In silico method for inferring genotypes in pedigrees (original) (raw)
- Brief Communication
- Published: 20 August 2006
Nature Genetics volume 38, pages 1002–1004 (2006)Cite this article
- 877 Accesses
- 126 Citations
- 7 Altmetric
- Metrics details
Abstract
Our genotype inference method combines sparse marker data from a linkage scan and high-resolution SNP genotypes for several individuals to infer genotypes for related individuals. We illustrate the method's utility by inferring over 53 million SNP genotypes for 78 children in the Centre d'Etude du Polymorphisme Humain families. The method can be used to obtain high-density genotypes in different family structures, including nuclear families commonly used in complex disease gene mapping studies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Additional access options:
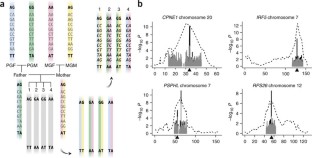
Figure 1: Genotype inference.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
- Matise, T.C. et al. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 73, 271–284 (2003).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - International HapMap Consortium. Nature 426, 789–796 (2003).
- The International HapMap Consortium. Nature 437, 1299–1320 (2005).
- Gunderson, K.L., Steemers, F.J., Lee, G., Mendoza, L.G. & Chee, M.S. Nat. Genet. 37, 549–554 (2005).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Syvanen, A.C. Nat. Genet. 37, S5–10 (2005).
Article PubMed Google Scholar - Matsuzaki, H. et al. Nat. Methods 1, 109–111 (2004).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Sobel, E. & Lange, K. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 58, 1323–1337 (1996).
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Abecasis, G.R., Cherny, S.S., Cookson, W.O. & Cardon, L.R. Nat. Genet. 30, 97–101 (2002).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Kruglyak, L., Daly, M.J., Reeve-Daly, M.P. & Lander, E.S. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 58, 1347–1363 (1996).
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - S.A.G.E. Statistical Analysis for Genetic Epidemiology (Statistical Solutions, Cork, Ireland, 2003).
- Gudbjartsson, D.F., Jonasson, K., Frigge, M.L. & Kong, A. Nat. Genet. 25, 12–13 (2000).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Morley, M. et al. Nature 430, 743–747 (2004).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar - Abecasis, G.R., Cardon, L.R. & Cookson, W.O. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 66, 279–292 (2000).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Abecasis, G.R., Cookson, W.O. & Cardon, L.R. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 8, 545–551 (2000).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Acknowledgements
We thank J. Devlin and M. Morley for technical assistance, M. Boehnke and R. Spielman for discussion and critical reading of the manuscript. This work was supported by grants from the US National Institutes of Health to G.R.A. and V.G.C.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- Department of Pediatrics, University of Pennsylvania, 3516 Civic Center Blvd., Philadelphia, 19104, Pennsylvania, USA
Joshua T Burdick & Vivian G Cheung - Department of Biostatistics and Center for Statistical Genetics, University of Michigan, 1420 Washington Heights, Ann Arbor, 48109-2029, Michigan, USA
Wei-Min Chen & Gonçalo R Abecasis - Department of Genetics, University of Pennsylvania, 3516 Civic Center Blvd., Philadelphia, 19104, Pennsylvania, USA
Vivian G Cheung
Authors
- Joshua T Burdick
- Wei-Min Chen
- Gonçalo R Abecasis
- Vivian G Cheung
Corresponding author
Correspondence toVivian G Cheung.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burdick, J., Chen, WM., Abecasis, G. et al. In silico method for inferring genotypes in pedigrees.Nat Genet 38, 1002–1004 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1863
- Received: 19 May 2006
- Accepted: 20 July 2006
- Published: 20 August 2006
- Issue Date: 01 September 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1863