pagesvd - Page-wise singular value decomposition - MATLAB (original) (raw)
Page-wise singular value decomposition
Since R2021b
Syntax
Description
[S](#mw%5Fc7e6d682-10b0-49f8-b1be-9db0cc20f842) = pagesvd([X](#mw%5Fbda08fbd-8a08-4357-ad86-555df3d2f60b)) returns the singular values of each page of a multidimensional array. Each page of the output S(:,:,i) is a column vector containing the singular values of X(:,:,i) in decreasing order. If each page of X is anm-by-n matrix, then the number of singular values returned on each page of S is min(m,n).
[[U](#mw%5Fceb8696c-e787-4a20-8a12-057267840c00),[S](#mw%5Fc7e6d682-10b0-49f8-b1be-9db0cc20f842),[V](#mw%5Fdb01df1e-c826-4b82-aac1-b21424a90b49)] = pagesvd([X](#mw%5Fbda08fbd-8a08-4357-ad86-555df3d2f60b)) computes the singular value decomposition of each page of a multidimensional array. The pages in the output arrays satisfy: U(:,:,i) * S(:,:,i) * V(:,:,i)' = X(:,:,i).
S has the same size as X, and each page ofS is a diagonal matrix with nonnegative singular values in decreasing order. The pages of U and V are unitary matrices.
If X has more than three dimensions, thenpagesvd returns arrays with the same number of dimensions:U(:,:,i,j,k) * S(:,:,i,j,k) * V(:,:,i,j,k)' = X(:,:,i,j,k)
[___] = pagesvd([X](#mw%5Fbda08fbd-8a08-4357-ad86-555df3d2f60b),"econ") produces an economy-size decomposition of the pages of X using either of the previous output argument combinations. If X is anm-by-n-by-p array, then:
m > n— Only the firstncolumns of each page ofUare computed, andShas sizen-by-n-by-p.m = n—pagesvd(X,"econ")is equivalent topagesvd(X).m < n— Only the firstmcolumns of each page ofVare computed, andShas sizem-by-m-by-p.
The economy-size decomposition removes extra rows or columns of zeros from the pages of singular values in S, along with the columns in eitherU or V that multiply those zeros in the expressionU(:,:,i) * S(:,:,i) * V(:,:,i)'. Removing these zeros and columns can improve execution time and reduce storage requirements without compromising the accuracy of the decomposition.
[___] = pagesvd(___,[outputForm](#mw%5F3f7af09c-d961-4021-a954-a24fd0117faa)) specifies the output format for the singular values returned in S. You can use this option with any of the previous input or output argument combinations. Specify"vector" to return each page of S as a column vector, or "matrix" to return each page of S as a diagonal matrix.
Examples
Create two 6-by-6 matrices. Use the cat function to concatenate them along the third dimension into a 6-by-6-by-2 array.
A = magic(6); B = hilb(6); X = cat(3,A,B);
Calculate the singular values of each page by calling pagesvd with one output.
S = S(:,:,1) =
111.0000 50.6802 34.3839 10.1449 5.5985 0.0000
S(:,:,2) =
1.6189
0.2424
0.0163
0.0006
0.0000
0.0000Create two 5-by-5 matrices. Use the cat function to concatenate them along the third dimension into a 5-by-5-by-2 array.
A = magic(5); B = hilb(5); X = cat(3,A,B);
Calculate the singular values of each array page.
s = s(:,:,1) =
65.0000 22.5471 21.6874 13.4036 11.9008
s(:,:,2) =
1.5671
0.2085
0.0114
0.0003
0.0000Perform a complete singular value decomposition on each array page.
U = U(:,:,1) =
-0.4472 -0.5456 -0.5117 -0.1954 -0.4498 -0.4472 -0.4498 0.1954 0.5117 0.5456 -0.4472 -0.0000 0.6325 -0.6325 0.0000 -0.4472 0.4498 0.1954 0.5117 -0.5456 -0.4472 0.5456 -0.5117 -0.1954 0.4498
U(:,:,2) =
-0.7679 0.6019 -0.2142 0.0472 0.0062 -0.4458 -0.2759 0.7241 -0.4327 -0.1167 -0.3216 -0.4249 0.1205 0.6674 0.5062 -0.2534 -0.4439 -0.3096 0.2330 -0.7672 -0.2098 -0.4290 -0.5652 -0.5576 0.3762
S = S(:,:,1) =
65.0000 0 0 0 0 0 22.5471 0 0 0 0 0 21.6874 0 0 0 0 0 13.4036 0 0 0 0 0 11.9008
S(:,:,2) =
1.5671 0 0 0 0
0 0.2085 0 0 0
0 0 0.0114 0 0
0 0 0 0.0003 0
0 0 0 0 0.0000V = V(:,:,1) =
-0.4472 -0.4045 -0.2466 0.6627 0.3693 -0.4472 -0.0056 -0.6627 -0.2466 -0.5477 -0.4472 0.8202 0.0000 0.0000 0.3568 -0.4472 -0.0056 0.6627 0.2466 -0.5477 -0.4472 -0.4045 0.2466 -0.6627 0.3693
V(:,:,2) =
-0.7679 0.6019 -0.2142 0.0472 0.0062 -0.4458 -0.2759 0.7241 -0.4327 -0.1167 -0.3216 -0.4249 0.1205 0.6674 0.5062 -0.2534 -0.4439 -0.3096 0.2330 -0.7672 -0.2098 -0.4290 -0.5652 -0.5576 0.3762
Verify the relation X=U S VH for each array page, within machine precision.
e1 = norm(X(:,:,1) - U(:,:,1)*S(:,:,1)*V(:,:,1)',"fro")
e2 = norm(X(:,:,2) - U(:,:,2)*S(:,:,2)*V(:,:,2)',"fro")
Alternatively, you can use pagemtimes to check the relation for both pages simultaneously.
US = pagemtimes(U,S); USV = pagemtimes(US,"none",V,"ctranspose"); e = max(abs(X - USV),[],"all")
Create two 6-by-6 matrices. Use the cat function to concatenate them along the third dimension into a 6-by-6-by-2 array.
A = magic(6); B = hilb(6); X = cat(3,A,B);
Calculate the SVD of each array page. By default, pagesvd returns each page of singular values as a diagonal matrix when you specify multiple outputs.
U = U(:,:,1) =
-0.4082 0.5574 0.0456 -0.4182 0.3092 0.5000 -0.4082 -0.2312 0.6301 -0.2571 -0.5627 0.0000 -0.4082 0.4362 0.2696 0.5391 0.1725 -0.5000 -0.4082 -0.3954 -0.2422 -0.4590 0.3971 -0.5000 -0.4082 0.1496 -0.6849 0.0969 -0.5766 0.0000 -0.4082 -0.5166 -0.0182 0.4983 0.2604 0.5000
U(:,:,2) =
-0.7487 0.6145 -0.2403 -0.0622 0.0111 -0.0012 -0.4407 -0.2111 0.6977 0.4908 -0.1797 0.0356 -0.3207 -0.3659 0.2314 -0.5355 0.6042 -0.2407 -0.2543 -0.3947 -0.1329 -0.4170 -0.4436 0.6255 -0.2115 -0.3882 -0.3627 0.0470 -0.4415 -0.6898 -0.1814 -0.3707 -0.5028 0.5407 0.4591 0.2716
S = S(:,:,1) =
111.0000 0 0 0 0 0 0 50.6802 0 0 0 0 0 0 34.3839 0 0 0 0 0 0 10.1449 0 0 0 0 0 0 5.5985 0 0 0 0 0 0 0.0000
S(:,:,2) =
1.6189 0 0 0 0 0
0 0.2424 0 0 0 0
0 0 0.0163 0 0 0
0 0 0 0.0006 0 0
0 0 0 0 0.0000 0
0 0 0 0 0 0.0000V = V(:,:,1) =
-0.4082 0.6234 -0.3116 0.2495 0.2511 0.4714 -0.4082 -0.6282 0.3425 0.1753 0.2617 0.4714 -0.4082 -0.4014 -0.7732 -0.0621 -0.1225 -0.2357 -0.4082 0.1498 0.2262 -0.4510 0.5780 -0.4714 -0.4082 0.1163 0.2996 0.6340 -0.3255 -0.4714 -0.4082 0.1401 0.2166 -0.5457 -0.6430 0.2357
V(:,:,2) =
-0.7487 0.6145 -0.2403 -0.0622 0.0111 -0.0012 -0.4407 -0.2111 0.6977 0.4908 -0.1797 0.0356 -0.3207 -0.3659 0.2314 -0.5355 0.6042 -0.2407 -0.2543 -0.3947 -0.1329 -0.4170 -0.4436 0.6255 -0.2115 -0.3882 -0.3627 0.0470 -0.4415 -0.6898 -0.1814 -0.3707 -0.5028 0.5407 0.4591 0.2716
Specify the "vector" option to return each page of singular values as a column vector.
[U,S,V] = pagesvd(X,"vector")
U = U(:,:,1) =
-0.4082 0.5574 0.0456 -0.4182 0.3092 0.5000 -0.4082 -0.2312 0.6301 -0.2571 -0.5627 0.0000 -0.4082 0.4362 0.2696 0.5391 0.1725 -0.5000 -0.4082 -0.3954 -0.2422 -0.4590 0.3971 -0.5000 -0.4082 0.1496 -0.6849 0.0969 -0.5766 0.0000 -0.4082 -0.5166 -0.0182 0.4983 0.2604 0.5000
U(:,:,2) =
-0.7487 0.6145 -0.2403 -0.0622 0.0111 -0.0012 -0.4407 -0.2111 0.6977 0.4908 -0.1797 0.0356 -0.3207 -0.3659 0.2314 -0.5355 0.6042 -0.2407 -0.2543 -0.3947 -0.1329 -0.4170 -0.4436 0.6255 -0.2115 -0.3882 -0.3627 0.0470 -0.4415 -0.6898 -0.1814 -0.3707 -0.5028 0.5407 0.4591 0.2716
S = S(:,:,1) =
111.0000 50.6802 34.3839 10.1449 5.5985 0.0000
S(:,:,2) =
1.6189
0.2424
0.0163
0.0006
0.0000
0.0000V = V(:,:,1) =
-0.4082 0.6234 -0.3116 0.2495 0.2511 0.4714 -0.4082 -0.6282 0.3425 0.1753 0.2617 0.4714 -0.4082 -0.4014 -0.7732 -0.0621 -0.1225 -0.2357 -0.4082 0.1498 0.2262 -0.4510 0.5780 -0.4714 -0.4082 0.1163 0.2996 0.6340 -0.3255 -0.4714 -0.4082 0.1401 0.2166 -0.5457 -0.6430 0.2357
V(:,:,2) =
-0.7487 0.6145 -0.2403 -0.0622 0.0111 -0.0012 -0.4407 -0.2111 0.6977 0.4908 -0.1797 0.0356 -0.3207 -0.3659 0.2314 -0.5355 0.6042 -0.2407 -0.2543 -0.3947 -0.1329 -0.4170 -0.4436 0.6255 -0.2115 -0.3882 -0.3627 0.0470 -0.4415 -0.6898 -0.1814 -0.3707 -0.5028 0.5407 0.4591 0.2716
If you specify one output argument, such as S = pagesvd(X), then pagesvd switches behavior to return each page of singular values as a column vector by default. In that case, you can specify the "matrix" option to return each page of singular values as a diagonal matrix.
Create a 10-by-3 matrix with random integer elements.
Perform both a complete decomposition and an economy-size decomposition on the matrix.
U = 10×10
-0.2554 -0.1828 0.6086 -0.6120 -0.0623 -0.2365 -0.1841 0.0165 -0.2369 -0.0792 -0.3408 0.4291 0.0365 0.1237 -0.2953 0.3040 0.0346 -0.3966 -0.3014 -0.5041 -0.3018 -0.3274 -0.6272 -0.0847 -0.3313 -0.3920 -0.2374 -0.2006 -0.1896 0.0717 -0.3560 -0.2919 0.3996 0.7531 -0.0136 -0.1963 -0.1046 0.0518 -0.0521 0.0788 -0.3711 -0.0109 -0.1957 -0.0519 0.8784 0.0025 -0.0413 -0.1224 -0.1273 -0.1289 -0.1298 -0.5635 -0.0331 -0.0842 -0.0685 0.7933 -0.1005 0.0004 -0.0259 0.1119 -0.2002 -0.2327 -0.0099 -0.0782 -0.0595 -0.0962 0.9398 -0.0274 -0.0524 0.0117 -0.3278 0.1769 -0.1847 -0.0238 -0.0987 0.0714 -0.0078 0.8775 -0.1186 -0.1662 -0.4273 0.0534 0.0145 -0.1222 -0.0872 -0.0131 -0.0467 -0.0828 0.8772 -0.1140 -0.3408 0.4291 0.0365 -0.0661 -0.0416 0.1247 0.0203 -0.0831 -0.1055 0.8114
S = 10×3
10.9594 0 0 0 4.6820 0 0 0 3.4598 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
V = 3×3
-0.6167 0.3011 0.7274 -0.6282 0.3686 -0.6852 -0.4744 -0.8795 -0.0382
[Ue,Se,Ve] = pagesvd(X,"econ")
Ue = 10×3
-0.2554 -0.1828 0.6086 -0.3408 0.4291 0.0365 -0.3018 -0.3274 -0.6272 -0.3560 -0.2919 0.3996 -0.3711 -0.0109 -0.1957 -0.1298 -0.5635 -0.0331 -0.2002 -0.2327 -0.0099 -0.3278 0.1769 -0.1847 -0.4273 0.0534 0.0145 -0.3408 0.4291 0.0365
Se = 3×3
10.9594 0 0 0 4.6820 0 0 0 3.4598
Ve = 3×3
-0.6167 0.3011 0.7274 -0.6282 0.3686 -0.6852 -0.4744 -0.8795 -0.0382
With the economy-size decomposition, pagesvd only calculates the first 3 columns of Ue, and Se is 3-by-3.
Input Arguments
Input array, specified as a matrix or multidimensional array.
Data Types: single | double
Complex Number Support: Yes
Output format of singular values, specified as one of these values:
"vector"— Each page ofSis a column vector. This is the default behavior when you specify one output, as inS = pagesvd(X)."matrix"— Each page ofSis a diagonal matrix. This is the default behavior when you specify multiple outputs, as in[U,S,V] = pagesvd(X).
Example: [U,S,V] = pagesvd(X,"vector") returns the pages ofS as column vectors instead of diagonal matrices.
Example: S = pagesvd(X,"matrix") returns the pages ofS as diagonal matrices instead of column vectors.
Data Types: char | string
Output Arguments
Left singular vectors, returned as a multidimensional array. Each pageU(:,:,i) is a matrix whose columns are the left singular vectors ofX(:,:,i).
- For an
m-by-nmatrixX(:,:,i)withm > n, the economy-size decompositionpagesvd(X,"econ")computes only the firstncolumns of each page ofU. In this case, the columns ofU(:,:,i)are orthogonal andU(:,:,i)is anm-by-nmatrix that satisfies UHU=In. - Otherwise,
pagesvd(X)returns each pageU(:,:,i)as anm-by-munitary matrix satisfying UUH=UHU=Im. The columns ofU(:,:,i)that correspond to nonzero singular values form a set of orthonormal basis vectors for the range ofX(:,:,i).
Different machines and releases of MATLAB® can produce different singular vectors that are still numerically accurate. Corresponding columns in U(:,:,i) andV(:,:,i) can flip their signs, since this does not affect the value of the expression U(:,:,i) * S(:,:,i) * V(:,:,i)'.
Singular values, returned as a multidimensional array. Each pageS(:,:,i) contains the singular values ofX(:,:,i) in decreasing order.
For an m-by-n matrixX(:,:,i):
- The economy-size decomposition
[U,S,V] = pagesvd(X,"econ")returnsS(:,:,i)as a square matrix of ordermin([m,n]). - The complete decomposition
[U,S,V] = pagesvd(X)returnsSwith the same size asX.
Additionally, the singular values on each page of S are returned as column vectors or diagonal matrices depending on how you callpagesvd and whether you specify theoutputForm option:
- If you call
pagesvdwith one output or specify the"vector"option, then each page ofSis a column vector. - If you call
pagesvdwith multiple outputs or specify the"matrix"option, then each page ofSis a diagonal matrix.
Right singular vectors, returned as a multidimensional array. Each pageV(:,:,i) is a matrix whose columns are the right singular vectors of X(:,:,i).
- For an
m-by-nmatrixX(:,:,i)withm < n, the economy-size decompositionpagesvd(X,"econ")computes only the firstmcolumns of each page ofV. In this case, the columns ofV(:,:,i)are orthogonal andV(:,:,i)is ann-by-mmatrix that satisfies VHV=Im. - Otherwise,
pagesvd(X)returns each pageV(:,:,i)as ann-by-nunitary matrix satisfying VVH=VHV=In. The columns ofV(:,:,i)that do_not_ correspond to nonzero singular values form a set of orthonormal basis vectors for the null space ofX(:,:,i).
Different machines and releases of MATLAB can produce different singular vectors that are still numerically accurate. Corresponding columns in U(:,:,i) andV(:,:,i) can flip their signs, since this does not affect the value of the expression U(:,:,i) * S(:,:,i) * V(:,:,i)'.
More About
Page-wise functions like pagesvd operate on 2-D matrices that have been arranged into a multidimensional array. For example, the elements in the third dimension of a 3-D array are commonly called pages because they stack on top of each other like pages in a book. Each page is a matrix that the function operates on.
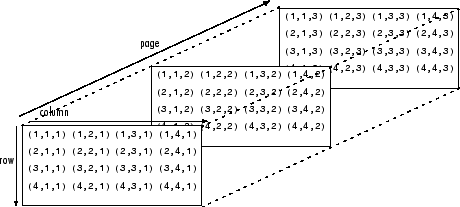
You can also assemble a collection of 2-D matrices into a higher dimensional array, like a 4-D or 5-D array, and in these cases pagesvd still treats the fundamental unit of the array as a 2-D matrix that the function operates on, such asX(:,:,i,j,k,l).
The cat function is useful for assembling a collection of matrices into a multidimensional array, and the zeros function is useful for preallocating a multidimensional array.
Tips
- Results obtained using
pagesvdare numerically equivalent to computing the singular value decomposition of each of the same matrices in afor-loop. However, the two results might differ slightly due to floating-point round-off error.
Extended Capabilities
The pagesvd function supports GPU array input with these usage notes and limitations:
- The row and column sizes of the input array must not be larger than 32.
For more information, see Run MATLAB Functions on a GPU (Parallel Computing Toolbox).
Version History
Introduced in R2021b