Sequence variation in SORL1 and dementia risk in Swedes (original) (raw)
Abstract
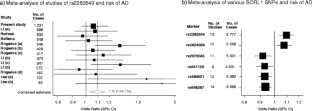
The gene encoding the neuronal sortilin-related receptor SORL1 has been claimed to be associated with Alzheimer's disease (AD) by independent groups and across various human populations. We evaluated six genetic markers in SORL1 in a sample of 1,558 Swedish dementia cases (including 1,270 AD cases) and 2,179 controls. For both single-marker-based and haplotype-based analyses, we found no strong support for SORL1 as a dementia or AD risk-modifying gene in our sample in isolation nor did we observe association with AD/dementia-related traits, including cerebrospinal fluid β-amyloid1–42, tau levels, or age at onset. However, meta-analyses of markers in this study together with previously published studies on SORL1 encompassing in excess of 13,000 individuals does suggest significant association with AD (best odds ratio = 1.097; 95% confidence interval = 1.038–1.158, p = 0.001). All six markers were significant in meta-analyses and it is notable that they occur in two distinct linkage disequilibrium blocks. These data are consistent with either allelic heterogeneity or the existence of as yet untested functional variants and these will be important considerations in further attempts to evaluate the importance of sequence variation in SORL1 with AD risk.
Access this article
Subscribe and save
- Starting from 10 chapters or articles per month
- Access and download chapters and articles from more than 300k books and 2,500 journals
- Cancel anytime View plans
Buy Now
Price excludes VAT (USA)
Tax calculation will be finalised during checkout.
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Fig. 1
References
- Strittmatter WJ, Saunders AM, Schmechel D, Pericak-Vance M, Enghild J, Salvesen GS, Roses AD (1993) Apolipoprotein E: high-avidity binding to beta-amyloid and increased frequency of type 4 allele in late-onset familial Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90:1977–1981
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Rogaeva E, Meng Y, Lee JH, Gu Y, Kawarai T et al (2007) The neuronal sortilin-related receptor SORL1 is genetically associated with Alzheimer disease. Nat Genet 39:168–177
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Minster RL, DeKosky ST, Kamboh MI (2008) No association of SORL1 SNPs with Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett 440:190–192
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Bettens K, Brouwers N, Engelborghs S, De Deyn PP, Van Broeckhoven C, Sleegers K (2008) SORL1 is genetically associated with increased risk for late-onset Alzheimer disease in the Belgian population. Hum Mutat 29:769–770
Article PubMed Google Scholar - Webster JA, Myers AJ, Pearson JV, Craig DW, Hu-Lince D et al (2008) Sorl1 as an Alzheimer's disease predisposition gene? Neurodegener Dis 5:60–64
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Li Y, Rowland C, Catanese J, Morris J, Lovestone S, O'Donovan MC, Goate A, Owen M, Williams J, Grupe A (2008) SORL1 variants and risk of late-onset Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Dis 29:293–296
Article PubMed Google Scholar - Lee JH, Cheng R, Schupf N, Manly J, Lantigua R, Stern Y, Rogaeva E, Wakutani Y, Farrer L, St George-Hyslop P, Mayeux R (2007) The association between genetic variants in SORL1 and Alzheimer disease in an urban, multiethnic, community-based cohort. Arch Neurol 64:501–506
Article PubMed Google Scholar - Lichtenstein P, De Faire U, Floderus B, Svartengren M, Svedberg P, Pedersen NL (2002) The Swedish Twin Registry: a unique resource for clinical, epidemiological and genetic studies. J Intern Med 252:184–205
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Pedersen NL, Lichtenstein P, Svedberg P (2002) The Swedish Twin Registry in the third millennium. Twin Res 5:427–432
Article PubMed Google Scholar - Katzov H, Chalmers K, Palmgren J, Andreasen N, Johansson B, Cairns NJ, Gatz M, Wilcock GK, Love S, Pedersen NL, Brookes AJ, Blennow K, Kehoe PG, Prince JA (2004) Genetic variants of ABCA1 modify Alzheimer disease risk and quantitative traits related to beta-amyloid metabolism. Hum Mutat 23:358–367
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Andreasen N, Minthon L, Clarberg A, Davidsson P, Gottfries J, Vanmechelen E, Vanderstichele H, Winblad B, Blennow K (1999) Sensitivity, specificity, and stability of CSF-tau in AD in a community-based patient sample. Neurology 53:1488–1494
CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Vanmechelen E, Vanderstichele H (1998) Towards an earlier diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. J Biotechnol 66:229–231
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Blennow K, Wallin A, Agren H, Spenger C, Siegfried J, Vanmechelen E (1995) Tau protein in cerebrospinal fluid: a biochemical marker for axonal degeneration in Alzheimer disease? Mol Chem Neuropathol 26:231–245
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Carey V, Zeger SL, Diggle P (1993) Modelling multivariate binary data with alternating logistic regressions. Biometrika 80:517–526
Article Google Scholar - Jansson M, Gatz M, Berg S, Johansson B, Malmberg B, McClearn GE, Schalling M, Pedersen NL (2003) Association between depressed mood in the elderly and a 5-HTR2A gene variant. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 120B:79–84
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ (2005) Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 21:263–265
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Prince JA, Zetterberg H, Andreasen N, Marcusson J, Blennow K (2004) APOE epsilon4 allele is associated with reduced cerebrospinal fluid levels of Abeta42. Neurology 62:2116–2118
CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Bertram L, McQueen MB, Mullin K, Blacker D, Tanzi RE (2007) Systematic meta-analyses of Alzheimer disease genetic association studies: the AlzGene database. Nat Genet 39:17–23
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Dixon AL, Liang L, Moffatt MF, Chen W, Heath S, Wong KC, Taylor J, Burnett E, Gut I, Farrall M, Lathrop GM, Abecasis GR, Cookson WO (2007) A genome-wide association study of global gene expression. Nat Genet 39:1202–1207
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Myers AJ, Gibbs JR, Webster JA, Rohrer K, Zhao A et al (2007) A survey of genetic human cortical gene expression. Nat Genet 39:1494–1499
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Reiman EM, Webster JA, Myers AJ, Hardy J, Dunckley T et al (2007) GAB2 alleles modify Alzheimer's risk in APOE epsilon4 carriers. Neuron 54:713–720
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for the generous funding from the US National Institutes of Health (grants AG028555, AG08724, and AG08861) and the Swedish Medical Research Council (grant 2007-2722).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- Department of Psychology, University of California at Riverside, Riverside, CA, 92521, USA
Chandra A. Reynolds - Department of Medical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Karolinska Institutet, Nobels väg 12A, 171 77, Stockholm, Sweden
Mun-Gwan Hong, Ulrika K. Eriksson, Margaret Gatz, Nancy L. Pedersen, Anna M. Bennet & Jonathan A. Prince - Institute of Neuroscience and Physiology, Sahlgrenska Academy at University of Gothenburg, 431 80, Mölndal, Sweden
Kaj Blennow - Department of Psychology, University of Gothenburg, 405 30, Gothenburg, Sweden
Boo Johansson - Institute of Gerontology, School of Health Sciences, Jönköping University, 551 11, Jönköping, Sweden
Bo Malmberg & Stig Berg - Department of Psychology, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA, 90089-1061, USA
Margaret Gatz & Nancy L. Pedersen
Authors
- Chandra A. Reynolds
- Mun-Gwan Hong
- Ulrika K. Eriksson
- Kaj Blennow
- Boo Johansson
- Bo Malmberg
- Stig Berg
- Margaret Gatz
- Nancy L. Pedersen
- Anna M. Bennet
- Jonathan A. Prince
Corresponding author
Correspondence toJonathan A. Prince.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reynolds, C.A., Hong, MG., Eriksson, U.K. et al. Sequence variation in SORL1 and dementia risk in Swedes.Neurogenetics 11, 139–142 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-009-0210-4
- Received: 15 April 2009
- Accepted: 21 July 2009
- Published: 04 August 2009
- Issue date: February 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-009-0210-4