One-Class SVM versus One-Class SVM using Stochastic Gradient Descent (original) (raw)
Note
Go to the endto download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via JupyterLite or Binder
This example shows how to approximate the solution ofsklearn.svm.OneClassSVM in the case of an RBF kernel withsklearn.linear_model.SGDOneClassSVM, a Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) version of the One-Class SVM. A kernel approximation is first used in order to apply sklearn.linear_model.SGDOneClassSVM which implements a linear One-Class SVM using SGD.
Note that sklearn.linear_model.SGDOneClassSVM scales linearly with the number of samples whereas the complexity of a kernelizedsklearn.svm.OneClassSVM is at best quadratic with respect to the number of samples. It is not the purpose of this example to illustrate the benefits of such an approximation in terms of computation time but rather to show that we obtain similar results on a toy dataset.
Authors: The scikit-learn developers
SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
import matplotlib import matplotlib.lines as mlines import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np
from sklearn.kernel_approximation import Nystroem from sklearn.linear_model import SGDOneClassSVM from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline from sklearn.svm import OneClassSVM
font = {"weight": "normal", "size": 15}
matplotlib.rc("font", **font)
random_state = 42 rng = np.random.RandomState(random_state)
Generate train data
X = 0.3 * rng.randn(500, 2) X_train = np.r_[X + 2, X - 2]
Generate some regular novel observations
X = 0.3 * rng.randn(20, 2) X_test = np.r_[X + 2, X - 2]
Generate some abnormal novel observations
X_outliers = rng.uniform(low=-4, high=4, size=(20, 2))
OCSVM hyperparameters
nu = 0.05 gamma = 2.0
Fit the One-Class SVM
clf = OneClassSVM(gamma=gamma, kernel="rbf", nu=nu) clf.fit(X_train) y_pred_train = clf.predict(X_train) y_pred_test = clf.predict(X_test) y_pred_outliers = clf.predict(X_outliers) n_error_train = y_pred_train[y_pred_train == -1].size n_error_test = y_pred_test[y_pred_test == -1].size n_error_outliers = y_pred_outliers[y_pred_outliers == 1].size
Fit the One-Class SVM using a kernel approximation and SGD
transform = Nystroem(gamma=gamma, random_state=random_state) clf_sgd = SGDOneClassSVM( nu=nu, shuffle=True, fit_intercept=True, random_state=random_state, tol=1e-4 ) pipe_sgd = make_pipeline(transform, clf_sgd) pipe_sgd.fit(X_train) y_pred_train_sgd = pipe_sgd.predict(X_train) y_pred_test_sgd = pipe_sgd.predict(X_test) y_pred_outliers_sgd = pipe_sgd.predict(X_outliers) n_error_train_sgd = y_pred_train_sgd[y_pred_train_sgd == -1].size n_error_test_sgd = y_pred_test_sgd[y_pred_test_sgd == -1].size n_error_outliers_sgd = y_pred_outliers_sgd[y_pred_outliers_sgd == 1].size
from sklearn.inspection import DecisionBoundaryDisplay
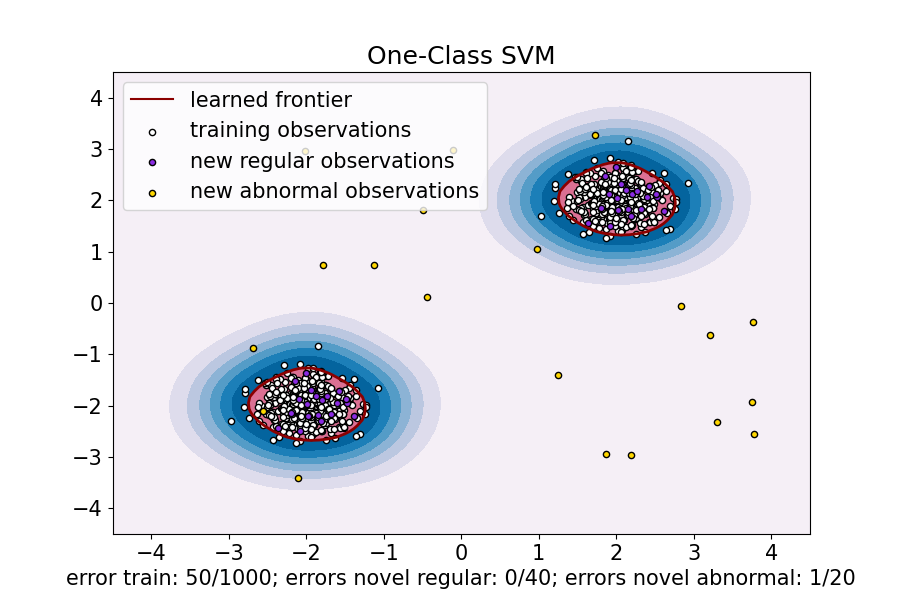
_, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(9, 6))
