Critical Temperatures and Pressures for some Common Substances (original) (raw)
Critical temperatures and pressures for some common substances like air, alcohol, ether, oxygen and more.
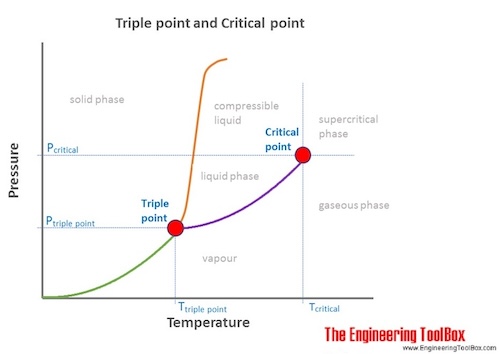
Gases can be converted to liquids by compressing the gas at a suitable temperature. However, they become more difficult to liquefy as the temperature increases because the kinetic energies of the particles that make up the gas also increase. At the critical temperature they cannot longer be liquified.
- Critical Temperature: The temperature which above, a substance can not exist as a liquid, no matter how much pressure is applied. Every substance has a critical temperature.
- Critical Pressure: The pressure required to liquify a substance vapor at its critical temperature
- Critical point: The end point of the pressure-temperature curve that designates conditions under which a liquid and its vapor can coexist. At higher temperatures, the gas cannot be liquefied by pressure alone. At the critical point, defined by the critical temperature Tc and the critical pressure pc, phase boundaries vanish.
- Triple point: The temperature and pressure at which the three phases (gas, liquid, and solid) of a substance coexist in thermodynamic equilibrium.
The table below shows critical temperature and pressure for some common substances, together with boiling temperature.
See Triple point for listing of triple point values for common substances.
Critical Temperatures and Pressures Common Substances
| Substance | Critical temperature | Critical pressure | Boiling temperature (1 atm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (°F) | (°C) | (psi), (lb/in2) | (bar) | (°F) | (°C) | |
| Air | -220.94 | -140.52 | 549.08 | 37.858 | - | - |
| Ammonia (NH3) | 270 | 132.4 | 1636 | 112.8 | -27.4 | -33 |
| Argon | -188 | -122 | 705.6 | 48.7 | -302.5 | -185.8 |
| Butane | 305.6 | 152 | 550.4 | 38 | 32 | 0 |
| Carbon-dioxide (CO2) | 87.8 | 31.2 | 1071.6 | 73.8 | -110 | -79 |
| Carbon-monoxide (CO) | -220.5 | -140.3 | 507.5 | 35 | -310 | -190 |
| Chlorine | 291 | 144 | 1118.7 | 77.1 | -29.3 | -34 |
| Decane | 653 | 345 | 301.7 | 20.8 | 345 | 174 |
| Dowtherm A | 465 | 32.1 | ||||
| Ethane | 90.0 | 32.2 | 708 | 48.9 | -127.4 | -88.5 |
| Ethanol (alcohol) | 467 | 242 | 914 | 63 | 173 | 78.4 |
| Ethylether | 381 | 194 | 522 | 36 | 94.2 | 34.6 |
| Ethylene | 48.9 | 9.4 | 735 | 50.7 | -272.6 | -169.2 |
| Fluorine | -200 | -129 | 808.5 | 55.8 | -307 | -188 |
| Helium | -456 | -271 | 33.2 | 2.3 | -452 | -269 |
| Hydrogen (H) | -400 | -240 | 188.2 | 13.0 | -423 | -253 |
| Hydrogen Chloride | 125 | 51.6 | 1198 | 82.7 | -121.1 | -85.1 |
| Isobutane | 274 | 135 | 529.2 | 36.5 | 10.9 | -11.7 |
| Isobutylene | 293 | 145 | 580 | 40.0 | 19.6 | -6.9 |
| Isononane | 590 | 310 | 335.1 | 23.1 | 303 | 151 |
| Methane | -117 | -82.6 | 673.3 | 46.5 | -259 | -162 |
| Nitrogen (N) | -232.6 | -147 | 492.4 | 34.0 | -321 | -195 |
| Nitrous Oxide (N2O) | 97.4 | 36.4 | 1047.6 | 72.3 | -127 | -88.5 |
| Oxygen (O2) | -181.5 | -118.6 | 732 | 50.5 | -297 | -183 |
| Phosgene | 823.2 | 56.8 | 46.9 | 8.3 | ||
| Propane | 206.1 | 96.7 | 617.4 | 42.6 | -44 | -42 |
| Propylbenzene | 689 | 365 | 464.2 | 32 | 319 | 159 |
| Propylene | 198 | 92.4 | 670.3 | 46.3 | -54 | -48 |
| Refrigerants | ||||||
| Undecane | 691 | 366 | 287.2 | 19.8 | 385 | 196 |
| Water | 705 | 374 | 3206.2 | 220.5 | 212 | 100 |
Related Topics
Properties of air, LNG, LPG and other common gases. Pipeline capacities and sizing of relief valves.
Work, heat and energy systems.
Related Documents
Acetone - Thermophysical Properties
Chemical, physical and thermal properties of acetone, also called 2-propanone, dimethyl ketone and pyroacetic acid. Phase diagram included.
Ammonia - Properties at Gas-Liquid Equilibrium Conditions
Figures and tables showing how the properties of liquid and gaseous ammonia changes along the boiling/condensation curve (temperature and pressure between triple point and critical point conditions). An ammonia phase diagram are included.
Ammonia - Specific Heat vs. Temperature and Pressure
Online calculator, figures and tables showing specific heat, CP and CV, of gasous and liquid ammonia at temperatures ranging from -73 to 425°C (-100 to 800°F) at pressure ranging from 1 to 100 bara (14.5 - 1450 psia) - SI and Imperial Units.
Ammonia Gas - Density vs. Temperature and Pressure
Online calculator with figures and tables showing density and specific weight of ammonia for temperatures ranging -50 to 425 °C (-50 to 800 °F) at atmospheric and higher pressure - Imperial and SI Units.
Heavy Water - Thermophysical Properties
Thermodynamic properties of heavy water (D2O) like density, melting temperature, boiling temperature, latent heat of fusion, latent heat of evaporation, critical temperature and more.
The Ideal Gas Law
The relationship between volume, pressure, temperature and quantity of a gas, including definition of gas density.

