pH - Basic (alkaline) vs. Acidic (original) (raw)
Introduction to pH - the acidic and basic (alkaline) definition.
pH can be viewed as an abbreviation for power of Hydrogen - or more completely, power of the concentration of the Hydrogen ionin a liquid.
The mathematical definition of pH is a bit less intuitive but in general more useful. It says that the pH is equal to to the negative logarithmic value of the Hydrogen ion (H+) concentration, or
pH = -log(H+)
pH can alternatively be defined mathematically as the negative logarithmic value of the Hydroxonium ion (H3O+) concentration. Using the Bronsted-Lowry approach
pH = -log(H3O+)
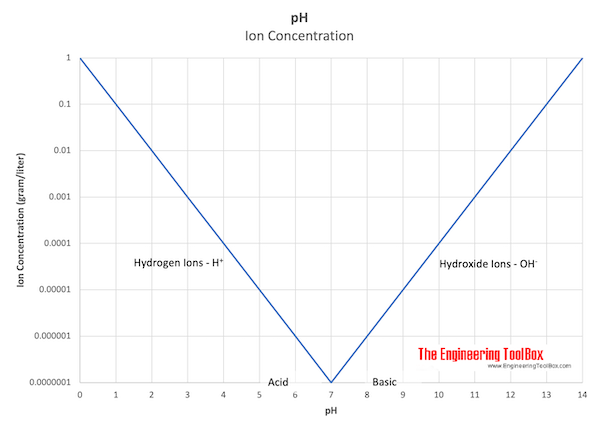
pH values are calculated in powers of 10. The hydrogen ion concentration in a solution with pH 1.0 is 10 times larger than the hydrogen concentration in a solution with pH 2.0. The larger the hydrogen ion concentration - the smaller the pH.
- when the pH is above 7 the solution is basic (alkaline)
- when the pH is below 7 the solution is acidic
In pure neutral water the concentration of hydrogen and hydroxide ions are both 10-7 equivalents per liter.
pH - Ion Concentration
| pH | Ion Concentration (gram equivalent per liter) | Type of Solution |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.0 | Acid Solution - Hydrogen ions - H+ |
| 1 | 0.1 | |
| 2 | 0.01 | |
| 3 | 0.001 | |
| 4 | 0.0001 | |
| 5 | 0.00001 | |
| 6 | 0.000001 | |
| 7 | 0.0000001 | Neutral Solution (pure neutral water) |
| 8 | 0.000001 | Basic (alkaline) Solution - Hydroxide ions - OH- |
| 9 | 0.00001 | |
| 10 | 0.0001 | |
| 11 | 0.001 | |
| 12 | 0.01 | |
| 13 | 0.1 | |
| 14 | 1.0 |
Download and print pH Ion Concentration Chart
Some common Products and their pH Values
pH values in some common products:
pH in Common Products
| Product | pH |
|---|---|
| Battery Acid | 0 |
| HCl in stomach acid | 1 |
| Lemon juice, vinegar | 2-3 |
| Orange juice | 3-4 |
| Acid rain | 4 |
| Black coffee | 5 |
| Urine, saliva | 6 |
| Pure water | 7 |
| Sea water | 8 |
| Baking soda | 9 |
| Ammonia solution | 10-11 |
| Soapy water | 12 |
| Bleach | 13 |
| Oven cleaner | 13-14 |
| Drain cleaner | 14 |
Acid-Base Indicators
pH - Acid-Base Indicators
| Indicator | pH - Range | Color Cange | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acid | Base | ||
| Thymol blue | 1.2 - 2.8 | red | yellow |
| Pentamethoxy red | 1.2 - 2.3 | red - violet | colorless |
| Tropeolin | 1.3 - 3.2 | red | yellow |
| 2,4 - Dinitrophenol | 2.4 - 4.0 | colorless | yellow |
| Methyl yellow | 2.9 - 4.0 | red | yellow |
| Methyl orange | 3.1 - 4.4 | red | orange |
| Congo red | 3.0 - 4.2 | blue-violet | red-orange |
| Bromphenol blue | 3.0 - 4.6 | yellow | blue - violet |
| Tetrabromphenol blue | 3.0 - 4.6 | yellow | blue |
| Alizarin sodium sulfonate | 3.7 - 5.2 | yellow | violet |
| α - Naphthyl red | 3.7 - 5.0 | red | yellow |
| p - Ethoxychrysoidine | 3.5 - 5.5 | red | yellow |
| Bromcresol green | 4.0 - 5.6 | yellow | blue |
| Methyl red | 4.4 - 6.2 | red | yellow |
| Bromcresol purple | 5.2 - 6.8 | yellow | purple |
| Chlorphenol red | 5.4 - 6.8 | yellow | red |
| Bromphenol blue | 6.2 - 7.6 | yellow | blue |
| p - Nitrophenol | 5.0 - 7.0 | colorless | yellow |
| Litmus | 5.0 - 8.0 | red | blue |
| Azolitmin | 5.0 - 8.0 | red | blue |
| Phenol red | 6.4 - 8.0 | yellow | red |
| Neutral red | 6.4 - 8.0 | red | yellow |
| Rosolic acid | 6.8 - 8.0 | yellow | red |
| Cresol red | 7.2 - 8.8 | yellow | red |
| α - Naphtholphthalein | 7.3 - 8.7 | rose | green |
| Tropeolin | 7.6 - 8.9 | yellow | rose - red |
| Thymol blue | 8.0 - 9.6 | yellow | blue |
| Phenolphthalein | 8.0 - 10.0 | colorless | red |
| α - Naphtholbenzein | 9.0 - 11.0 | yellow | blue |
| Thymolphthalein | 9.4 - 10.6 | colorless | blue |
| Nile blue | 10.1 - 11.1 | blue | red |
| Alizarin yellow | 10.0 - 12.0 | yellow | lilac |
| Salicyl yellow | 10.0 - 12.0 | yellow | orange - brown |
| Diazo violet | 10.1 - 12.0 | yellow | violet |
| Tropeolin | 11.0 - 13.0 | yellow | orange - brown |
| Nitramine | 11.0 - 13.0 | colorless | orange - brown |
| Poirrier's blue | 11.0 - 13.0 | blue | violet - pink |
| Trinitrobenzoic acid | 12.0 - 13.4 | colorless | orange - red |
My Short List
Related Topics
Basic engineering data. SI-system, unit converters, physical constants, drawing scales and more.
Engineering related topics like Beaufort Wind Scale, CE-marking, drawing standards and more.
Related Documents
Acid and Base pH Indicators
pH range vs. color change for acid and base indicators - together with pKa and structures of the indicators.
Logarithms
The rules of logarithms - log10 and loge for numbers ranging 1 to 1000.
Strong and Weak Acids and Bases
The most common strong acids and bases, and some examples of weak acids and bases, together with definition of strong and weak acids and bases.