Air - Composition and Molecular Weight (original) (raw)
Components in Dry Air
Air is a mixture of several gases, where the two most dominant components in dry air are 21 vol% oxygen and 78 vol% nitrogen . Oxygen has a molar mass of 15.9994 g/mol and nitrogen has a molar mass of 14.0067 g/mol. Since both of these elements are diatomic in air - O2 and N2, the molar mass of oxygen gas is 32 g/mol and the molar mass of nitrogen gas is 28 g/mol.
The average molar mass is equal to the sum of the mole fractions of each gas multiplied by the molar mass of that particular gas:
Mmixture = x1 M1 +......+ xn Mn (1)
where
xi = mole fractions of each gas
Mi = the molar mass of each gas
The molar mass of dry air is 28.9647 g/mol. Composition and content of each gas in air is given in the figures and the table below.
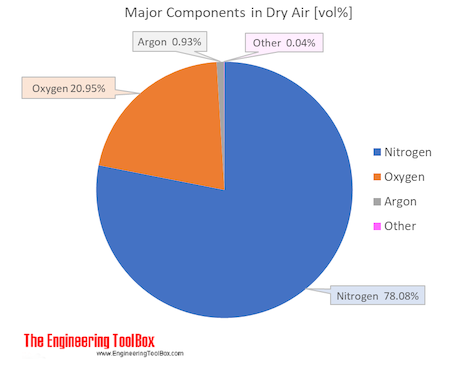
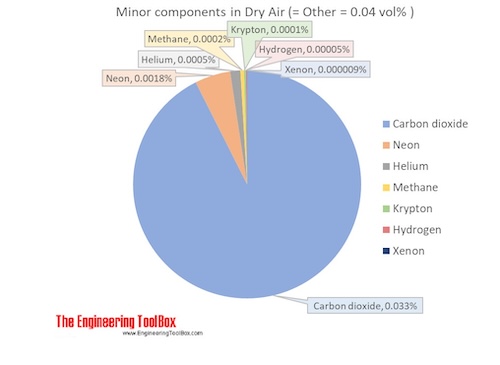
See also Air Density at varying pressure, Density and specific weight at varying temperature, Diffusion Coefficients for Gases in Air, Dynamic (absolute) and kinematic viscosity, Prandtl Number, Specific heat at varying temperature and Specific heat at varying pressure, Thermal Conductivity, Thermal Diffusivity, Properties at gas-liquid equilibrium conditions and Air properties, for other properties of air.
Air is usually modeled as a uniform (no variation or fluctuation) gas with properties averaged from the individual components.
For full table - rotate the screen!
Air - Composition and Molecular Weight
| Components in dry air | Volume ratio = Molar ratio compared to dry air | Molar mass | Molar mass in air | Atmospheric boiling point | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Formula | (mol/molair ) | (vol%) | (g/mol), (kg/kmol) | (g/molair ), (kg/kmolair ) | (wt%) | (K) | (°C) | (°F) |
| Nitrogen | N2 | 0.78084 | 78.084 | 28.013 | 21.872266 | 75.511 | 77.4 | -195.8 | -320.4 |
| Oxygen | O2 | 0.20946 | 20.946 | 31.999 | 6.701942 | 23.14 | 90.2 | -183.0 | -297.3 |
| Argon | Ar | 0.00934 | 0.934 | 39.948 | 0.373025 | 1.29 | 87.3 | -185.8 | -302.5 |
| Carbon dioxide1) | CO2 | 0.000412 | 0.0412 | 44.010 | 0.018132 | 0.063 | 194.7 | -78.5 | -109.2 |
| Neon | Ne | 0.00001818 | 0.001818 | 20.180 | 0.000367 | 0.0013 | 27.2 | -246.0 | -410.7 |
| Helium | He | 0.00000524 | 0.000524 | 4.003 | 0.000021 | 0.00007 | 4.2 | -269.0 | -452.1 |
| Methane | CH4 | 0.00000179 | 0.000179 | 16.042 | 0.000029 | 0.00010 | 111.7 | -161.5 | -258.7 |
| Krypton | Kr | 0.0000010 | 0.0001 | 83.798 | 0.000084 | 0.00029 | 119.8 | -153.4 | -244.0 |
| Hydrogen | H2 | 0.0000005 | 0.00005 | 2.016 | 0.000001 | 0.000003 | 20.3 | -252.9 | -423.1 |
| Xenon | Xe | 0.00000009 | 0.000009 | 131.293 | 0.000012 | 0.00004 | 165.1 | -108.1 | -162.5 |
| Average molar mass of air | 28.9647 |
- According NASA CO2level in 1960 aprox. 320 ppm, 1970 aprox. 328 ppm, 1980 aprox. 341 ppm, 1990 aprox. 356 ppm, 2000 aprox. 372 ppm, 2010 aprox. 390 ppm and 2020 aprox. 412 ppm
- The water or vapor content in air varies. The maximum moisture carrying capacity of air depends primarily on temperature
- The composition of air is unchanged until elevation of approximately 10.000 m
- The average air temperature diminishes at the rate of 0.6 oC for each 100 m vertical height
- "One Standard Atmosphere" is defined as the pressure equivalent to that exerted by a 760 mm column of mercury at 0 oC sea level and at standard gravity (32.174 ft/sec2)
Other components in air
- Sulfur dioxide - SO2 - 1.0 parts/million (ppm)
- Nitrous oxide - N2O - 0.5 parts/million (ppm)
- Ozone - O3 - 0 to 0.07 parts/million (ppm)
- Nitrogen dioxide - NO2 - 0.02 parts/million (ppm)
- Iodine - I2 - 0.01 parts/million (ppm)
- Carbon monoxide - CO - 0 to trace (ppm)
- Ammonia - NH3 - 0 to trace (ppm)
Common Pressure Units frequently used as alternative to " one Atmosphere"
- 76 Centimeters (760 mm) of Mercury
- 29.921 Inches of Mercury
- 10.332 Meters of Water
- 406.78 Inches of Water
- 33.899 Feet of Water
- 14.696 Pound-Force per Square Inch
- 2116.2 Pounds-Force per Square Foot
- 1.033 Kilograms-Force per Square Centimeter
- 101.33 kiloPascal
See also Air Density at varying pressure, Density and specific weight at varying temperature, Diffusion Coefficients for Gases in Air, Dynamic (absolute) and kinematic viscosity, Prandtl Number, Specific heat at varying temperature and Specific heat at varying pressure, Thermal Conductivity, Thermal Diffusivity, Properties at gas-liquid equilibrium conditions and Air properties, for other properties of air
Related Documents
Air - Specific Heat Ratio
Specific Heat Ratio of air at temperatures ranging -40 - 1000 degC (-40 - 1500 degF) at standard atmospheric pressure - Imperial and SI Units.
Air Properties - Density, Viscosity, Heat Capacity, Thermal Conductivity, and more
Thermal properties of air, including density, viscosity, thermal conductivity, specific heat and more at different temperatures and pressures. Comprehensive reference with formulas, tables, and charts to support engineering calculations.
Solubility of Air in Water
The amount of air that can be dissolved in water decreases with temperature and increases with pressure.

