Block D (original) (raw)

Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
Block D

Block D / 11D68
Aft view of the Block D lunar crasher stage and its 11D68 engine. The Block D would have taken the LK lunar lander to near the surface of the moon. This stage remains in use today atop the Proton rocket.
Credit: © Mark Wade
LOx/Kerosene propellant rocket stage. Adaptation of Block D for Energia payload low earth orbital insertion. Used when Buran orbiter not carried.
AKA: Energia RCS;Retro and Correction Stage. Status: Design 1987. Thrust: 84.94 kN (19,094 lbf). Gross mass: 17,000 kg (37,000 lb). Unfuelled mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Specific impulse: 352 s. Burn time: 680 s. Height: 5.70 m (18.70 ft). Diameter: 3.70 m (12.10 ft). Span: 3.70 m (12.10 ft).
Cost $ : 4.000 million.
Subtopics
| Soyuz 7K-L1E Russian manned lunar orbiter. Modification of Soyuz circumlunar configuration used in propulsion tests of the Block D stage. Technology satellite, Russia. Launched 1969 - 1970. Used the Blok-D bus. |
|---|
| N1 Block D LOx/Kerosene propellant rocket stage. Block D as originally designed as a lunar crasher stage. |
|---|
| Proton 11S824 LOx/Kerosene propellant rocket stage. Originally designed as N1-L3 lunar expedition launch vehicle lunar orbit insertion/lunar crasher stage. Before it could fly on the N1, it was adapted for use with Proton UR-500K as a fourth stage for manned circumlunar flight. It was then further used to launch large Lavochkin bureau unmanned lunar/planetary spacecraft. In the 1970's it was adopted by the Soviet military and standardized for launch of geostationary satellites. |
|---|
| Proton 11S824M LOx/Kerosene propellant rocket stage. Also known as Block D-1; article number 11S824M. Without guidance unit (navigation commands come from payload). Successor to 11S824. Used to launch large Lavochkin bureau unmanned lunar/planetary/high earth orbit spacecraft from 1976 to 1989. |
|---|
| Proton 11S86 LOx/Kerosene propellant rocket stage. Also known as Block DM; article number 11S86. With guidance unit, designed for insertion of military spacecraft into geosynchronous/ medium earth orbit. Used from 1974 to 1990. Succeeded by 11S861. |
|---|
| Proton 11S824F LOx/Kerosene propellant rocket stage. Also known as Block D-2; article number 11S824F. Without guidance unit (navigation commands come from payload). Successor to 11S824M. Used for launch of Lavochkin Mars-bound spacecraft in 1988 and 1996. |
|---|
| Zenit-V Zenit stage 3. LOx/Kerosene propellant rocket stage. Adaptation of Block D for Zenit. |
|---|
| Proton 17S40 LOx/Kerosene propellant rocket stage. Also known as Block DM-5. Commercial version is Block DM2, with Iridium dispenser, designed for insertion of multiple LM 700 (Iridium) spacecraft into medium earth orbit. With guidance unit, modification of 11S861 stage for heavier payloads and with different payload adapter. |
|---|
| Proton 11S861 LOx/Kerosene propellant rocket stage. Also known as Block DM-2 (different from commercial Block DM2 (no hyphen!)), article number 11S861. Commercial version designated Block DM1 and is equipped with Saab payload adapter for insertion of AS 4000 bus spacecraft into geosynchronous orbit. With improved guidance system as compared to 11S86, originally designed for insertion of military spacecraft into geosynchronous orbit. Used from 1982 to present. |
|---|
| Proton 11S861-01 LOx/Kerosene propellant rocket stage. Also known as Block DM-2M, article number 11S861-01. Commercial versions are Block DM3, with Saab payload dispenser, for insertion of Hughes HS 601 bus spacecraft into geosynchronous orbit; and Block DM4, for insertion of FS-1300 bus spacecraft into geosynchronous orbit. With guidance unit, originally designed for insertion of military spacecraft into geosynchronous orbit. Capable of boosting heavier payloads than 11S861 through use of higher-performance 'Sintin' synthetic kerosene fuel. |
|---|
Country: Russia. Engines: RD-58. Launch Vehicles: Groza. Propellants: Lox/Kerosene.
