2.31 |
| Klra8 | Killer cell lectin-like receptor A, member 8 | Mm.358615 | Defense response | −2.66 |
| Klra7 | Killer cell lectin-like receptor A, member 7 | Mm.193478 | Defense response | −2.81 |
| Klra3 | Killer cell lectin-like receptor A, member 3 | Mm.358615 | Defense response | −3.87 |
| Immunoglobulin | ||||
| Igh-6 | Ig heavy chain 6 of IgM | Mm.342177 | Antigen binding | 2.56 |
| H2-Eb1 | Major histocompatibility complex class II antigen Eβ | Mm.22564 | Antigen presentation | 2.51 |
| Sema4a | Sema and Ig domains (semaphorin) 4A | Mm.22061 | Immunoglobulin | 2.04 |
| Gm900 | Gene model 900 | Mm.360834 | Immunoglobulin | −2.05 |
| LOC434035 | IgV(κ) chain 1 | Mm.305094 | Immunoglobulin | −2.35 |
| Igk-V8 | Immunoglobulin κ chain variable 8 | Mm.333117 | Immunoglobulin | −2.50 |
| Igh-VJ558 | Immunoglobulin heavy chain (J558 family) | Mm.240437 | Immunoglobulin | −2.63 |
| Nucleic acid binding | ||||
| Cntn1 | Contactin 1 | Mm.4911 | DNA binding | 6.54 |
| Upp | Uridine phosphorylase | Mm.4610 | Nucleoside metabolism | 4.82 |
| Cbx2 | Chromobox homolog 2 | Mm.14547 | Chromatin | 3.48 |
| Lass2 | Longevity assurance homolog 2 | Mm.181009 | Transcription factor activity | 2.53 |
| Hoxd3 | Hoxd-3 | Mm.3578607 | Regulation transcription | 2.35 |
| Dmc1h | Disrupted meiotic cDNA 1 homolog | Mm.2524 | DNA repair | 2.05 |
| Dlx6 | Distal-less homeobox 6 | Mm.5152 | DNA binding | −2.02 |
| Hspa1a | Heat shock protein 1A | Mm.6388 | DNA repair | −2.06 |
| Sox6 | SRY box-containing gene 6 | Mm.323365 | Transcription factor activity | −2.09 |
| Setdb1 | SET domain, bifurcated 1 | Mm.181661 | DNA binding | −2.21 |
| Ddx6 | DEAD/H (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp/His) box polypeptide 6 | Mm.267061 | RNA binding | −2.82 |
| Mef2c | Myocyte enhancer factor 2C | Mm.24001 | Transcription factor activity | −2.96 |
| Nab1 | Ngfi-A binding protein 1 | Mm.25903 | Transcription repression | |
| Zfp40 | Zinc finger protein 40 | Mm.21025 | Nucleic acid binding | −3.42 |
| Protein binding | ||||
| Nedd8 | Neural, developmentally down-regulated gene 8 | Mm.296566 | Protein binding | 2.91 |
| Snx10 | Sorting nexin 10 | Mm.294166 | Protein transport | 2.08 |
| Vps45 | Vacuolar protein sorting 45 (yeast) | Mm.263185 | Protein transport | 2.07 |
| Ltbp4 | Latent transforming growth factor beta binding protein 4 | Mm.272251 | Protein binding | −2.04 |
| Dsc2 | Desmocollin 2 | Mm.280547 | Protein binding | −2.06 |
| Epb4.1 | Erythrocyte protein band 4.1 | Mm.30038 | Actin binding | −2.06 |
| Sos1 | Son of sevenless homolog 1 (Drosophila) | Mm.60975 | Protein binding | −2.42 |
| Arl4 | ADP-ribosylation factor-like 4 | Mm.12723 | Protein transport | −2.76 |
| Metabolism | ||||
| Chi3l1 | Chitinase 3-like 1 | Mm.38274 | Metabolism | 3.29 |
| Acrp30 | Adipocyte complement-related protein | Mm.3969 | Glucose metabolism | 2.61 |
| Clecsf8 | C-type lectin, superfamily member 8 | Mm.299633 | Sugar binding | 2.35 |
| Bpgm | 2,3-Bisphosphoglycerate mutase | Mm.282863 | Metabolism | −2.00 |
| Lipe | Hormone-sensitive lipase | Mm.333679 | Cholesterol metabolism | −2.04 |
| Enzyme activity | ||||
| Ptgs2 | Prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase 2 | Mm.292547 | Oxidoreductase activity | 3.34 |
| Dapk2 | Death-associated kinase 2 | Mm.335252 | Protein kinase | 2.88 |
| Ctla2b | Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 2β | Mm.358584 | Cysteine protease inhibitor | 2.51 |
| Aoah | Acyloxyacyl hydrolase | Mm.314046 | Hydrolase activity | 2.48 |
| Timp1 | Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 | Mm.8245 | Metalloendopeptidase inhibitor | 2.46 |
| Ptpro | Protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type O | Mm.186361 | Hydrolase activity | 2.43 |
| Gzmk | Mus musculus granzyme K gene | Mm.56993 | Proteolysis and peptidolysis | 2.19 |
| Blmh | Bleomycin hydrolase | Mm.22876 | Proteolysis and peptidolysis | 2.17 |
| Bst1 | Bone marrow stromal cell antigen 1 | Mm.246332 | Hydrolase activity | 2.07 |
| Cd160 | CD160 antigen | Mm.34693 | Oxidoreductase activity | 2.02 |
| Atp2a3 | ATPase, Ca2+ transporting | Mm.6306 | ATPase | −2.01 |
| Cat | Catalase | Mm.4215 | Oxidoreductase activity | −2.05 |
| Adam22 | A disintegrin and metalloprotease domain 22 | Mm.275895 | Proteolysis and peptidolysis | −2.12 |
| Pdpk1 | 3-Phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 | Mm.10504 | Protein kinase | −2.37 |
| Oaz1 | Ornithine decarboxylase antizyme | Mm.683 | Enzyme inhibitor | −2.41 |
| Eps8 | Epidermal growth factor receptor pathway substrate 8 | Mm.235346 | Proteolysis and peptidolysis | −2.43 |
| Cpe | Carboxypeptidase E | Mm.31395 | Proteolysis and peptidolysis | −2.84 |
| Reln | Reelin | Mm.3057 | Endopeptidase activity | −3.02 |
| Acat2 | Acetyl-coenzyme A acetyltransferase 2 | Mm.360538 | Acetyl-coenzyme A acetyltransferase | −3.06 |
| Cell maintenance | ||||
| Socs3 | Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 | Mm.3468 | Signaling | 3.09 |
| Slfn4 | Schlafen 4 | Mm.38192 | Cell proliferation | 2.45 |
| Emp1 | Emp-1 | Mm.182785 | Cell growth | 2.07 |
| Cdkn1a | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A | Mm.195663 | Cell cycle | 2.01 |
| Other | ||||
| Arfgef1 | ADP-ribosylation factor guanine nucleotide-exchange factor 1 | Mm.229141 | NAd | 2.47 |
| Procr | Protein C receptor, endothelial | Mm.3243 | Blood coagulation | 2.24 |
| Edr | Erythroid differentiation regulator | Mm.358827 | NA | 2.09 |
| Gp49a | Glycoprotein 49A | Mm.358601 | Cell surface antigen | 2.03 |
| Serf2 | Small EDRK-rich factor 2 | Mm.262252 | NA | −2.01 |
| Snca | Synuclein alpha | Mm.17484 | Synaptic vesicle transport | −2.05 |
| Ddit4 | DNA damage-inducible transcript 4 | Mm.21697 | NA | −2.13 |
| Mdm1 | Transformed mouse 3T3 cell double minute 1 | Mm.101191 | NA | −2.14 |
| Cdr2 | Cerebellar degeneration-related 2 | Mm.1640 | NA | −2.18 |
| Clcn3 | Chloride channel 3 | Mm.259751 | Ion transport | −2.21 |
| Sparcl1 | Extracellular matrix-associated protein (Sc1) | Mm.29027 | Calcium binding | −2.25 |
| Als2cr3 | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 2 candidate 3 | Mm.222887 | γ-Aminobutyric acid receptor binding | −2.58 |
| Shoc2 | Soc-2 (suppressor of clear) homolog (Caenorhabditis elegans) | Mm.33376 | NA | −2.59 |
| FHOS2 | Diaphanous protein homolog 3 | Mm.329322 | NA | −2.67 |
| Mab21l2 | MAb 21-like 2 (C. elegans) | Mm.214385 | Development | −3.54 |
| Adm | Adrenomedullin | Mm.1408 | Neuropeptide signaling pathway | −3.99 |
At day 42 postinfection, we observed a decrease in the expression of inflammatory genes in both strains of mice (Table 3). Interestingly, there was an up-regulation of genes (Slpi and Sli12) known to have an inhibitory effect on the inflammatory response in 129S6 mice concomitantly with an increase in the expression of several Ig genes (Table 3). The expression of Ig genes was down regulated in the 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice at day 42 postinfection. Overall, the transcriptional activity was returned to uninfected status by day 42 in _Slc11a1_-deficient mice. It is clear from these experiments that the reprogramming of the transcriptome during an S. enterica serovar Enteritidis infection is temporally different in 129S6 and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice. In addition, preferential early induction of genes in specific cells is different in 129S6 and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg spleens such that genes involved with macrophages and/or dendritic cell activation predominate in 129S6 mice whereas induction of genes involved in lymphocyte activation are present in 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice.
TABLE 3.
Genes differentially expressed in 129S6 versus 129S6-Slc11a1tm1Mcg mice at day 42 following an S. enterica serotype Enteritidis challengea
| Group and designation | Gene name, product, or descriptionb | Identifierc | Function | Fold change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immunoglobulin | ||||
| LOC213156 | Gamma variable region | Mm.313444 | Antigen binding | 5.00 |
| LOC382694 | Similar to Ig heavy chain | Mm.304472 | Antigen binding | 3.02 |
| LOC382692 | Similar to Ig heavy chain | Mm.313423 | Antigen binding | 2.87 |
| Igh-6 | Ig heavy chain of IgM | Mm.342177 | Antigen binding | 2.57 |
| LOC435905 | Similar to Ig light chain | Mm.333142 | Antigen binding | 2.51 |
| Igh-VJ558 | Similar to IgH chain VJ558 | Mm.300219 | Antigen binding | 2.42 |
| Igh-1a | Ig heavy chain 1a | Mm.342177 | Antigen binding (IgG2a) | 2.42 |
| LOC381784 | Similar to IgV(κ) gene | Mm.305097 | Antigen binding | 2.33 |
| Igh-VS107 | Ig heavy-chain S107 family | Mm.234287 | Antigen binding | 2.24 |
| Igh-V | Ig heavy-chain variable region | Mm.313476 | Antigen binding | 2.16 |
| Igh-VJ558 | Ig heavy chain | Mm.313411 | Antigen binding | 2.01 |
| Gm1067 | Gene model 1067 | Mm.333118 | Antigen binding | 2.01 |
| Immune response | ||||
| Pik3cd | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase catalytic delta | Mm.229108 | Signal transduction B cell | 2.35 |
| Ncf1 | Neutrophil cytosolic factor 1 | Mm.4149 | Inflammation | 2.09 |
| Saa3 | Serum amyloid A3 | Mm.14277 | Acute immune response | 2.03 |
| Klrd1 | Killer cell lectin-like receptor D, member 1 | Mm.8186 | Defense response | −2.00 |
| Ifit1 | IFN-induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeats 1 | Mm.6718 | Inflammation | −2.28 |
| Klra3 | Killer cell lectin-like receptor A, member 3 | Mm.333433 | Defense response | −2.34 |
| Klra13 | Killer cell lectin-like receptor A, member 13 | Mm.333434 | Defense response | −2.34 |
| Ifi202a | IFN-induced protein | Mm.218770 | Inflammation | −2.38 |
| Klra8 | Killer cell lectin-like receptor A, member 8 | Mm.321961 | Defense response | −2.61 |
| DNA binding | ||||
| Nr3c1 | Nuclear receptor 3, group C, member 1 | Mm.129481 | Regulation of transcription | 2.51 |
| Cbx1 | Chromobox homolog 1 | Mm.29055 | Chromatin binding | 2.30 |
| Swap70 | SWAP complex protein | Mm.334144 | ATP/DNA binding | 2.26 |
| Lipid metabolism | ||||
| Psap | Prosaposin gene | Mm.277498 | Lipid metabolism | 3.34 |
| Pla2g12 | Phospholipase A2, group XII | Mm.151951 | Lipid metabolism | 2.48 |
| Pltp | Matrix metalloproteinase 13 | Mm.6105 | Lipid transport | −2.02 |
| Fabp7 | Fatty acid binding protein 7 | Mm.3644 | Lipid transport | −2.37 |
| Enzyme activity | ||||
| Spi12 | Serine protease inhibitor 12 | Mm.36526 | Inhibitor of leukoproteinase | 3.34 |
| Arg2 | Arginase type II | Mm.3506 | Arginase | 2.58 |
| Slpi | Secretory leukoprotease inhibitor | Mm.371583 | Inhibitor of leukoproteinase | 2.54 |
| Ptpn12 | Protein tyrosine phosphatase, nonreceptor type 12 | Mm.319117 | Phosphatase | 2.27 |
| St6gal1 | β-Galactoside α2,6-sialyltransferase 1 | Mm.149029 | Transferase | 2.26 |
| Mapkapk2 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2 | Mm.221235 | Protein kinase | 2.09 |
| Dapk2 | Death-associated kinase 2 | Mm.335252 | Protein kinase | 2.08 |
| Usp22 | Ubiquitin-specific protease 22 | Mm.30602 | Peptidase | 2.02 |
| Mmp13 | RIKEN cDNA 4833432B22 | Mm.5022 | Proteolysis and peptidolysis | −2.01 |
| Mmp3 | Matrix metalloproteinase 3 | Mm.4993 | Proteolysis and peptidolysis | −2.06 |
| Plau | Phospholipid transfer protein | Mm.4183 | Proteolysis and peptidolysis | −2.17 |
| Other | ||||
| F13b | Coagulation factor XIIIβ | Mm.30105 | Coagulation | 3.46 |
| Pdlim3 | PDZ and LIM domain 3 | Mm.282900 | Cytoskeleton | 2.31 |
| Xin | Cardiac morphogenesis | Mm.10117 | Cell adhesion | 2.22 |
| Fbxw1b | F box and WD40 domain | Mm.28017 | Ubiquitin cycle | 2.17 |
| Sept6 | Septin6 | Mm.260036 | Cell cycle | −2.16 |
Transcriptional regulation of Th1 and Th2 cells by Slc11a1.
To evaluate the possibility that Slc11a1 has an impact on bacterial persistence in the spleen through local Th cell polarization, we selected cytokines known to be specific to the Th1 (IL-12 and IFN-γ) or Th2 (IL-4) response for quantitative PCR validation. In addition, we selected costimulatory molecules (CD28, CD80, and CD86) that were shown to have a key role in regulating T-cell activation and T-dependent B-cell responses, as well as critical transcription factors that have a role in gene expression of Th1 (T-box transcription factor T-bet or Tbx21) and Th2 (the zinc finger transcription factor Gata3) cells.
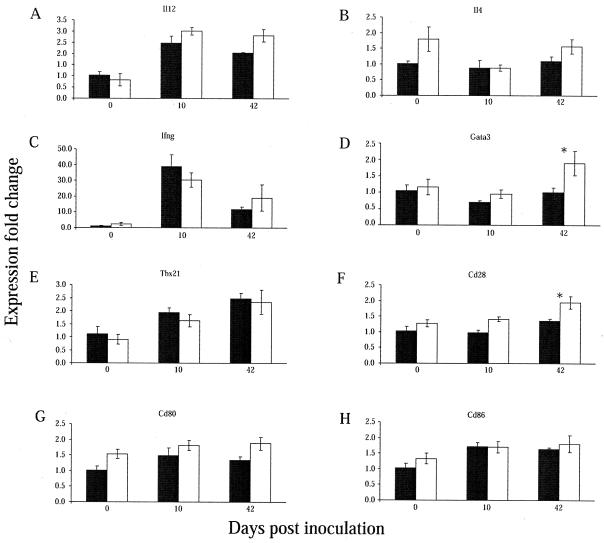
The Th1 cytokines (Ifng and Il12) and transcription factor (Tbx21) were up-regulated during infection in both 129S6 and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice (Fig. 3A, C, and E). At day 10, higher expression of Ifng was observed in 129S6 mice although it did not reach the significance threshold (Fig. 3C). The expression of the Th2 cytokine gene Il4 was constant throughout infection in both 129S6 and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice (Fig. 3B). The expression of Gata3, a transcription factor known to stimulate the expression of Il4, was markedly increased in _Slc11a1_-deficient mice at day 42 postinfection (Fig. 3D). Different studies have proposed that costimulatory molecules may have a role in determining the dominance of Th cell responses. We detected a progressive up-regulation of Cd28 in 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice; the expression levels of Cd28 were significantly higher in _Slc11a1_-deficient mice at day 42 postinfection (Fig. 3F). Expression levels of Cd80 and Cd86 were not significantly regulated during infection, although Cd80 transcripts were more abundant in 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice (Fig. 3G and H). These results complement the observations made by transcription analyses and suggest that bacterial clearance in 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice is associated with a local mixed Th1 and Th2 response, with a predominant Th2 bias. Determining Th profiles based on the expression of cytokines at specific time points after infection may not be optimal because of their temporal expression. To support and complement these studies, we measured cytokines in the serum at early time points and evaluated Ig class switch recombination following S. enterica serovar Enteritidis infection in 129S6 and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice.
FIG. 3.
Gene expression profiling by quantitative reverse transcription-PCR. (A to H) Real-time PCR analyses of selected genes induced during S. enterica serovar Enteritidis infection. The y axis shows the fold changes in _Salmonella_-responsive gene expression in infected 129S6 (black columns) and 129S6-Slc11a1tm1Mcg (white columns) mice compared to control mice and each other over time. The results were normalized to the endogenous levels of TATA box-binding protein (Tbp). The error bars were calculated on the relative fold changes in expression. The experiments were done in duplicate with RNAs from four to eight mice. An asterisk indicates a significant difference in the fold change in expression between the two strains of mice (P < 0.05).
Serum cytokine levels in S. enterica serovar Enteritidis-infected wild-type and Slc11a1 knockout mice.
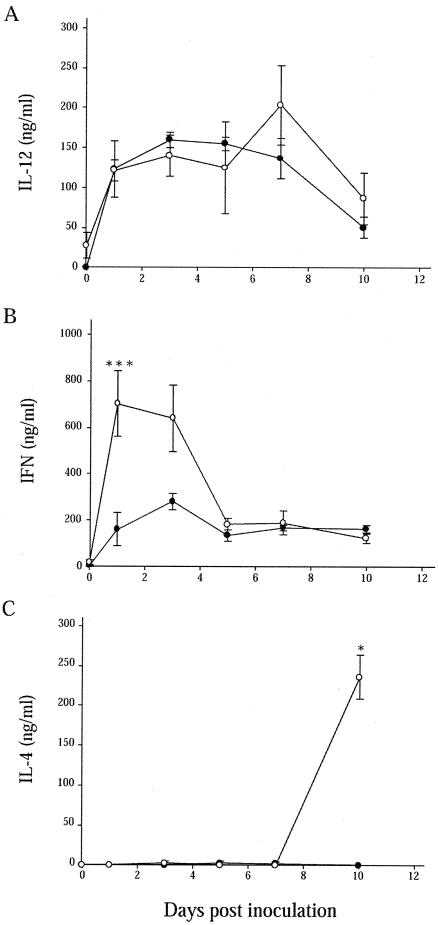
S. enterica serovar Enteritidis infection induced modest IL-12 p70 production in vivo in both wild-type and Slc11a1 knockout mice at all time points. No significant differences were noted between the two groups, reflecting the expression data (Fig. 4A). We also observed significant increases in serum IFN-γ levels in wild-type and Slc11a1 knockout mice compared to those in the uninfected controls (Fig. 4B). IFN-γ levels were, however, significantly higher in _Slc11a1_-deficient mice of both sexes on day 1 (P = 0.0146) postinfection compared to the levels observed in 129S6 mice. At day 10, levels of IFN-γ in the serum were slightly higher in wild-type compared to 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice, which was consistent with the expression studies. At day 42, IFN-γ levels returned to control values in both groups. IL-4 was detected only in the serum of Slc11a1 knockout mice at day 10 postinfection (P = 0.0210), which may reflect the constitutively higher expression levels of Il4 in these mice (Fig. 4C).
