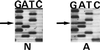Mutation in the tau gene in familial multiple system tauopathy with presenile dementia - PubMed (original) (raw)
Mutation in the tau gene in familial multiple system tauopathy with presenile dementia
M G Spillantini et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998.
Abstract
Familial multiple system tauopathy with presenile dementia (MSTD) is a neurodegenerative disease with an abundant filamentous tau protein pathology. It belongs to the group of familial frontotemporal dementias with Parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17 (FTDP-17), a major class of inherited dementing disorders whose genetic basis is unknown. We now report a G to A transition in the intron following exon 10 of the gene for microtubule-associated protein tau in familial MSTD. The mutation is located at the 3' neighboring nucleotide of the GT splice-donor site and disrupts a predicted stem-loop structure. We also report an abnormal preponderance of soluble tau protein isoforms with four microtubule-binding repeats over isoforms with three repeats in familial MSTD. This most likely accounts for our previous finding that sarkosyl-insoluble tau protein extracted from the filamentous deposits in familial MSTD consists only of tau isoforms with four repeats. These findings reveal that a departure from the normal ratio of four-repeat to three-repeat tau isoforms leads to the formation of abnormal tau filaments. The results show that dysregulation of tau protein production can cause neurodegeneration and imply that the FTDP-17 gene is the tau gene. This work has major implications for Alzheimer's disease and other tauopathies.
Figures
Figure 1
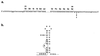
Pedigree of the family with MSTD. Blackened symbols denote affected individuals. Black dots indicate individuals from whom DNA was available and tested by sequencing for the presence of the G to A mutation in the nucleotide adjacent to the exon 10 splice-donor site of the tau gene. The triangle identifies twins (it is not known whether they were mono- or dizygotic). Generation numbers are shown to the left.
Figure 2
Double-stranded DNA sequence of the exon 10-intron junction of the tau gene from an unaffected (labeled N) and an affected (labeled A) member of the family with MSTD. The position of the heterozygous G to A mutation is marked by the arrow.
Figure 3
Nucleotide sequence of the exon 10–intron junctions of the tau gene (a) and structure of the predicted stem-loop in the pre-mRNA (b). The exon sequences are shown in capital and the intron sequences in small letters. Amino acid numbering corresponds to the 441-amino acid isoform of human brain tau. The G to A transition responsible for familial MSTD is shown.
Figure 4
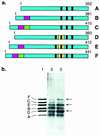
(a) Schematic representation of the six human brain tau isoforms, with the alternatively spliced exons shown in red (exon 2), green (exon 3), and yellow (exon 10). The microtubule-binding repeats are indicated by black bars. (b) Immunoblots of dephosphorylated soluble tau protein from the frontal cortex of a control subject (lane 2) and a patient with familial MSTD (lane 3) using anti-tau serum BR133. Similar results were obtained with anti-tau serum BR134. Six tau isoforms are present in lanes 2 and 3. They align with the six recombinant human brain tau isoforms (lane 1). In the frontal cortex from the familial MSTD patient, tau isoforms with four repeats (isoforms D, E, and F) are more abundant and tau isoforms with three repeats (isoforms A, B, and C) are less abundant than in frontal cortex from the control. Arrows indicate the positions of tau isoforms with four repeats.
Similar articles
- Pathogenic implications of mutations in the tau gene in pallido-ponto-nigral degeneration and related neurodegenerative disorders linked to chromosome 17.
Clark LN, Poorkaj P, Wszolek Z, Geschwind DH, Nasreddine ZS, Miller B, Li D, Payami H, Awert F, Markopoulou K, Andreadis A, D'Souza I, Lee VM, Reed L, Trojanowski JQ, Zhukareva V, Bird T, Schellenberg G, Wilhelmsen KC. Clark LN, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Oct 27;95(22):13103-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.22.13103. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9789048 Free PMC article. - Tau gene mutations in frontotemporal dementia and parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17 (FTDP-17).
Spillantini MG, Van Swieten JC, Goedert M. Spillantini MG, et al. Neurogenetics. 2000 Mar;2(4):193-205. doi: 10.1007/pl00022972. Neurogenetics. 2000. PMID: 10983715 Review. - A new case of frontotemporal dementia and parkinsonism resulting from an intron 10 +3-splice site mutation in the tau gene: clinical and pathological features.
Tolnay M, Grazia Spillantini M, Rizzini C, Eccles D, Lowe J, Ellison D. Tolnay M, et al. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2000 Aug;26(4):368-78. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2990.2000.00109.x. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2000. PMID: 10931371 - Mutations in the tau gene (MAPT) in FTDP-17: the family with Multiple System Tauopathy with Presenile Dementia (MSTD).
Spillantini MG, Murrell JR, Goedert M, Farlow M, Klug A, Ghetti B. Spillantini MG, et al. J Alzheimers Dis. 2006;9(3 Suppl):373-80. doi: 10.3233/jad-2006-9s342. J Alzheimers Dis. 2006. PMID: 16914875 - Tau gene mutations in frontotemporal dementia and parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17 (FTDP-17). Their relevance for understanding the neurogenerative process.
Goedert M, Ghetti B, Spillantini MG. Goedert M, et al. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000;920:74-83. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb06907.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000. PMID: 11193179 Review.
Cited by
- Tau pathology: predictive diagnostics, targeted preventive and personalized medicine and application of advanced research in medical practice.
Gozes I. Gozes I. EPMA J. 2010 Jun;1(2):305-16. doi: 10.1007/s13167-010-0029-y. Epub 2010 Jun 12. EPMA J. 2010. PMID: 23199066 Free PMC article. - Tau and tauopathies.
Lee G, Leugers CJ. Lee G, et al. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2012;107:263-93. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385883-2.00004-7. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2012. PMID: 22482453 Free PMC article. Review. - FTD and ALS--translating mouse studies into clinical trials.
Ittner LM, Halliday GM, Kril JJ, Götz J, Hodges JR, Kiernan MC. Ittner LM, et al. Nat Rev Neurol. 2015 Jun;11(6):360-6. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2015.65. Epub 2015 May 5. Nat Rev Neurol. 2015. PMID: 25939274 Review. - Regulation of Diabetes: a Therapeutic Strategy for Alzheimer's Disease?
Ahn KC, Learman CR, Baker GB, Weaver CL, Chung PS, Kim HG, Song MS. Ahn KC, et al. J Korean Med Sci. 2019 Dec 2;34(46):e297. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2019.34.e297. J Korean Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31779058 Free PMC article. Review. - Advances in the cellular and molecular biology of the beta-amyloid protein in Alzheimer's disease.
Sambamurti K, Greig NH, Lahiri DK. Sambamurti K, et al. Neuromolecular Med. 2002;1(1):1-31. doi: 10.1385/NMM:1:1:1. Neuromolecular Med. 2002. PMID: 12025813 Review.
References
- Foster N L, Wilhelmsen K, Sima A A F, Jones M Z, D’Amato C, Gilman S, Spillantini M G, Lynch T, Mayeux R P, Gaskell P C, et al. Ann Neurol. 1997;41:706–715. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous