Ethylene Gas - Specific Heat vs. Temperature (original) (raw)
Specific heat (C) is the amount of heat required to change the temperature of a mass unit of a substance by one degree.
- Isobaric specific heat (Cp) is used for substances in a constant pressure (ΔP = 0) system.
- I sochoric specific heat (Cv) is used for substances in a constant-volume , (= isovolumetric or isometric ) closed system.
The specific heat - CP and CV - will vary with temperature. When calculating mass and volume flow of a substance in heated or cooled systems with high accuracy - the specific heat (= heat capacity) should be corrected according values in the figures and the table below.
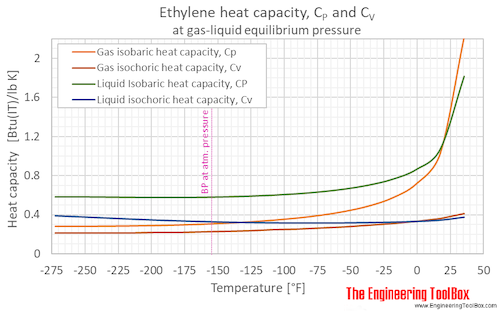
Isobaric, CP, and isochoric, CV, specific heat of ethylene at gas-liquid equilibrium pressure and varying temperature, °C and °F:

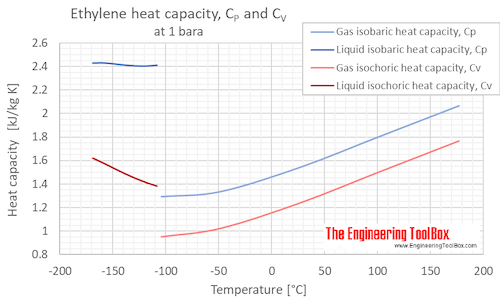
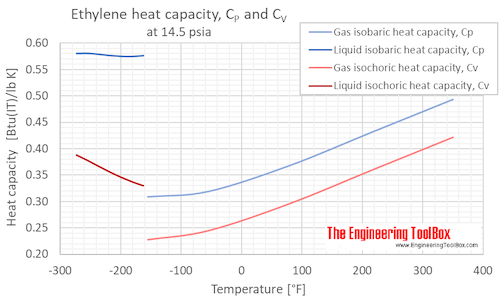
Isobaric, CP, and isochoric, CV, specific heat of ethylene at atmospheric pressure and varying temperature, °C and °F:
Specific heat of Ethylene Gas - C2H4 - at temperatures ranging 175 - 900 K :
Ethylene Gas - C2H4 - Specific Heat vs. Temperature
| Temperature - T - (K) | Specific Heat - cp - (kJ/kgK) |
|---|---|
| 175 | 1.295 |
| 200 | 1.305 |
| 225 | 1.337 |
| 250 | 1.380 |
| 275 | 1.453 |
| 300 | 1.535 |
| 325 | 1.621 |
| 350 | 1.709 |
| 375 | 1.799 |
| 400 | 1.891 |
| 450 | 2.063 |
| 500 | 2.227 |
| 550 | 2.378 |
| 600 | 2.519 |
| 650 | 2.649 |
| 700 | 2.770 |
| 750 | 2.883 |
| 800 | 2.989 |
| 850 | 3.088 |
| 900 | 3.180 |
See also other properties of Ethylene at varying temperature and pressure: Density and Specific Weight, Dynamic and kinematic viscosity and Thermal conductivity, and Thermophysical properties at standard conditions,
as well as Specific heat of Air - at Constant Pressure and Varying Temperature, Air - at Constant Temperature and Varying Pressure, Ammonia, Butane, Carbon dioxide, Carbon monoxide, Ethane, Ethanol, Hydrogen, Methane, Methanol, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Propane and Water.