Photo Gallery
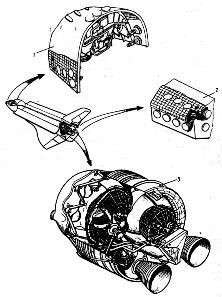 |
Buran ODUBuran ODU engine system diagramCredit: from Semenov, et. al., Buran, 1995. |
|---|
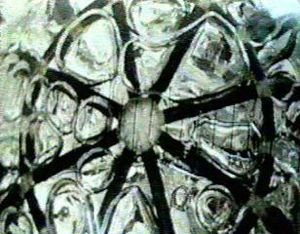 |
Block D 0-GBlock D Liquid Behaviour in Zero-GCredit: RKK Energia |
|---|
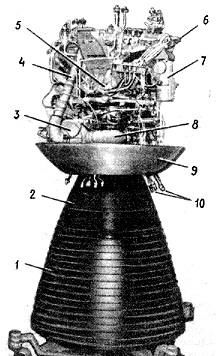 |
Buran main engineCredit: from Semenov, et. al., Buran, 1995. |
|---|
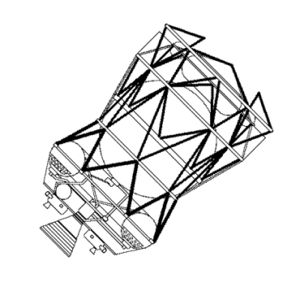 |
Block DCredit: © Mark Wade |
|---|
 |
Block D StagesBlock D Stages in AssemblyCredit: RKK Energia |
|---|
 |
Block D StageBlock D Stage in Assembly ShopCredit: RKK Energia |
|---|
1965 September 15 - . LV Family: , Proton, .
- Korolev conceived of podsadka over a month before before the UR-500K-L1 was authorized. - . Related Persons: Korolev, Mishin. Spacecraft: Block D, Soyuz 7K-L1.
Korolev conceived of podsadka over a month before before the UR-500K-L1 was authorized.Initial calculations by OKB-1 showed that the developmental L1 would have a dry mass of 4641 kg, or 4847 kg after delivery of cosmonauts via podsadka. On the other hand, Kolyako in Division 2 estimated the translunar payload of the Block D as ~ 5000 kg in the single launch scenario, or ~ 5300 kg in the podsadka scenario.
1966 March 23 - .
- Inconsistent Soviet lunar program - . Related Persons: Mishin, Chertok. Spacecraft: Block D, Soyuz, Soyuz 7K-L1, Soyuz 7K-LOK, Soyuz 7K-OK, Soyuz Kontakt.
Acting director Mishin held a brainstorming session with this top managers to address "...our inconsistent lunar program". He noted then-current contradictory approaches: 1. Return to a two-launch scheme (podsadka, as baseline); 2. Keep with direct landing; 3. Use a Block D with storable propellants; 4. Use the 7K-OK as the designated return spacecraft. He noted that the L1 program was a diversion for the bureau to the core objective of landing a cosmonaut on the moon (the L3 program). Among the advantages of continuing with the L1, he noted that it "Utilizes the 7K-OK" - evidently there was no purpose for the spacecraft beyond the L1 mission in the podsadka scenario. He asks for frank opinions from his managers. V Rauschenbach noted that they "..have to do the L-1 � and therefore we will have to use a 2-launch scheme based on the L1-S". BE Chertok: discussed the rendezvous and docking systems for the various spacecraft: L1-S - "Igla"; LOK - "Kontakt" (since "Igla" cannot be used on the LOK (due to mass considerations); or a new system for the LOK. (Mishin Diaries 1-226) Here we have an indication that the L1 podsadka version did use the Igla system, which makes complete sense, since the Soyuz 7K-OK missions conducted dress rehearsals for podsadka using this system to rendezvous and dock two 7K-OK spacecraft in earth orbit.
1966 April 1 - .
- Production rates for the podsadka program. - . Related Persons: Mishin. Spacecraft: Block D, Soyuz, Soyuz 7K-L1, Soyuz 7K-OK.
Ministry of Defense directive laid out the production rate for both the L1, Block D, and 7K-OK for the podsadka program. Ministry of Defense directive (Mishin Diaries 1-234) laid out the production rate for both the L1, Block D, and 7K-OK for the podsadka program:
7K-L1: one unit per month beginning 15 Sept 66
7K-OK for podsadka delivery of crews to L1: 1 unit per month beginning Oct 66
Block D deliveries: 1 unit 15 Sept; 1 unit 15 Oct; 1 further unit in October; and 1 unit per month thereafter.(Mishin Diaries 1-234)
1966 April 27 - .
- VPK Resolution No. 101 (Mishin Diaries 1-266) mandated an aggressive L1 flight test program. - . Related Persons: Mishin. Spacecraft: Block D, Soyuz, Soyuz 7K-L1, Soyuz 7K-OK.
No 1 - August - Proton-2 (this may refer to the Proton / Block D full-mass mockup that was tested in October 1966 but then abandoned for safety reasons).
2-4: Flyby of the moon with the unpiloted version:
No 2 - October
No 3 - November
No 4 - December
No 5 - No 9: 7K-L1 flyby of the moon at intervals of one month with crew delivery by 7K-OK
No 10 - No 14: Direct flyby of the moon at one month intervals.
This indicates that podsadka was the baseline approach for early missions, for both safety and launch mass considerations. Only the last five missions would be direct flights. It was probably anticipated that by then the Proton booster would be reliable enough and that improvements to the Block D and the weight reduction on the L1 would make the single-launch approach feasible. (Mishin Diaries 1-266)
1966 December 2 - . LV Family: N1, Proton, .
- The 2-launch N1 scenario was discussed in an interdepartmental technical review with MV Keldysh. - . Related Persons: Mishin, Bushuyev, Keldysh, . Spacecraft: Block D, Soyuz 7K-LOK, LK, Luna Ye-8.
At this point the Ye-8 would be delivered to the moon by a UR-500K launch vehicle. The basic constraint was the 5300 kg payload capability of the Block D to translunar injection. This meant tradeoffs in the accuracy of the Ye-8's initial landing versus its lifetime on the surface waiting for arrival of the LK. It was agreed that a working group would meet the next day to develop final specifications Ye-8 and a more detailed outline of the N1-L3 expedition using Ye-8. (start-up sequence, the time, the connections between LK, LOK and Ye-8, the means for determining the location). KD Bushuyev was to study the backup LK concept. (Mishin Diaries 1-235)
1967 May 5 - . LV Family: N1, Proton, N11.
- Recommendation that podsadka be dropped and L1 direct flight become the baseline. - . Related Persons: Mishin. Spacecraft: Block D, Soyuz, Soyuz 7K-L1, Soyuz 7K-OK.
The Soviet of Chief Designers met with the Civil Chief Designer UR500K-L1 and recommended that podsadka be dropped and direct flight become the baseline. This was evidently to make possible the objective of a Soviet man around the moon before 4 October 1967. The reasons given were:
a) The successful flights of the UR-500K and Block D on the L1 2P and 3P and the further 4 separate UR-500 launches provided confidence in the launch vehicle's reliability.
b) The main delays with L1 development will be in relation to development by BTsVM of the Argon-11 digital computer for its control system.
c) The failure of 7K-OK number 4 (Soyuz 1) indicated a delay in development of docking in earth orbit.
It was recommended that the 7K-L1 launch sequence be revised to two missions per month as follows:
- 4L - "Zond" unmanned 17 - 29 June 1966
- 5L - unmanned, circumlunar, 27 June - 5 July
- 6L - "Zond", unmanned, 12 - 17 July
- 7L - unmanned, circumlunar, 25 July - 3 August
Followed by manned launches according to astronomical constraints (which would mean 23 August, 21 September, 19 October). (Mishin Diaries 2-22)
1967 October 4 - . LV Family: N1.
- Mishin conducts a rather grim review of the cut backs to his OKB's budget for 1968. - . Related Persons: Mishin. Spacecraft: Block D, Soyuz, Soyuz 7K-LOK, Soyuz 7K-OK, MKBS, LK.
Consider the shortfall in his request compared with the challenge of beating the Americans to the moon!
Review with Company Management on Occasion of Tenth Anniversary of Sputnik 1
Plan for 1968.
1. Funding:
R&D - 7.5 million Rubles. (26 million requested).
including YaRD nuclear rocket engine- 6 million., MKBS - 0.5 million., L-5 - 0.5 mln., Yantar - 0.5 million.
Experimental design work - 266 million. (Requested 333 million).
Funded 3 sets N1-L3 instead of 6 sets.
For 7K-OK - 11, 12, 13, 14 (shortfall 20%).
N1-L3 (3 sets - 207 million., Including 38 million experimental work. Stages A, B, V, G - 22.8 million. Payloads (LOK, LK, Block D, GO) - 9.5 million. Blocks E and I - free of charge. (under direct contract with Isayev).
2. Plan - does not meet the 5-year plan. Not included at all:
- Modernization of the N1-L3.
- In R&D - Modernization of the RT-2M (in full).
- EYaRD (nuclear electric propulsion)- instead of in R&D - to search for funding.
1968 February 1 - .
- Preparations for Soviet of Chief Designers - . Related Persons: Mishin. Spacecraft: Block D, Soyuz 7K-LOK, LK.
In preparation for a Soviet of Chief Designers four days later, detailed consideration of many issues was underway. Among them, changes to the baseline LK orbit and ascent trajectories to allow rendezvous with the waiting LOK even after a delay of more than six orbits in departure; and changes to the landing profile to prevent shrapnel from jettison of the LKR's Block D lunar crasher stage impacting the waiting cosmonaut's LK. 250 liters of increased propellant would be required in the LKR for a higher Block D jettison; or the Block D could make a maneuver after separation to assure it would impact well away from the active landing site. (Mishin Diaries 2-119)
1969 November 28 - . 09:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D. FAILURE: First stage malfunction.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Soyuz 7K-L1E s/n 1 - first stage malfunction - . Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1E s/n 1. Mass: 10,380 kg (22,880 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: RVSN. Program: Luna. Class: Moon. Type: Manned lunar spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Block D. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1E. Decay Date: 1969-11-16 .
Attempted test flight of Block D upper stage in N1 lunar crasher configuration. Payload was a modified Soyuz 7K-L1 circumlunar spacecraft, which provided guidance to the Block D and was equipped with television cameras that viewed the behavior of the Block D stage propellants under zero-G conditions. Mission flown successfully over a year later as Cosmos 382.
1970 December 2 - . 17:00 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC81/23. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-K/D.
- Cosmos 382 - . Payload: Soyuz 7K-L1E s/n 2K. Mass: 10,380 kg (22,880 lb). Nation: Russia. Agency: MOM. Program: Lunar L3. Class: Manned. Type: Manned spacecraft. Spacecraft Bus: Block D. Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-L1E. Duration: 8,549.30 days. USAF Sat Cat: 4786 . COSPAR: 1970-103A. Apogee: 5,269 km (3,273 mi). Perigee: 2,384 km (1,481 mi). Inclination: 55.90 deg. Period: 171.00 min.
Test of Block D upper stage in its N1 lunar crasher configuration in earth orbit. The three maneuvers simulated the lunar orbit insertion burn; the lunar orbit circularization burn; and the descent burn to bring the LK lunar lander just over the surface. Payload was a modified Soyuz 7K-L1 circumlunar spacecraft, which provided guidance to the Block D and was equipped with television cameras that viewed the behavior of the Block D stage propellants under zero-G conditions.
Maneuver Summary:
190km X 300km orbit to 303km X 5038km orbit. Delta V: 982 m/s
318km X 5040km orbit to 1616km X 5071km orbit. Delta V: 285 m/s
1616km X 5071km orbit to 2577km X 5082km orbit. Delta V: 1311 m/s
Total Delta V: 2578 m/s.
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use
