Demo of OPTICS clustering algorithm (original) (raw)
Note
Go to the endto download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via JupyterLite or Binder
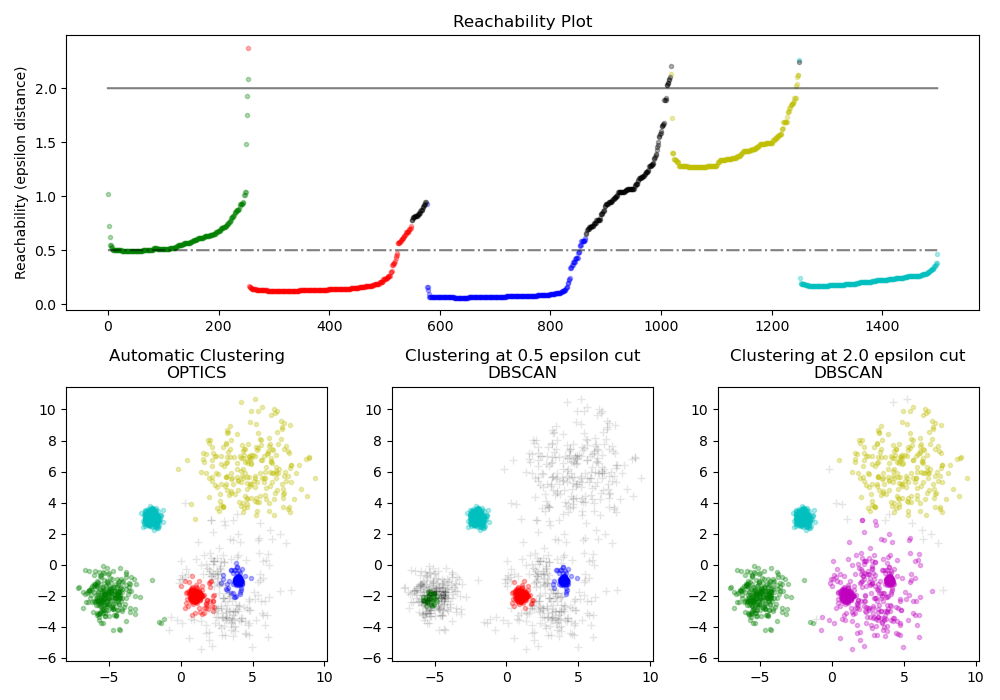
Finds core samples of high density and expands clusters from them. This example uses data that is generated so that the clusters have different densities.
The OPTICS is first used with its Xi cluster detection method, and then setting specific thresholds on the reachability, which corresponds to DBSCAN. We can see that the different clusters of OPTICS’s Xi method can be recovered with different choices of thresholds in DBSCAN.
Authors: The scikit-learn developers
SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
import matplotlib.gridspec as gridspec import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np
from sklearn.cluster import OPTICS, cluster_optics_dbscan
Generate sample data
np.random.seed(0) n_points_per_cluster = 250
C1 = [-5, -2] + 0.8 * np.random.randn(n_points_per_cluster, 2) C2 = [4, -1] + 0.1 * np.random.randn(n_points_per_cluster, 2) C3 = [1, -2] + 0.2 * np.random.randn(n_points_per_cluster, 2) C4 = [-2, 3] + 0.3 * np.random.randn(n_points_per_cluster, 2) C5 = [3, -2] + 1.6 * np.random.randn(n_points_per_cluster, 2) C6 = [5, 6] + 2 * np.random.randn(n_points_per_cluster, 2) X = np.vstack((C1, C2, C3, C4, C5, C6))
clust = OPTICS(min_samples=50, xi=0.05, min_cluster_size=0.05)
Run the fit
clust.fit(X)
labels_050 = cluster_optics_dbscan( reachability=clust.reachability_, core_distances=clust.core_distances_, ordering=clust.ordering_, eps=0.5, ) labels_200 = cluster_optics_dbscan( reachability=clust.reachability_, core_distances=clust.core_distances_, ordering=clust.ordering_, eps=2, )
space = np.arange(len(X)) reachability = clust.reachability_[clust.ordering_] labels = clust.labels_[clust.ordering_]
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 7)) G = gridspec.GridSpec(2, 3) ax1 = plt.subplot(G[0, :]) ax2 = plt.subplot(G[1, 0]) ax3 = plt.subplot(G[1, 1]) ax4 = plt.subplot(G[1, 2])
Reachability plot
colors = ["g.", "r.", "b.", "y.", "c."] for klass, color in enumerate(colors): Xk = space[labels == klass] Rk = reachability[labels == klass] ax1.plot(Xk, Rk, color, alpha=0.3) ax1.plot(space[labels == -1], reachability[labels == -1], "k.", alpha=0.3) ax1.plot(space, np.full_like(space, 2.0, dtype=float), "k-", alpha=0.5) ax1.plot(space, np.full_like(space, 0.5, dtype=float), "k-.", alpha=0.5) ax1.set_ylabel("Reachability (epsilon distance)") ax1.set_title("Reachability Plot")
OPTICS
colors = ["g.", "r.", "b.", "y.", "c."] for klass, color in enumerate(colors): Xk = X[clust.labels_ == klass] ax2.plot(Xk[:, 0], Xk[:, 1], color, alpha=0.3) ax2.plot(X[clust.labels_ == -1, 0], X[clust.labels_ == -1, 1], "k+", alpha=0.1) ax2.set_title("Automatic Clustering\nOPTICS")
DBSCAN at 0.5
colors = ["g.", "r.", "b.", "c."] for klass, color in enumerate(colors): Xk = X[labels_050 == klass] ax3.plot(Xk[:, 0], Xk[:, 1], color, alpha=0.3) ax3.plot(X[labels_050 == -1, 0], X[labels_050 == -1, 1], "k+", alpha=0.1) ax3.set_title("Clustering at 0.5 epsilon cut\nDBSCAN")
DBSCAN at 2.
colors = ["g.", "m.", "y.", "c."] for klass, color in enumerate(colors): Xk = X[labels_200 == klass] ax4.plot(Xk[:, 0], Xk[:, 1], color, alpha=0.3) ax4.plot(X[labels_200 == -1, 0], X[labels_200 == -1, 1], "k+", alpha=0.1) ax4.set_title("Clustering at 2.0 epsilon cut\nDBSCAN")
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.631 seconds)
Related examples