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-4.5, 4.5, 50), np.linspace(-4.5, 4.5, 50)) X = np.concatenate([xx.ravel().reshape(-1, 1), yy.ravel().reshape(-1, 1)], axis=1) DecisionBoundaryDisplay.from_estimator( clf, X, response_method="decision_function", plot_method="contourf", ax=ax, cmap="PuBu", ) DecisionBoundaryDisplay.from_estimator( clf, X, response_method="decision_function", plot_method="contour", ax=ax, linewidths=2, colors="darkred", levels=[0], ) DecisionBoundaryDisplay.from_estimator( clf, X, response_method="decision_function", plot_method="contourf", ax=ax, colors="palevioletred", levels=[0, clf.decision_function(X).max()], )
s = 20 b1 = plt.scatter(X_train[:, 0], X_train[:, 1], c="white", s=s, edgecolors="k") b2 = plt.scatter(X_test[:, 0], X_test[:, 1], c="blueviolet", s=s, edgecolors="k") c = plt.scatter(X_outliers[:, 0], X_outliers[:, 1], c="gold", s=s, edgecolors="k")
ax.set( title="One-Class SVM", xlim=(-4.5, 4.5), ylim=(-4.5, 4.5), xlabel=( f"error train: {n_error_train}/{X_train.shape[0]}; " f"errors novel regular: {n_error_test}/{X_test.shape[0]}; " f"errors novel abnormal: {n_error_outliers}/{X_outliers.shape[0]}" ), ) _ = ax.legend( [mlines.Line2D([], [], color="darkred", label="learned frontier"), b1, b2, c], [ "learned frontier", "training observations", "new regular observations", "new abnormal observations", ], loc="upper left", )
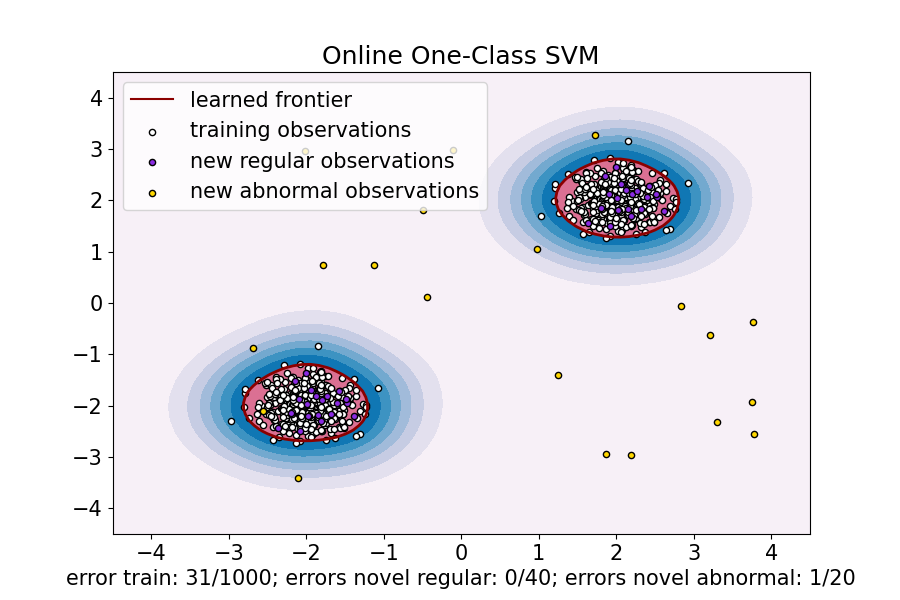
_, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(9, 6))
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-4.5, 4.5, 50), np.linspace(-4.5, 4.5, 50)) X = np.concatenate([xx.ravel().reshape(-1, 1), yy.ravel().reshape(-1, 1)], axis=1) DecisionBoundaryDisplay.from_estimator( pipe_sgd, X, response_method="decision_function", plot_method="contourf", ax=ax, cmap="PuBu", ) DecisionBoundaryDisplay.from_estimator( pipe_sgd, X, response_method="decision_function", plot_method="contour", ax=ax, linewidths=2, colors="darkred", levels=[0], ) DecisionBoundaryDisplay.from_estimator( pipe_sgd, X, response_method="decision_function", plot_method="contourf", ax=ax, colors="palevioletred", levels=[0, pipe_sgd.decision_function(X).max()], )
s = 20 b1 = plt.scatter(X_train[:, 0], X_train[:, 1], c="white", s=s, edgecolors="k") b2 = plt.scatter(X_test[:, 0], X_test[:, 1], c="blueviolet", s=s, edgecolors="k") c = plt.scatter(X_outliers[:, 0], X_outliers[:, 1], c="gold", s=s, edgecolors="k")
ax.set( title="Online One-Class SVM", xlim=(-4.5, 4.5), ylim=(-4.5, 4.5), xlabel=( f"error train: {n_error_train_sgd}/{X_train.shape[0]}; " f"errors novel regular: {n_error_test_sgd}/{X_test.shape[0]}; " f"errors novel abnormal: {n_error_outliers_sgd}/{X_outliers.shape[0]}" ), ) ax.legend( [mlines.Line2D([], [], color="darkred", label="learned frontier"), b1, b2, c], [ "learned frontier", "training observations", "new regular observations", "new abnormal observations", ], loc="upper left", ) plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.418 seconds)
Related examples