FIG. 4.
Cytokine responses in 129S6 and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice infected with S. enterica serovar Enteritidis. IL-12 (A), IFN-γ (B), and IL-4 (C) levels in serum have been quantitated by ELISA following an intravenous challenge with 1,000 CFU of S. enterica serovar Enteritidis in 129S6 (black circles) and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg (white circles) mice. The data are the mean concentrations of cytokine (nanograms per milliliter) ± the standard error of the mean from groups of six mice at 1, 3, 5, 7, and 10 days postinfection. The serum of each mouse was tested in triplicate. Asterisks indicate significant differences between the cytokine levels of the two strains of mice (*, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001).
Slc11a1 influences IgG class switching during infection with S. enterica serovar Enteritidis.
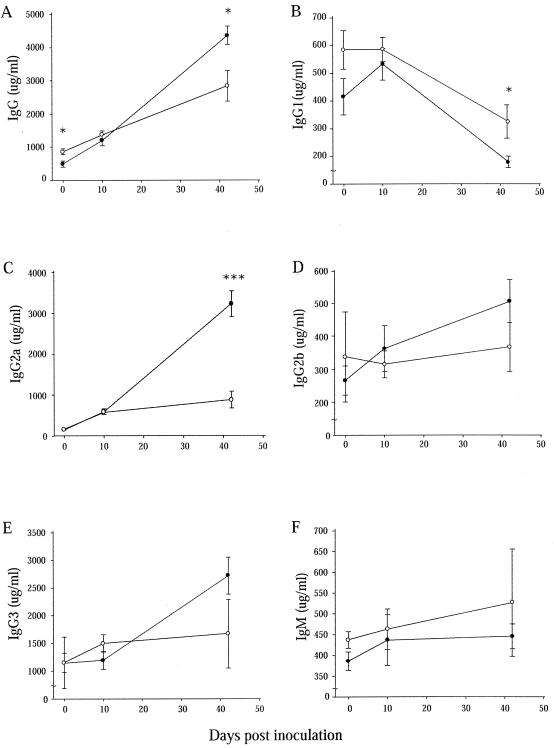
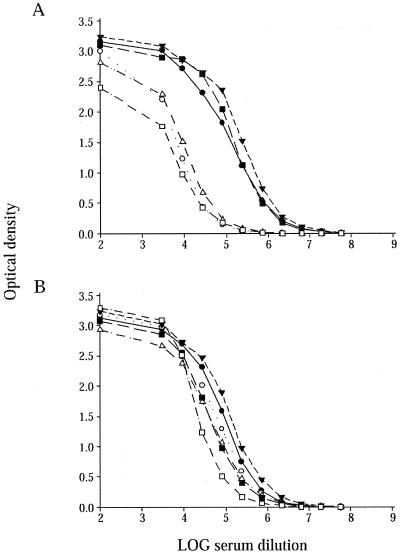
Th1 cells are known to enhance IgG2a synthesis by B cells through IFN-γ, whereas Th2 cells induce IgE and IgG1 production and secretion by IL-4. Total serum levels of IgG, IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b, IgG3, and IgM were quantitated in naive and infected 129S6 and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice. As shown in Fig. 5A, the concentration of total IgG increased in both strains of mice following infection. 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice presented higher serum IgG levels at day 0 compared to 129S6 mice and lower levels at day 42 postinoculation (P = 0.0313), consistent with the expression analyses. The high IgG levels present in 129S6 mice at day 42 were explained by high IgG2a levels. More importantly, the 129S6 animals had significantly higher levels of IgG2a (P < 10−4) compared to 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice. IgG1 levels decreased throughout the infection in both strains; however, the IgG1 concentration remained significantly higher at day 42 postinfection in 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice in comparison to that in wild-type animals (P = 0.0137) (Fig. 5B). An increase in IgG2b and IgG3 production was detected only in 129S6 mice during the course of infection (Fig. 5D and E). IgM levels did not increase significantly following Salmonella infection and were not different between the two groups of mice (Fig. 5F). S. enterica serovar Enteritidis-specific IgG1 and IgG2a responses were measured at day 42 postinfection (Fig. 6). Levels of _Salmonella_-specific IgG1 were similar in wild-type and Slc11a1 knockout mice; IgG1 titers were 3.9 ± 0.1 and 3.5 ± 0.2 in 129S6 and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice, respectively. However, evident differences in the IgG2a isotype between wild-type and _Slc11a1_-deficient mice were observed at day 42 (Fig. 6). Infected wild-type 129S6 mice had significantly higher levels of IgG2a than their Slc11a1 knockout mouse counterparts. Differences in IgG2a titers were more pronounced in female mice (Fig. 6A) than in male mice (Fig. 6B). Slc11a1 knockout mice have a profound deficiency in the development of _Salmonella_-specific IgG2a and do not appear to develop a compensatory IgG1 response. All together, these results suggest that persistence of bacteria in the spleens of 129S6 mice correlates with a predominant Th1 differentiation in response to infection and that clearance of the bacteria in _Slc11a1_-deficient mice is associated with a Th2 response.
FIG. 5.
Kinetics of serum antibodies following S. enterica serovar Enteritidis infection. Ig isotypes were quantitated by ELISA following an intravenous challenge with 1,000 CFU of S. enterica serovar Enteritidis in 129S6 (black circles) and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg (white circles) mice. Total IgG (A), IgG1 (B), IgG2a (C), IgG2b (D), IgG3 (E), and IgM (F) levels were measured. The data obtained from groups of four control and six infected (days 10 and 42) mice are represented as the mean concentration of antibodies (micrograms per milliliter) ± the standard error of the mean. Each serum was tested twice in triplicate. Asterisks represent significant differences between the antibody titers of the two strains of mice (*, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001).
FIG. 6.
S. enterica serovar Enteritidis-specific IgG2a antibody levels of individual female (A) and male (B) mice 42 days after infection. Black and white symbols represent the log of the antibody concentrations in the sera of infected 129S6 and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice, respectively. The experiments were done in duplicate, and each line represents the average log antibody concentration value obtained for one mouse.
DISCUSSION
In the present study, we investigated the role of Slc11a1 in the chronic persistence of S. enterica serovar Enteritidis in mice. The candidacy of Slc11a1 was based on the previous identification of a locus named Ses1 that was shown to control spleen bacterial clearance in C57BL/6J mice by linkage and genome-wide two-locus interaction analyses (13, 14). Slc11a1 is located at the maximum peak logarithm of the odds score of Ses1 and is known to be a critical component of the innate immune response of the host to infection with highly virulent S. enterica serovar Typhimurium. In the chronically S. enterica serovar Enteritidis-infected mouse model, Slc11a1 does not appear to be as critical in the initial phase of infection in that mice carrying a null allele at Slc11a1 survive as well as mice carrying the wild-type allele; however, in this model, the wild-type allele at Slc11a1 has been associated with persistent infection (13, 14). The kinetics of a sublethal challenge with S. enterica serovar Enteritidis in 129S6 and 129S6-Slc11a1 deficient mice demonstrated that Slc11a1 had an impact on bacterial clearance starting at day 7 postinfection. By day 42, 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice presented an 18-fold decrease in the spleen bacterial load compared to 129S6 mice. Congenic mice carrying the Ses1 interval from C57BL/6J (Asp169) mice on a 129S6 (Gly169) background presented kinetics of infection that were similar to those observed in 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg animals, lending further support for the candidacy of Slc11a1 as the molecular determinant of Ses1.
There was a clear influence of gender on the phenotype in both mouse strains, consistent with previous observations that females had a significantly better rate of S. enterica serovar Enteritidis clearance (13, 14). Sexual dimorphism in the extent of the host response to infection has been reported with other type of infections (2, 32, 64). Estrogen is known to regulate the differentiation, survival, and function of diverse immune cells (30, 37, 50). In addition, female mice produce significantly more specific antibody in response to various infections (27). The difference in gender may also be explained by the immunoregulatory effect of testosterone, which is know to act directly on CD4+ T lymphocytes to increased IL-10 production (39). The difference between genders in our study was observed in wild-type and Slc11a1 knockout mice and is clearly not dependent on Slc11a1.
To get a better understanding of the impact of Slc11a1 on the Salmonella carrier state, we examined different aspects of the immune response of 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice during infection with S. enterica serovar Enteritidis. A significant feature of Salmonella pathogenesis is the requirement of both innate and adaptive immune systems for the clearance of infections (43, 49, 58). Global gene expression profiling of the whole spleen with microarrays in conjunction with quantitative PCR analyses revealed different molecular signatures of specific cell types in 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg and 129S6 mice during a chronic S. enterica serovar Enteritidis infection. Not surprisingly, inflammatory genes constitute the major class of mRNAs expressed in response to S. enterica serovar Enteritidis infection. Several of these genes were in common with the core set of human genes, defining a shared host transcriptional response to various pathogens (8, 20, 36, 52). A high representation of microbially activated macrophage genes known to have a role during acute Salmonella infection, including those for macrophage receptors (Cd14, Marco, and Msr), proinflammatory cytokines (Ifng, Il1a, and Tnfa), and several chemokines (Ccl2, Ccl7, Ccl8, and Cxcl5), were up-regulated in 129S6 mice at day 10 postinfection. Increased T-cell-, monocyte-, and granulocyte-tropic chemokines may have had an impact on the higher number of cells recruited to the spleens of 129S6 mice during chronic infection with S. enterica serovar Enteritidis. In 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice, genes associated with activated T- and B-cell populations, including cell surface lymphocyte antigen (Cd8b and Klra7), costimulatory molecule (Cd28), and Ig genes, were more abundantly expressed during infection. The preferential induction of cell-specific clusters of genes in 129S6 and 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice was consistent with the activation of different cell populations during the immune response.
Transcriptional profiling also suggests that Th polarization may be involved in the host response to infection with S. enterica serovar Enteritidis in _Slc11a1_-deficient animals. The cytokine microenvironment is a critical determinant for Th cell lineage development. The proinflammatory cytokines IL-12 and IFN-γ play a fundamental role in Th1 phenotype differentiation and provide a link between innate and adaptive immunity, whereas IL-4 drives Th2 cells (51). In addition, the combined action of several cytokines, including IFN-γ, IL-12, and TNF, is essential to suppress the growth of the bacteria in target organs during infection and coincides with the formation of macrophage-rich granulomas and nitric oxide and NADPH oxidase macrophage-mediated killing of the bacteria (48, 66). In humans, mutations identified in the genes IFNGR1, IFNGR2, IL12B, and IL12RB1 clearly affect susceptibility to persistent infections with salmonellae (15). In our model, we observed an early (day 1) IFN-γ response in serum of Slc11a1 knockout mice infected with S. enterica serovar Enteritidis which may be important in establishing an effective innate immune response that can control early bacterial replication and limit chronic infection. The early IFN-γ production observed in 129S6-Slc11a1 tm1Mcg mice may contribute to the more rapid decrease in Salmonella CFU observed in the spleens of these mice. Comparable up-regulation of Ifng and Il12 was detected at day 10 postinfection in both strains of mice, correlating with the control of the bacterial load in the spleen. At the same time period, up-regulation of the transcription factor gene Gata3 and production of IL-4 in the serum were observed only in _Slc11a1_-deficient mice. Gata3 is a zinc finger protein activated by Stat6 and is known to play a role in the transcriptional regulation of Th2 cytokines, including IL-4 (73).
Clearance of salmonellae from tissues requires efficient CD4+ T-cell activation by TCR and costimulatory signals (44). _Slc11a1_-deficient mice showed a higher basal expression of Cd80 and Cd86 and a progressive up-regulation of Cd28 during infection, coinciding with the more efficient bacterial clearance seen in these animals. CD28 costimulation has been reported to increase the expression of Gata3 (57) and to play an important role in resistance to S. enterica serovar Typhimurium infection, T-cell differentiation, and Ig class switching (47, 61). Mice deficient in both the Cd80 and Cd86 genes also have an impaired ability to undergo Ig class switching (9). The CD80/CD86/CD28 costimulatory pathway not only promotes initial T-cell activation but also contributes to the down-regulation of the immune response. Furthermore, it stimulates Th2 cell differentiation by transducing a positive signal to B cells that increases IgG1 and IgE production (11, 12, 41, 55, 56). Mice that are persistently infected with S. enterica serovar Typhimurium present high anti-Salmonella IgG titers (47). Our study has shown that Slc11a1 has a profound impact in the induction of IgG2a class switching.
Th polarization of the immune response to salmonellae was shown to be influenced by the quantity the antigen and the context in which it is presented. Low-dose flagellin (a major antigen for the CD4+ T-cell response to salmonellae) or defined peptide antigens promote a Th2 response, whereas high doses induce Th1 cells in vivo (17, 54). In addition, Th1 or Th2 phenotypes can be induced in mice depending on how flagellin is presented (19, 21, 45). Soluble flagellin and polymerized flagellin induce a strong Th2 response, while flagellin presented on live salmonellae induces a Th1 response, in C57BL/6J mice (19, 21, 45). A role for Slc11a1 in the adaptive immune response to salmonellae was proposed previously but remains controversial. Slc11a1 has been shown to increase the surface expression of major histocompatibility complex class II molecules and production of inflammatory cytokines by macrophages stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (7). Other studies have reported that cytokine production and antibody response following a Salmonella infection are not influenced by Slc11a1 (22, 53, 62). A vaccine S. enterica serovar Typhimurium strain was shown previously to induce different Th subsets in wild-type and Slc11a1 mutant mice on a C57BL/10J background; however, there was no impact of the Slc11a1 genotype on the clearance of S. enterica serovar Typhimurium (63). The complex interactions between the host genetic background (C57BL/10J versus 129S6) and the pathogen (avirulent S. enterica serovar Typhimurium versus S. enterica serovar Enteritidis) may explain the different impacts of Slc11a1 in different models of Salmonella infection.
Our experiments demonstrate that the Slc11a1 influence on the outcome of an S. enterica serovar Enteritidis infection is associated with Th polarization. We have shown that the presence of Slc11a1 promotes the development of a robust proinflammatory response in 129S6 mice, which has the consequence of delaying the activation of the adaptive immunity essential for clearance of the bacteria. The exact molecular mechanisms involved are not known; however, we can postulate that Slc11a1 may have an impact on the quantity and/or the processing of the antigen presented to T cells because of its known function in controlling bacterial proliferation and phagosome maturation (18, 34). On the other hand, Slc11a1 may act on bacterial mechanisms of persistence. A wild-type genotype at Slc11a1 has been shown to promote the expression of specific Salmonella genes both in vivo and in vitro (71, 72). Two of these genes, sitA and mntH, encode high-affinity metal ion uptake systems in S. enterica serovar Typhimurium (10). These genes are essential for the survival and dissemination of salmonellae and therefore may play a role in promoting the persistence of Salmonella infection in mice with a wild-type genotype at Slc11a1.
In humans, SLC11A1 polymorphisms have been associated with the progression of tuberculosis (1, 3, 28) and with the clinical manifestations of leprosy (46), suggesting that variation within SLC11A1 may influence the type of cellular immune response. In our chronic model of infection, we can conclude that 129S6 mice are not inherently susceptible to S. enterica serovar Enteritidis infection but that the presence of Slc11a1 contributes to the establishment of a Salmonella carrier state in these mice. Although the exact mechanisms are not completely understood, we have provided good evidence that Slc11a1 plays a role during chronic S. enterica serovar Enteritidis infection by influencing the adaptive immune response of the host.
Acknowledgments
We thank Rosalie Wilkinson and Line Laroche for technical expertise. We also thank Laurent Salez for help with the microarray analyses.
This work was supported by grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI; Infectious Diseases and Parasitology Program). J.C. is the recipient of a CIHR fellowship. D.M. is a scholar of CIHR and an International Research Scholar of the HHMI. P.G. is a Distinguished Scientist of the CIHR.
REFERENCES
- 1.Abel, L., F. O. Sanchez, J. Oberti, N. V. Thuc, L. V. Hoa, V. D. Lap, E. Skamene, P. H. Lagrange, and E. Schurr. 1998. Susceptibility to leprosy is linked to the human NRAMP1 gene. J. Infect. Dis. 177**:**133-145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Aebischer, T., S. Laforsch, R. Hurwitz, F. Brombacher, and T. F. Meyer. 2001. Immunity against Helicobacter pylori: significance of interleukin-4 receptor alpha chain status and gender of infected mice. Infect. Immun. 69**:**556-558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Alcais, A., F. O. Sanchez, N. V. Thuc, V. D. Lap, J. Oberti, P. H. Lagrange, E. Schurr, and L. Abel. 2000. Granulomatous reaction to intradermal injection of lepromin (Mitsuda reaction) is linked to the human NRAMP1 gene in Vietnamese leprosy sibships. J. Infect. Dis. 181**:**302-308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Beal, R. K., P. Wigley, C. Powers, S. D. Hulme, P. A. Barrow, and A. L. Smith. 2004. Age at primary infection with Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium in the chicken influences persistence of infection and subsequent immunity to re-challenge. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 100**:**151-164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Beaumont, C., J. Protais, F. Pitel, G. Leveque, D. Malo, F. Lantier, F. Plisson-Petit, P. Colin, M. Protais, P. Le Roy, J. M. Elsen, D. Milan, I. Lantier, A. Neau, G. Salvat, and A. Vignal. 2003. Effect of two candidate genes on the Salmonella carrier state in fowl. Poult. Sci. 82**:**721-726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bellamy, R. 2003. Susceptibility to mycobacterial infections: the importance of host genetics. Genes Immun. 4**:**4-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Blackwell, J. M. 1996. Structure and function of the natural-resistance-associated macrophage protein (Nramp1), a candidate protein for infectious and autoimmune disease susceptibility. Mol. Med. Today 2**:**205-211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Boldrick, J. C., A. A. Alizadeh, M. Diehn, S. Dudoit, C. L. Liu, C. E. Belcher, D. Botstein, L. M. Staudt, P. O. Brown, and D. A. Relman. 2002. Stereotyped and specific gene expression programs in human innate immune responses to bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99**:**972-977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Borriello, F., M. P. Sethna, S. D. Boyd, A. N. Schweitzer, E. A. Tivol, D. Jacoby, T. B. Strom, E. M. Simpson, G. J. Freeman, and A. H. Sharpe. 1997. B7-1 and B7-2 have overlapping, critical roles in immunoglobulin class switching and germinal center formation. Immunity 6**:**303-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Boyer, E., I. Bergevin, D. Malo, P. Gros, and M. F. Cellier. 2002. Acquisition of Mn(II) in addition to Fe(II) is required for full virulence of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Infect. Immun. 70**:**6032-6042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Broeren, C. P., G. S. Gray, B. M. Carreno, and C. H. June. 2000. Costimulation light: activation of CD4+ T cells with CD80 or CD86 rather than anti-CD28 leads to a Th2 cytokine profile. J. Immunol. 165**:**6908-6914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Burr, J. S., S. L. Kimzey, D. R. Randolph, and J. M. Green. 2001. CD28 and CTLA4 coordinately regulate airway inflammatory cell recruitment and T-helper cell differentiation after inhaled allergen. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 24**:**563-568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Caron, J., J. C. Loredo-Osti, L. Laroche, E. Skamene, K. Morgan, and D. Malo. 2002. Identification of genetic loci controlling bacterial clearance in experimental Salmonella enteritidis infection: an unexpected role of Nramp1 (Slc11a1) in the persistence of infection in mice. Genes Immun. 3**:**196-204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Caron, J., J. C. Loredo-Osti, K. Morgan, and D. Malo. 2005. Mapping of interactions and mouse congenic strains identified novel epistatic QTLs controlling the persistence of Salmonella Enteritidis in mice. Genes Immun. 6**:**500-508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Casanova, J. L., and L. Abel. 2004. The human model: a genetic dissection of immunity to infection in natural conditions. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 4**:**55-66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. December. 2003. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report. Division of Bacterial and Mycotic Diseases. Disease Information. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, Ga.
- 17.Constant, S., C. Pfeiffer, A. Woodard, T. Pasqualini, and K. Bottomly. 1995. Extent of T cell receptor ligation can determine the functional differentiation of naive CD4+ T cells. J. Exp. Med. 182**:**1591-1596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Cuellar-Mata, P., N. Jabado, J. Liu, W. Furuya, B. B. Finlay, P. Gros, and S. Grinstein. 2002. Nramp1 modifies the fusion of Salmonella typhimurium-containing vacuoles with cellular endomembranes in macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 277**:**2258-2265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Cunningham, A. F., M. Khan, J. Ball, K. M. Toellner, K. Serre, E. Mohr, and I. C. MacLennan. 2004. Responses to the soluble flagellar protein FliC are Th2, while those to FliC on Salmonella are Th1. Eur. J. Immunol. 34**:**2986-2995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Detweiler, C. S., D. B. Cunanan, and S. Falkow. 2001. Host microarray analysis reveals a role for the Salmonella response regulator phoP in human macrophage cell death. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98**:**5850-5855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Didierlaurent, A., I. Ferrero, L. A. Otten, B. Dubois, M. Reinhardt, H. Carlsen, R. Blomhoff, S. Akira, J. P. Kraehenbuhl, and J. C. Sirard. 2004. Flagellin promotes myeloid differentiation factor 88-dependent development of Th2-type response. J. Immunol. 172**:**6922-6930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Eckmann, L., J. Fierer, and M. F. Kagnoff. 1996. Genetically resistant (Ityr) and susceptible (Itys) congenic mouse strains show similar cytokine responses following infection with Salmonella dublin. J. Immunol. 156**:**2894-2900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Fitness, J., S. Floyd, D. K. Warndorff, L. Sichali, S. Malema, A. C. Crampin, P. E. Fine, and A. V. Hill. 2004. Large-scale candidate gene study of tuberculosis susceptibility in the Karonga district of northern Malawi. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 71**:**341-349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Fitness, J., K. Tosh, and A. V. Hill. 2002. Genetics of susceptibility to leprosy. Genes Immun. 3**:**441-453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Forbes, J. R., and P. Gros. 2003. Iron, manganese, and cobalt transport by Nramp1 (Slc11a1) and Nramp2 (Slc11a2) expressed at the plasma membrane. Blood 102**:**1884-1892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Forget, A., E. Skamene, P. Gros, A. C. Miailhe, and R. Turcotte. 1981. Differences in response among inbred mouse strains to infection with small doses of Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Infect. Immun. 32**:**42-47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Fuller, A. C., B. Kang, H. K. Kang, H. Yahikozowa, M. C. Dal Canto, and B. S. Kim. 2005. Gender bias in Theiler's virus-induced demyelinating disease correlates with the level of antiviral immune responses. J. Immunol. 175**:**3955-3963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Greenwood, C. M., T. M. Fujiwara, L. J. Boothroyd, M. A. Miller, D. Frappier, E. A. Fanning, E. Schurr, and K. Morgan. 2000. Linkage of tuberculosis to chromosome 2q35 loci, including NRAMP1, in a large aboriginal Canadian family. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 67**:**405-416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Gruenheid, S., E. Pinner, M. Desjardins, and P. Gros. 1997. Natural resistance to infection with intracellular pathogens: the Nramp1 protein is recruited to the membrane of the phagosome. J. Exp. Med. 185**:**717-730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hall, J. M., J. F. Couse, and K. S. Korach. 2001. The multifaceted mechanisms of estradiol and estrogen receptor signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 276**:**36869-36872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hu, J., N. Bumstead, P. Barrow, G. Sebastiani, L. Olien, K. Morgan, and D. Malo. 1997. Resistance to salmonellosis in the chicken is linked to NRAMP1 and TNC. Genome Res. 7**:**693-704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Huygen, K., and K. Palfliet. 1984. Strain variation in interferon gamma production of BCG-sensitized mice challenged with PPD II. Importance of one major autosomal locus and additional sexual influences. Cell. Immunol. 85**:**75-81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Jabado, N., F. Canonne-Hergaux, S. Gruenheid, V. Picard, and P. Gros. 2002. Iron transporter Nramp2/DMT-1 is associated with the membrane of phagosomes in macrophages and Sertoli cells. Blood 100**:**2617-2622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Jabado, N., P. Cuellar-Mata, S. Grinstein, and P. Gros. 2003. Iron chelators modulate the fusogenic properties of Salmonella-containing phagosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100**:**6127-6132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Jabado, N., A. Jankowski, S. Dougaparsad, V. Picard, S. Grinstein, and P. Gros. 2000. Natural resistance to intracellular infections: natural resistance-associated macrophage protein 1 (Nramp1) functions as a pH-dependent manganese transporter at the phagosomal membrane. J. Exp. Med. 192**:**1237-1248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Jenner, R. G., and R. A. Young. 2005. Insights into host responses against pathogens from transcriptional profiling. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 3**:**281-294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kanda, N., and S. Watanabe. 2004. 17β-Estradiol enhances the production of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in human keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 123**:**329-337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Leveque, G., V. Forgetta, S. Morroll, A. L. Smith, N. Bumstead, P. Barrow, J. C. Loredo-Osti, K. Morgan, and D. Malo. 2003. Allelic variation in TLR4 is linked to susceptibility to Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium infection in chickens. Infect. Immun. 71**:**1116-1124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Liva, S. M., and R. R. Voskuhl. 2001. Testosterone acts directly on CD4+ T lymphocytes to increase IL-10 production. J. Immunol. 167**:**2060-2067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Livak, K. J., and T. D. Schmittgen. 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔC(T) method. Methods 25**:**402-408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lumsden, J. M., J. A. Williams, and R. J. Hodes. 2003. Differential requirements for expression of CD80/86 and CD40 on B cells for T-dependent antibody responses in vivo. J. Immunol. 170**:**781-787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Malo, D., K. Vogan, S. Vidal, J. Hu, M. Cellier, E. Schurr, A. Fuks, N. Bumstead, K. Morgan, and P. Gros. 1994. Haplotype mapping and sequence analysis of the mouse Nramp gene predict susceptibility to infection with intracellular parasites. Genomics 23**:**51-61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Mastroeni, P. 2002. Immunity to systemic Salmonella infections. Curr. Mol. Med. 2**:**393-406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Mastroeni, P., and N. Menager. 2003. Development of acquired immunity to Salmonella. J. Med. Microbiol. 52**:**453-459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.McSorley, S. J., B. T. Cookson, and M. K. Jenkins. 2000. Characterization of CD4+ T cell responses during natural infection with Salmonella typhimurium. J. Immunol. 164**:**986-993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Meisner, S. J., S. Mucklow, G. Warner, S. O. Sow, C. Lienhardt, and A. V. Hill. 2001. Association of NRAMP1 polymorphism with leprosy type but not susceptibility to leprosy per se in West Africans. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 65**:**733-735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Mittrucker, H. W., A. Kohler, T. W. Mak, and S. H. Kaufmann. 1999. Critical role of CD28 in protective immunity against Salmonella typhimurium. J. Immunol. 163**:**6769-6776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Monack, D. M., D. M. Bouley, and S. Falkow. 2004. Salmonella typhimurium persists within macrophages in the mesenteric lymph nodes of chronically infected Nramp1+/+ mice and can be reactivated by IFN-γ neutralization. J. Exp. Med. 199**:**231-241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Monack, D. M., A. Mueller, and S. Falkow. 2004. Persistent bacterial infections: the interface of the pathogen and the host immune system. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2**:**747-765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Mouihate, A., X. Chen, and Q. J. Pittman. 1998. Interleukin-1β fever in rats: gender difference and estrous cycle influence. Am. J. Physiol. 275**:**R1450-R1454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Murphy, K. M., and S. L. Reiner. 2002. The lineage decisions of helper T cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2**:**933-944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Nau, G. J., J. F. Richmond, A. Schlesinger, E. G. Jennings, E. S. Lander, and R. A. Young. 2002. Human macrophage activation programs induced by bacterial pathogens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99**:**1503-1508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Nauciel, C., F. Vilde, and E. Ronco. 1985. Host response to infection with a temperature-sensitive mutant of Salmonella typhimurium in a susceptible and a resistant strain of mice. Infect. Immun. 49**:**523-527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Parish, C. R., and F. Y. Liew. 1972. Immune response to chemically modified flagellin. 3. Enhanced cell-mediated immunity during high and low zone antibody tolerance to flagellin. J. Exp. Med. 135**:**298-311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Podojil, J. R., N. W. Kin, and V. M. Sanders. 2004. CD86 and β2-adrenergic receptor signaling pathways, respectively, increase Oct-2 and OCA-B expression and binding to the 3′-IgH enhancer in B cells. J. Biol. Chem. 279**:**23394-23404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Podojil, J. R., and V. M. Sanders. 2003. Selective regulation of mature IgG1 transcription by CD86 and β2-adrenergic receptor stimulation. J. Immunol. 170**:**5143-5151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Rodriguez-Palmero, M., T. Hara, A. Thumbs, and T. Hunig. 1999. Triggering of T cell proliferation through CD28 induces GATA-3 and promotes T helper type 2 differentiation in vitro and in vivo. Eur. J. Immunol. 29**:**3914-3924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Roy, M. F., and D. Malo. 2002. Genetic regulation of host responses to Salmonella infection in mice. Genes Immun. 3**:**381-393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Searle, S., N. A. Bright, T. I. Roach, P. G. Atkinson, C. H. Barton, R. H. Meloen, and J. M. Blackwell. 1998. Localisation of Nramp1 in macrophages: modulation with activation and infection. J. Cell Sci. 111(Pt. 19)**:**2855-2866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Sebastiani, G., L. Olien, S. Gauthier, E. Skamene, K. Morgan, P. Gros, and D. Malo. 1998. Mapping of genetic modulators of natural resistance to infection with Salmonella typhimurium in wild-derived mice. Genomics 47**:**180-186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Shahinian, A., K. Pfeffer, K. P. Lee, T. M. Kundig, K. Kishihara, A. Wakeham, K. Kawai, P. S. Ohashi, C. B. Thompson, and T. W. Mak. 1993. Differential T cell costimulatory requirements in CD28-deficient mice. Science 261**:**609-612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Sirova, M., O. Hovorka, I. Riha, B. Rihova, M. Baudys, S. W. Kim, and E. Skamene. 1997. The in vivo antibody response against exogenous antigens is not influenced by the mouse Bcg (Nramp1) gene. Immunology 90**:**626-631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Soo, S. S., B. Villarreal-Ramos, C. M. Anjam Khan, C. E. Hormaeche, and J. M. Blackwell. 1998. Genetic control of immune response to recombinant antigens carried by an attenuated Salmonella typhimurium vaccine strain: Nramp1 influences T-helper subset responses and protection against leishmanial challenge. Infect. Immun. 66**:**1910-1917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Su, Z., and M. M. Stevenson. 2000. Central role of endogenous gamma interferon in protective immunity against blood-stage Plasmodium chabaudi AS infection. Infect. Immun. 68**:**4399-4406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Tamayo, P., D. Slonim, J. Mesirov, Q. Zhu, S. Kitareewan, E. Dmitrovsky, E. S. Lander, and T. R. Golub. 1999. Interpreting patterns of gene expression with self-organizing maps: methods and application to hematopoietic differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96**:**2907-2912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Vazquez-Torres, A., J. Jones-Carson, P. Mastroeni, H. Ischiropoulos, and F. C. Fang. 2000. Antimicrobial actions of the NADPH phagocyte oxidase and inducible nitric oxide synthase in experimental salmonellosis. I. Effects on microbial killing by activated peritoneal macrophages in vitro. J. Exp. Med. 192**:**227-236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Vidal, S., M. L. Tremblay, G. Govoni, S. Gauthier, G. Sebastiani, D. Malo, E. Skamene, M. Olivier, S. Jothy, and P. Gros. 1995. The Ity/Lsh/Bcg locus: natural resistance to infection with intracellular parasites is abrogated by disruption of the Nramp1 gene. J. Exp. Med. 182**:**655-666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Vidal, S. M., D. Malo, K. Vogan, E. Skamene, and P. Gros. 1993. Natural resistance to infection with intracellular parasites: isolation of a candidate for Bcg. Cell 73**:**469-485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Westfall, P. H., R. D. Tobias, D. Rom, R. D. Wolfinger, and Y. Hochberg. 1999. Multiple comparisons and multiple tests using the SAS system, p. 231-235. SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, N.C.
- 70.Young, D., T. Hussell, and G. Dougan. 2002. Chronic bacterial infections: living with unwanted guests. Nat. Immunol. 3**:**1026-1032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Zaharik, M. L., and B. B. Finlay. 2004. Mn2+ and bacterial pathogenesis. Front. Biosci. 9**:**1035-1042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Zaharik, M. L., B. A. Vallance, J. L. Puente, P. Gros, and B. B. Finlay. 2002. Host-pathogen interactions: host resistance factor Nramp1 up-regulates the expression of Salmonella pathogenicity island-2 virulence genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99**:**15705-15710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Zheng, W., and R. A. Flavell. 1997. The transcription factor GATA-3 is necessary and sufficient for Th2 cytokine gene expression in CD4 T cells. Cell 89**:**587-596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]