Tumorigenicity of the miR-17-92 cluster distilled - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comment
Tumorigenicity of the miR-17-92 cluster distilled
Gijs van Haaften et al. Genes Dev. 2010.
Abstract
The miR-17-92 gene cluster, with its six different mature microRNAs (miRNAs), has an established oncogenic function. However, the oncogenic contribution of each individual miRNA in the cluster has not been assigned. Two studies published in the December 15, 2009, issue of Genes & Development by Mu and colleagues (pp. 2806-2811) and Olive and colleagues (pp. 2839-2849) dissected the miR-17-92 cluster to its individual miRNA components and identified their relative contributions to oncogenic transformation in mouse model systems.
Figures
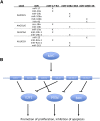
Figure 1.
(A) Clustering of the miRNAs of miR-17-92 and its paralogous clusters based on the regions most important for target selection (the seed sequences, nucleotides 2–7 of the mature miR). (B) Role of the miR-17-92 cluster in oncogenesis. The miR-17-92 cluster is a direct transcriptional target of c-Myc. miR-17/20a targets E2F1, a regulator of the cell cycle and apoptosis. miR-92 targets BIM, a proapoptotic gene that counteracts the anti-apoptotic activity of genes such as Bcl2. miR-19 targets PTEN, a negative regulator of the oncogenic prosurvival PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
Comment on
- Genetic dissection of the miR-17~92 cluster of microRNAs in Myc-induced B-cell lymphomas.
Mu P, Han YC, Betel D, Yao E, Squatrito M, Ogrodowski P, de Stanchina E, D'Andrea A, Sander C, Ventura A. Mu P, et al. Genes Dev. 2009 Dec 15;23(24):2806-11. doi: 10.1101/gad.1872909. Genes Dev. 2009. PMID: 20008931 Free PMC article. - miR-19 is a key oncogenic component of mir-17-92.
Olive V, Bennett MJ, Walker JC, Ma C, Jiang I, Cordon-Cardo C, Li QJ, Lowe SW, Hannon GJ, He L. Olive V, et al. Genes Dev. 2009 Dec 15;23(24):2839-49. doi: 10.1101/gad.1861409. Genes Dev. 2009. PMID: 20008935 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
- MicroRNAs of the mir-17~92 cluster regulate multiple aspects of pancreatic tumor development and progression.
Quattrochi B, Gulvady A, Driscoll DR, Sano M, Klimstra DS, Turner CE, Lewis BC. Quattrochi B, et al. Oncotarget. 2017 May 30;8(22):35902-35918. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16277. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28415794 Free PMC article. - A novel oncogenic role for the miRNA-506-514 cluster in initiating melanocyte transformation and promoting melanoma growth.
Streicher KL, Zhu W, Lehmann KP, Georgantas RW, Morehouse CA, Brohawn P, Carrasco RA, Xiao Z, Tice DA, Higgs BW, Richman L, Jallal B, Ranade K, Yao Y. Streicher KL, et al. Oncogene. 2012 Mar 22;31(12):1558-70. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.345. Epub 2011 Aug 22. Oncogene. 2012. PMID: 21860416 - miR-17∼92 in lymphocyte development and lymphomagenesis.
Labi V, Schoeler K, Melamed D. Labi V, et al. Cancer Lett. 2019 Apr 1;446:73-80. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.12.020. Epub 2019 Jan 17. Cancer Lett. 2019. PMID: 30660648 Review. - Functional links between clustered microRNAs: suppression of cell-cycle inhibitors by microRNA clusters in gastric cancer.
Kim YK, Yu J, Han TS, Park SY, Namkoong B, Kim DH, Hur K, Yoo MW, Lee HJ, Yang HK, Kim VN. Kim YK, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Apr;37(5):1672-81. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp002. Epub 2009 Jan 19. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19153141 Free PMC article. - Roles of miR-17-92 Cluster in Cardiovascular Development and Common Diseases.
Gu H, Liu Z, Zhou L. Gu H, et al. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:9102909. doi: 10.1155/2017/9102909. Epub 2017 Jan 10. Biomed Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28164128 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) regulates miR17-92 cluster through β-catenin pathway in colorectal cancer.
Li Y, Lauriola M, Kim D, Francesconi M, D'Uva G, Shibata D, Malafa MP, Yeatman TJ, Coppola D, Solmi R, Cheng JQ. Li Y, et al. Oncogene. 2016 Sep 1;35(35):4558-4568. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.522. Epub 2016 Jan 25. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26804172 Free PMC article. - Activation of gga-miR-155 by reticuloendotheliosis virus T strain and its contribution to transformation.
Yao Y, Vasoya D, Kgosana L, Smith LP, Gao Y, Wang X, Watson M, Nair V. Yao Y, et al. J Gen Virol. 2017 Apr;98(4):810-820. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.000718. Epub 2017 Apr 28. J Gen Virol. 2017. PMID: 28113043 Free PMC article. - Alterations of microRNAs throughout the malignant evolution of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: the role of miR-497 in epithelial to mesenchymal transition of keratinocytes.
Mizrahi A, Barzilai A, Gur-Wahnon D, Ben-Dov IZ, Glassberg S, Meningher T, Elharar E, Masalha M, Jacob-Hirsch J, Tabibian-Keissar H, Barshack I, Roszik J, Leibowitz-Amit R, Sidi Y, Avni D. Mizrahi A, et al. Oncogene. 2018 Jan 11;37(2):218-230. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.315. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 28925390 - Upregulation of miR-24 is associated with a decreased DNA damage response upon etoposide treatment in highly differentiated CD8(+) T cells sensitizing them to apoptotic cell death.
Brunner S, Herndler-Brandstetter D, Arnold CR, Wiegers GJ, Villunger A, Hackl M, Grillari J, Moreno-Villanueva M, Bürkle A, Grubeck-Loebenstein B. Brunner S, et al. Aging Cell. 2012 Aug;11(4):579-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2012.00819.x. Epub 2012 Apr 18. Aging Cell. 2012. PMID: 22435726 Free PMC article. - Apoptotic cell signaling in cancer progression and therapy.
Plati J, Bucur O, Khosravi-Far R. Plati J, et al. Integr Biol (Camb). 2011 Apr;3(4):279-96. doi: 10.1039/c0ib00144a. Epub 2011 Feb 22. Integr Biol (Camb). 2011. PMID: 21340093 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Adams JM, Harris AW, Pinkert CA, Corcoran LM, Alexander WS, Cory S, Palmiter RD, Brinster RL. The c-myc oncogene driven by immunoglobulin enhancers induces lymphoid malignancy in transgenic mice. Nature. 1985;318:533–538. - PubMed
- Bonauer A, Carmona G, Iwasaki M, Mione M, Koyanagi M, Fischer A, Burchfield J, Fox H, Doebele C, Ohtani K, et al. MicroRNA-92a controls angiogenesis and functional recovery of ischemic tissues in mice. Science. 2009;324:1710–1713. - PubMed
- Cui JW, Li YJ, Sarkar A, Brown J, Tan YH, Premyslova M, Michaud C, Iscove N, Wang GJ, Ben-David Y. Retroviral insertional activation of the Fli-3 locus in erythroleukemias encoding a cluster of microRNAs that convert Epo-induced differentiation to proliferation. Blood. 2007;110:2631–2640. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous