Antioxidant Activities and Caffeic Acid Content in New Zealand Asparagus (Asparagus officinalis) Roots Extracts - PubMed (original) (raw)
Antioxidant Activities and Caffeic Acid Content in New Zealand Asparagus (Asparagus officinalis) Roots Extracts
Abbey Symes et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2018.
Abstract
Asparagus officinalis are perennial plants that require re-planting every 10–20 years. The roots are traditionally mulched in the soil or treated as waste. The A. officinalis roots (AR) contain valuable bioactive compounds that may have some health benefiting properties. The aim of this study was to investigate the total polyphenol and flavonoid contents (TPC and TFC, respectively) and antioxidant (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity (ORAC) and Ferric Reducing/Antioxidant Power (FRAP) assays) activities of New Zealand AR extract. The antioxidant activity decreased with a longer extraction time.
Keywords: antioxidant activity; asparagus roots; bioactive compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
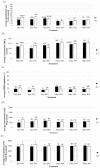
Figure 1
The effect of ethanol concentration, extraction order and extraction time on total phenolic content (a); total flavonoid content (b); 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) scavenging activity (c); Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity (ORAC) activity (d); and Ferric Reducing/Antioxidant Power (FRAP) activity (e) of the extract obtained from asparagus root powder after 2 and 10-h extraction time. Bars that do not share the same letter are significantly different (p < 0.05).
Similar articles
- Identification of Six Phytochemical Compounds from Asparagus officinalis L. Root Cultivars from New Zealand and China Using UAE-SPE-UPLC-MS/MS: Effects of Extracts on H₂O₂-Induced Oxidative Stress.
Zhang H, Birch J, Pei J, Mohamed Ahmed IA, Yang H, Dias G, Abd El-Aty AM, Bekhit AE. Zhang H, et al. Nutrients. 2019 Jan 7;11(1):107. doi: 10.3390/nu11010107. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 30621005 Free PMC article. - Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction of bioactive compounds from New Zealand and Chinese Asparagus officinalis L. roots.
Zhang H, Birch J, Ma ZF, Xie C, Yang H, Bekhit AE, Dias G. Zhang H, et al. J Food Sci Technol. 2019 Feb;56(2):799-810. doi: 10.1007/s13197-018-3540-0. Epub 2019 Jan 1. J Food Sci Technol. 2019. PMID: 30906038 Free PMC article. - A Review of the Pro-Health Activity of Asparagus officinalis L. and Its Components.
Olas B. Olas B. Foods. 2024 Jan 16;13(2):288. doi: 10.3390/foods13020288. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38254589 Free PMC article. Review. - Literature analysis on asparagus roots and review of its functional characterizations.
Guo Y, Liu Z, Wan Y, Zhang Y, Abdu HI, Yang M, Pei J, Yue T, Zhang X, Hacimuftuoglu A, Abd El-Aty AM. Guo Y, et al. Front Nutr. 2023 Apr 17;9:1024190. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1024190. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37139102 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- The influence of cultivation conditions on the formation of psychoactive salvinorin A, salvinorin B, rosmarinic acid and caffeic acid in Coleus scutellarioides.
Jakobina M, Łyczko J, Szumny A, Galek R. Jakobina M, et al. Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 20;14(1):6693. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-57399-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38509159 Free PMC article. - Sustainable valorization of co-products from asparagus cultivation by obtaining bioactive compounds.
Alcaide IV, Hamdi A, Guilleín-Bejarano R, Jiménez-Araujo A, Rodríguez-Arcos R. Alcaide IV, et al. Front Plant Sci. 2023 Jul 13;14:1199436. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1199436. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37521938 Free PMC article. - Optimization of bioactives extraction from grape marc via a medium scale ambient temperature system and stability study.
Castillo A, Celeiro M, Rubio L, Bañobre A, Otero-Otero M, Garcia-Jares C, Lores M. Castillo A, et al. Front Nutr. 2022 Oct 28;9:1008457. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1008457. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36386901 Free PMC article. - Identification and Quantification of Polyphenols in Croatian Traditional Apple Varieties.
Skoko AG, Šarkanj B, Lores M, Celeiro M, Babojelić MS, Kamenjak D, Flanjak I, Jozinović A, Kovač T, Lončarić A. Skoko AG, et al. Plants (Basel). 2022 Dec 15;11(24):3540. doi: 10.3390/plants11243540. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36559658 Free PMC article. - Identification of Six Phytochemical Compounds from Asparagus officinalis L. Root Cultivars from New Zealand and China Using UAE-SPE-UPLC-MS/MS: Effects of Extracts on H₂O₂-Induced Oxidative Stress.
Zhang H, Birch J, Pei J, Mohamed Ahmed IA, Yang H, Dias G, Abd El-Aty AM, Bekhit AE. Zhang H, et al. Nutrients. 2019 Jan 7;11(1):107. doi: 10.3390/nu11010107. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 30621005 Free PMC article.
References
- Fuentes-Alventosa J.M., Jaramillo-Carmona S., Rodríguez-Gutiérrez G., Rodríguez-Arcos R., Fernández-Bolaños J., Guillén-Bejarano R., Espejo-Calvo J., Jiménez-Araujo A. Effect of the extraction method on phytochemical composition and antioxidant activity of high dietary fibre powders obtained from asparagus by-products. Food Chem. 2009;116:484–490. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.02.074. - DOI
- Hossain M.I., Sharmin F.A., Akhter S., Bhuiyan M.A., Shahriar M. Investigation of cytotoxicity and in-vitro antioxidant activity of Asparagus racemosus root extract. ICPJ. 2012;1:250–257. doi: 10.3329/icpj.v1i9.11615. - DOI
- Dahanukar S., Thatte U., Pai N., Mose P., Karandikar S. Protective effect of Asparagus racemosus against induced abdominal sepsis. Research. 1986;24:125–128.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous