Mutations in SEPN1 cause congenital muscular dystrophy with spinal rigidity and restrictive respiratory syndrome (original) (raw)
- Brief Communication
- Published: 20 August 2001
- Nathalie Petit1,
- Céline Jaillard1,
- Martin Brockington2,
- Susana Quijano Roy3,
- Luciano Merlini4,
- Norma Romero1,
- Brigitte Estournet3,
- Isabelle Desguerre5,
- Denys Chaigne6,
- Francesco Muntoni2,
- Haluk Topaloglu7 &
- …
- Pascale Guicheney1
Nature Genetics volume 29, pages 17–18 (2001)Cite this article
- 1777 Accesses
- 336 Citations
- 3 Altmetric
- Metrics details
Abstract
One form of congenital muscular dystrophy, rigid spine syndrome (MIM 602771), is a rare neuromuscular disorder characterized by early rigidity of the spine and respiratory insufficiency. A locus on 1p35–36 (RSMD1) was recently found to segregate with rigid spine muscular dystrophy 1 (ref. 1). Here we refine the locus and find evidence of linkage disequilibrium associated with SEPN1, which encodes the recently described selenoprotein N (ref. 2). Our identification and analysis of mutations in SEPN1 is the first description of a selenoprotein implicated in a human disease.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Additional access options:
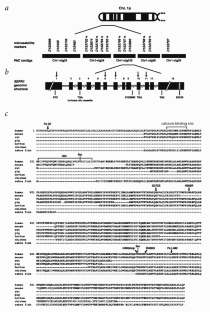
Figure 1: a, PAC sequences were assembled into contigs by the Sanger centre.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
- Moghadaszadeh, B. et al. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 62, 1439–1445 (1998).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Lescure, A., Gautheret, D., Carbon, P. & Krol, A. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 38147–38154 (1999).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Flanigan, K.M. et al. Ann. Neurol. 47, 152–161 (2000).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Lamand, M.C.R. Acad. Sci. Hebd. Sciences Acad. Sci. D. 270, 417–420 (1970).
CAS Google Scholar - Oldfield, J.E. Biol. Trace. Elem. Res. 20, 23–29 (1989).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Ge, K., Xue, A., Bai, J. & Wang, S. Virchows Arch. A. Pathol. Anat. Histopathol. 401, 1–15 (1983).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Berry, M.J., Banu, L., Harney, J.W. & Larsen, P.R. EMBO J. 12, 3315–3322 (1993).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Walczak, R., Westhof, E., Carbon, P. & Krol, A. RNA 2, 367–379 (1996).
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Gu, Q.P. et al. Gene 193, 187–196 (1997).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Holben, D.H. & Smith, A.M. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 99, 836–843 (1999).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Flohe, L., Andreesen, J.R., Brigelius-Flohe, R., Maiorino, M. & Ursini, F. IUBMB Life 49, 411–420 (2000).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Zhong, L., Arner, E.S. & Holmgren, A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 5854–5859 (2000).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Tomé, F.M.S., Guicheney, P. & Fardeau, M. Neuromuscular disorders: Clinical and molecular genetics (ed. Emery, A.E.H.) 21–57 (John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, Sussex, England, 1998).
Google Scholar - Merlini, L., Granata, C., Ballestrazzi, A. & Marini, M.L. J. Child. Neurol. 4, 274–282 (1989).
Article CAS Google Scholar - Moghadaszadeh, B. et al. Neuromuscul. Disord. 9, 376–382 (1999).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Acknowledgements
We thank the patients and their families for their participation; K. Schwartz, M. Fiszman, F. Tomé and M. Fardeau, for continuous support and constructive discussions; A. Lescure, V. Allamand and U. Wewer for comments and suggestions on the manuscript; G. Boccara, M. Bonay, E. Leguern, B. Riou and the AFM BTR for providing human tissues. This work was supported by funds from the Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale (INSERM), Association Française contre les Myopathies (AFM), the European Commission and a Muscular Dystrophy Campaign Grant. B.M. was supported by grants from La Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (FRM) and La Fondation Bettencourt Schueller.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- INSERM U523, Institut de Myologie, Groupe Hospitalier Pitié-Salpêtrière, 47 boulevard de l'Hôpital, Paris, 75651 CEDEX 13, France
Behzad Moghadaszadeh, Nathalie Petit, Céline Jaillard, Norma Romero & Pascale Guicheney - Department of Paediatrics and Neonatal Medicine, Imperial College School of Medicine, Hammersmith Hospital, London, UK
Martin Brockington & Francesco Muntoni - Hôpital Raymond Poincaré, Garches, France
Susana Quijano Roy & Brigitte Estournet - Rizzoli Orthopedic Institute, Bologna, Italy
Luciano Merlini - Service de Neuropédiatrie, Hôpital Saint-Vincent-de-Paul, Paris, France
Isabelle Desguerre - Clinique Sainte Odile, Strasbourg, France
Denys Chaigne - Department of Paediatric Neurology, Hacettepe Children's Hospital, Ankara, Turkey
Haluk Topaloglu
Authors
- Behzad Moghadaszadeh
- Nathalie Petit
- Céline Jaillard
- Martin Brockington
- Susana Quijano Roy
- Luciano Merlini
- Norma Romero
- Brigitte Estournet
- Isabelle Desguerre
- Denys Chaigne
- Francesco Muntoni
- Haluk Topaloglu
- Pascale Guicheney
Corresponding author
Correspondence toPascale Guicheney.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moghadaszadeh, B., Petit, N., Jaillard, C. et al. Mutations in SEPN1 cause congenital muscular dystrophy with spinal rigidity and restrictive respiratory syndrome.Nat Genet 29, 17–18 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng713
- Received: 28 February 2001
- Accepted: 26 June 2001
- Published: 20 August 2001
- Issue date: September 2001
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng713