Proteasome inhibitors induce p53-independent apoptosis in human cancer cells - PubMed (original) (raw)
Proteasome inhibitors induce p53-independent apoptosis in human cancer cells
Bulbul Pandit et al. Am J Pathol. 2011 Jan.
Abstract
Proteasome inhibitors are used against human cancer, but their mechanisms of action are not entirely understood. For example, the role of the tumor suppressor p53 is controversial. We reevaluated the role of p53 in proteasome inhibitor-induced apoptosis by using isogenic human cancer cell lines with different p53 status. We found that well-known proteasome inhibitors such as MG132 and bortezomib, as well as the recently discovered proteasome inhibitor thiostrepton, induced p53-independent apoptosis in human cancer cell lines that correlated with p53-independent induction of proapoptotic Noxa but not Puma protein. In addition, these drugs inhibited growth of several cancer cell lines independently of p53 status. Notably, thiostrepton induced more potent apoptosis in HepG2 cells with p53 knockdown than in parental cells with wild-type p53. Our data confirm that proteasome inhibitors generally induce p53-independent apoptosis in human cancer cells.
Copyright © 2011 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Figure 1
Proteasome inhibitors inhibit the viability of cancer cells in a p53-independent manner. A: Mid-log colon carcinoma HCT 116 (wild type [wt] p53) and p53−/− cells were treated with DMSO (control) or various concentrations of thiostrepton, MG132, and bortezomib for 72 hours and IC50 values were determined by using MTT cell viability assay as described under Materials and Methods. The values shown are mean ± SD for three separate experiments. The IC50 values were 2.1 ± 0.08 and 1.4 ± 0.06 μM/L for thiostrepton, 0.51 ± 0.09 and 0.35 ± 0.1 for MG132, and 18 ± 0.04 and 15 ± 0.07 nM/L for bortezomib against HCT-116 (wt p53 and p53−/−) cells, respectively. B: Mid-log breast carcinoma MCF-7 cells (wt p53 and shp53) were treated with dimethyl sulfoxide or various concentrations of thiostrepton, MG132, and bortezomib for 72 hours; IC50 values were determined by using MTT cell viability assay as described under Materials and Methods. The values shown are mean ± SD for three separate experiments. The IC50 values were 4.5 ± 0.34 and 4.7 ± 0.2 μmol/L for thiostrepton, 0.34 ± 0.08 and 0.28 ± 0.1 for MG132, and 8 ± 0.04 and 11 ± 0.06 nmol/L for bortezomib against MCF-7 wt p53 and shp53 cells, respectively.
Figure 2
p53-independent induction of apoptosis by proteasome inhibitors in colon cancer cells. Colon carcinoma HCT 116 wild type (wt) p53 cells were treated with 3 μmol/L thiostrepton (Thio), 2 μmol/L MG132, and 10 nmol/L bortezomib for 24 hours, then stained with annexin V-PE and 7AAD and analyzed by flow cytometry. Colon carcinoma cells with knockout of p53 (HCT 116 p53−/−) were treated with 3 mmol/L thiostrepton, 2 μmol/L MG132, and 10 nmol/L bortezomib for 24 hours, then stained with annexin V-PE and 7AAD and analyzed by flow cytometry. The values shown are mean ± SD for three separate experiments.
Figure 3
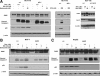
Caspase-3 and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) cleavage is p53-independent after treatment with proteasome inhibitor. A: Colon carcinoma HCT 116 wild type (w.t.) p53 and p53−/− cells were treated with 2.5 μmol/L thiostrepton, 2 μmol/L MG132, 25 nmol/L bortezomib, and 500 μmol/L 5-FU for 24 hours, then lysed and subjected to immunoblot analysis with antibodies against PARP, caspase-3 (cleaved), p53, and β-actin. HCT116 cells and HCT-116 cells overexpressing bcl-2 were treated with 2.5 μmol/L and 25 nmol/L bortezomib for 24 hours, then lysed and immunoblotted for PARP, bcl-2, and β-actin. B: Breast carcinoma MCF-7 w.t. p53 and shp53 cells were treated with 10 μmol/L thiostrepton, 2 μmol/L MG132, and 25 nmol/L bortezomib for 48 hours, then lysed and subjected to immunoblot analysis with antibodies against PARP, caspase-3 (cleaved), p53, and β-actin. C: Liver carcinoma HepG2 w.t. p53 and shp53 cells were treated with 2.5 μmol/L thiostrepton, 2 μmol/L MG132, and 25 nmol/L bortezomib for 24 hours, then lysed and subjected to immunoblot analysis with antibodies against PARP, caspase-3 (cleaved), p53, and β-actin.
Figure 4
Effect of PI on p53-regulated pro- and antiapoptotic proteins. A: Colon carcinoma HCT 116 wild-type (wt) p53 and p53−/− cells were treated with 2.5 μmol/L thiostrepton, 2 μmol/L MG132, and 25 nmol/L bortezomib for 24 hours, then lysed and subjected to immunoblot analysis with antibodies against Puma, Noxa, Mcl-1, p21, and β-actin. B: Breast carcinoma MCF-7 w.t. p53 and shp53 cells were treated with 10 μmol/L thiostrepton, 2 μmol/L MG132, and 25 nmol/L bortezomib for 48 hours, then lysed and subjected to immunoblot analysis with antibodies against Puma, Noxa, Mcl-1, p21, and β-actin C: Liver carcinoma HepG2 w.t. p53 and shp53 cells were treated with 2.5 μmol/L thiostrepton, 2 μmol/L MG132, and 25 nmol/L bortezomib for 24 hours, then lysed and subjected to immunoblot analysis with antibodies against Puma, Noxa, Mcl-1, p21, and β-actin.
Similar articles
- A proteomic analysis of p53-independent induction of apoptosis by bortezomib in 4T1 breast cancer cell line.
Yerlikaya A, Okur E, Baykal AT, Acılan C, Boyacı I, Ulukaya E. Yerlikaya A, et al. J Proteomics. 2015 Jan 15;113:315-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2014.09.010. Epub 2014 Oct 8. J Proteomics. 2015. PMID: 25305590 - Proteasome inhibitor MG132 induces thyroid cancer cell apoptosis by modulating the activity of transcription factor FOXO3a.
Qiang W, Sui F, Ma J, Li X, Ren X, Shao Y, Liu J, Guan H, Shi B, Hou P. Qiang W, et al. Endocrine. 2017 Apr;56(1):98-108. doi: 10.1007/s12020-017-1256-y. Epub 2017 Feb 20. Endocrine. 2017. PMID: 28220348 - A coordinated action of Bax, PUMA, and p53 promotes MG132-induced mitochondria activation and apoptosis in colon cancer cells.
Ding WX, Ni HM, Chen X, Yu J, Zhang L, Yin XM. Ding WX, et al. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007 Mar;6(3):1062-9. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0541. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007. PMID: 17363499 - A new target for proteasome inhibitors: FoxM1.
Gartel AL. Gartel AL. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2010 Feb;19(2):235-42. doi: 10.1517/13543780903563364. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20074015 Free PMC article. Review. - Suppression of the Oncogenic Transcription Factor FOXM1 by Proteasome Inhibitors.
Gartel AL. Gartel AL. Scientifica (Cairo). 2014;2014:596528. doi: 10.1155/2014/596528. Epub 2014 Jun 24. Scientifica (Cairo). 2014. PMID: 25093142 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- FOXM1 Inhibition in Ovarian Cancer Tissue Cultures Affects Individual Treatment Susceptibility Ex Vivo.
Brückner L, Reinshagen A, Hoang NA, Höhn AK, Lordick F, Bechmann I, Aktas B, Nel I, Kallendrusch S. Brückner L, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2021 Feb 25;13(5):956. doi: 10.3390/cancers13050956. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33668819 Free PMC article. - The Ubiquitin-Proteasome System Is Indispensable for the Maintenance of Muscle Stem Cells.
Kitajima Y, Suzuki N, Nunomiya A, Osana S, Yoshioka K, Tashiro Y, Takahashi R, Ono Y, Aoki M, Nagatomi R. Kitajima Y, et al. Stem Cell Reports. 2018 Dec 11;11(6):1523-1538. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2018.10.009. Epub 2018 Nov 8. Stem Cell Reports. 2018. PMID: 30416048 Free PMC article. - Differential effects of reticulophagy and mitophagy on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Pang L, Liu K, Liu D, Lv F, Zang Y, Xie F, Yin J, Shi Y, Wang Y, Chen D. Pang L, et al. Cell Death Dis. 2018 Jan 24;9(2):90. doi: 10.1038/s41419-017-0136-y. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 29367738 Free PMC article. - Targeting the ubiquitin-proteasome system for cancer treatment: discovering novel inhibitors from nature and drug repurposing.
Soave CL, Guerin T, Liu J, Dou QP. Soave CL, et al. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017 Dec;36(4):717-736. doi: 10.1007/s10555-017-9705-x. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017. PMID: 29047025 Free PMC article. - BAK and NOXA are critical determinants of mitochondrial apoptosis induced by bortezomib in mesothelioma.
Busacca S, Chacko AD, Klabatsa A, Arthur K, Sheaff M, Barbone D, Mutti L, Gunasekharan VK, Gorski JJ, El-Tanani M, Broaddus VC, Gaudino G, Fennell DA. Busacca S, et al. PLoS One. 2013 Jun 7;8(6):e65489. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065489. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23762382 Free PMC article.
References
- Rubin D.M., Finley D. Proteolysis. The proteasome: a protein-degrading organelle. Curr Biol. 1995;5:854–858. - PubMed
- Lenz H.J. Clinical update: proteasome inhibitors in solid tumors. Cancer Treat Rev. 2003;29(Suppl 1):41–48. - PubMed
- Vousden K.H., Prives C. Blinded by the light: the growing complexity of p53. Cell. 2009;137:413–431. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous