Resveratrol rescues mutant polyglutamine cytotoxicity in nematode and mammalian neurons (original) (raw)
- Brief Communication
- Published: 27 March 2005
- Margarita Arango1,
- Salima Abderrahmane1,
- Emmanuel Lambert1,
- Cendrine Tourette1,
- Hélène Catoire1 &
- …
- Christian Néri1
Nature Genetics volume 37, pages 349–350 (2005)Cite this article
- 1866 Accesses
- 413 Citations
- 10 Altmetric
- Metrics details
A Corrigendum to this article was published on 01 May 2005
Abstract
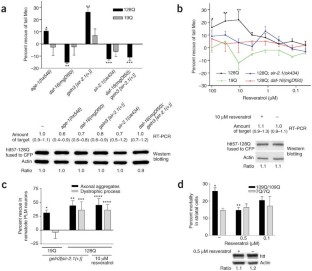
We report that Sir2 activation through increased sir-2.1 dosage or treatment with the sirtuin activator resveratrol specifically rescued early neuronal dysfunction phenotypes induced by mutant polyglutamines in transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans. These effects are dependent on daf-16 (Forkhead). Additionally, resveratrol rescued mutant polyglutamine–specific cell death in neuronal cells derived from HdhQ111 knock-in mice. We conclude that Sir2 activation may protect against mutant polyglutamines.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Additional access options:
Figure 1: Rescue of mutant polyQ toxicity by increased sirtuin activity in nematode and mammalian neurons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
- Morley, J.F., Brignull, H.R., Weyers, J.J. & Morimoto, R.I. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 10417–10422 (2002).
Article Google Scholar - Ogg, S. et al. Nature 389, 994–999 (1997).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Tissenbaum, H.A. & Guarente, L. Nature 410, 227–230 (2001).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Wood, J.G. et al. Nature 430, 686–689 (2004).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Brunet, A. et al. Science 303, 2011–2015 (2004).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Motta, M.C. et al. Cell 116, 551–563 (2004).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Howitz, K.T. et al. Nature 425, 191–196 (2003).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Araki, T., Sasaki, Y. & Milbrandt, J. Science 305, 1010–1013 (2004).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Rubinsztein, D.C. Trends Genet. 18, 202–209 (2002).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Levine, M.S., Cepeda, C., Hickey, M.A., Fleming, S.M. & Chesselet, M.F. Trends Neurosci. 27, 691–697 (2004).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Trettel, F. et al. Hum. Mol. Genet. 9, 2799–2809 (2000).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Fulco, M. et al. Mol. Cell 12, 51–62 (2003).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Murphy, C.T. et al. Nature 424, 277–283 (2003).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Lee, S.S., Kennedy, S., Tolonen, A.C. & Ruvkun, G. Science 300, 644–647 (2003).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Cohen, H.Y. et al. Science 305, 390–392 (2004).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale, the Cure Huntington's Disease Initiative of the High Q Foundation and the Association France Huntington. J.A.P. is supported by a postdoctoral fellowship from the Cure Huntington's Disease Initiative. M.A. is supported by a doctoral fellowship from the Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale and the Région Ile-de-France. H.C. is supported by a doctoral fellowship from the Ministère de la Recherche.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale, Avenir Group, Laboratory of Genomic Biology, Centre Paul Broca, Paris, 75014, France
J Alex Parker, Margarita Arango, Salima Abderrahmane, Emmanuel Lambert, Cendrine Tourette, Hélène Catoire & Christian Néri
Authors
- J Alex Parker
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Margarita Arango
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Salima Abderrahmane
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Emmanuel Lambert
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Cendrine Tourette
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Hélène Catoire
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar - Christian Néri
You can also search for this author inPubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence toChristian Néri.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parker, J., Arango, M., Abderrahmane, S. et al. Resveratrol rescues mutant polyglutamine cytotoxicity in nematode and mammalian neurons.Nat Genet 37, 349–350 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1534
- Received: 22 October 2004
- Accepted: 17 February 2005
- Published: 27 March 2005
- Issue Date: 01 April 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1534