Air - Humidity Ratio (original) (raw)
The humidity ratio of moist air can be expressed with
- the mass of water vapor in the humid air - to the mass of dry air, or by
- the partial pressure of vapor in the air - to the partial pressure of the dry air
Humidity Ratio by Mass
Humidity ratio by mass can be expressed as
- the ratio between the actual mass of water vapor present in moist air - to the mass of the dry air
Humidity ratio is normally expressed in kilograms (or pounds) of water vapor per kilogram (or pound) of dry air.
Humidity ratio expressed by mass:
x = mw / ma (1)
where
x = humidity ratio (kgwater/kgdry_air, lbwater/lbdry_air)
mw = mass of water vapor (kg, lb)
ma = mass of dry air (kg, lb)
Humidity Ratio by Vapor Partial Pressure
Based on the Ideal Gas Law the humidity ratio can be expressed as
x = 0.62198 pw / (pa - pw) (2)
where
pw = partial pressure of water vapor in moist air (Pa, psi)
pa = atmospheric pressure of moist air (Pa, psi)
The maximum amount of water vapor in the air is achieved when pw = pws the saturation pressure of water vapor at the actual temperature. (2) can be modified to:
xs = 0.62198 pws / (pa - pws) (3)
where
xs = maximum saturation humidity ratio of air (kgwater/kgair, lbwater/lbdry_air)
pws = saturation pressure of water vapor
The water vapor pressure is small regarding to the atmospheric pressure and the relation between the humidity ratio and the saturation pressure is almost linear.
Note! - be careful with these equations at higher temperatures - as indicated in Temperature and Moisture Holding Capacity of Air.
Maximum specific humidity at some common temperatures:
Air - Humidity Ratio
| Temperature (oC) | Water Vapor Saturation Pressure (Pa) | Maximum SaturationHumidity Ratio- x -(kgw/kga) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 609.9 | 0.003767 |
| 5 | 870 | 0.005387 |
| 10 | 1225 | 0.007612 |
| 15 | 1701 | 0.01062 |
| 20 | 2333 | 0.014659 |
| 25 | 3130 | 0.019826 |
| 30 | 4234 | 0.027125 |
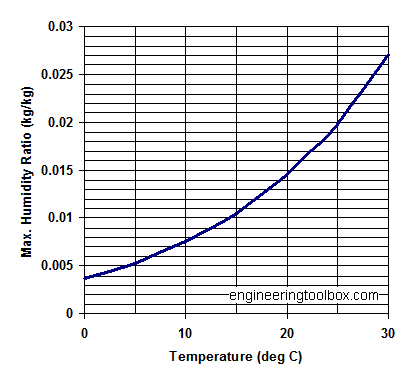
Note that the saturation pressure of water vapor, - and the maximum humidity ratio, increases dramatically with air temperature. This important for the capacity of drying processes.
Example - Humidity Ratio of Moist Air
The humidity ratio for saturated moist air at 20 oC with water vapor partial pressure 2333 Pa at atmospheric pressure of 101325 Pa (1013 mbar, 760 mmHg) can be calculated as:
x = 0. 62198 (2333 Pa) / ((101325 Pa) - (2333 Pa))
= 0.0147 (kg/kg)
= 14.7 (g/kg)
Related Documents
Air - Absolute Humidity
Absolute humidity is the actual mass of water vapor present in the air water vapor mixture.
Air - Drying Force
The drying force of air depends on the air moisture holding capacity and the water surface to air evaporation capacity.
Evaporation from a Water Surface
Evaporation of water from a water surface - like a swimming pool or an open tank - depends on water temperature, air temperature, air humidity and air velocity above the water surface - online calculator.
Latent Heat Flow
Latent heat is the heat when supplied to or removed from air results in a change in moisture content - the temperature of the air is not changed.
Mixing of Humid Air
The change in state wwhen mixing moist air - enthalpy, heat, temperature and specific humidity.