GitHub - LieberInstitute/HumanPilot: Spatial Transcriptomics human DLPFC pilot study part of the spatialLIBD project (original) (raw)
HumanPilot 
Welcome to the spatialLIBD project! It is composed of the HumanPilotdescribed here as well as:
- a shiny web application that we are hosting atspatial.libd.org/spatialLIBD/that can handle alimited set of concurrent users,
- a Bioconductor package atbioconductor.org/packages/spatialLIBD(or from here) that lets you analyze the data and run a local version of our web application (with our data or yours),
- and a research articlewith the scientific knowledge we drew from this dataset. The analysis code for our project is availablehere that you are looking at right now. The high quality figures for the manuscript are available throughFigshare.
The web application allows you to browse the LIBD human dorsolateral pre-frontal cortex (DLPFC) spatial transcriptomics data generated with the 10x Genomics Visium platform. Through the R/Bioconductor package you can also download the data as well as visualize your own datasets using this web application. Please check themanuscript or bioRxiv pre-printfor more details about this project.
If you tweet about this website, the data or the R package please use the #spatialLIBD hashtag. You can find previous tweets that way as shownhere. Thank you
Study design
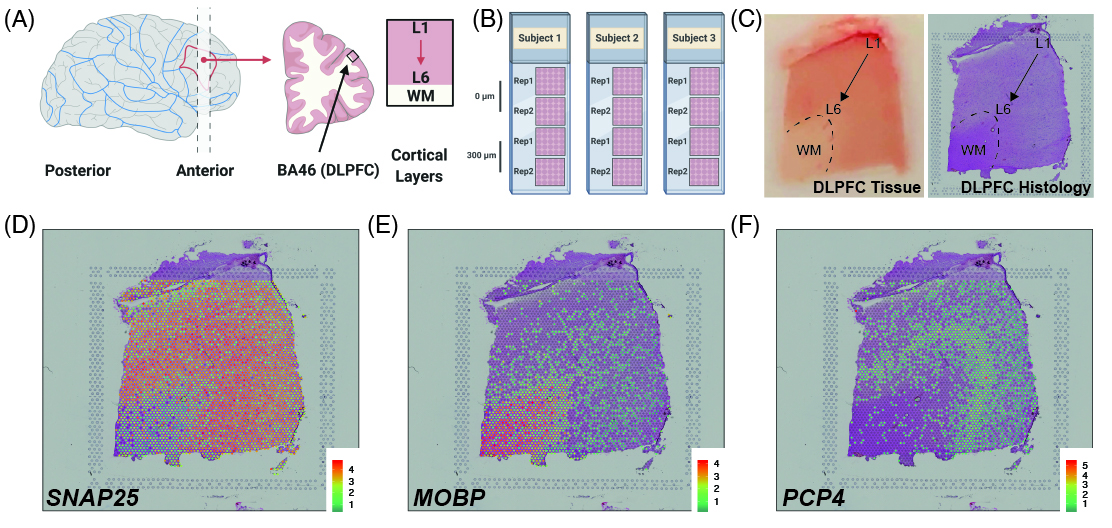
As a quick overview, the data presented here is from portion of the DLPFC that spans six neuronal layers plus white matter (A) for a total of three subjects with two pairs of spatially adjacent replicates (B). Each dissection of DLPFC was designed to span all six layers plus white matter (C). Using this web application you can explore the expression of known genes such as SNAP25 (D, a neuronal gene),MOBP (E, an oligodendrocyte gene), and known layer markers from mouse studies such as PCP4 (F, a known layer 5 marker gene).
This web application was built such that we could annotate the spots to layers as you can see under the spot-level data tab. Once we annotated each spot to a layer, we compressed the information by a pseudo-bulking approach into layer-level data. We then analyzed the expression through a set of models whose results you can also explore through this web application. Finally, you can upload your own gene sets of interest as well as layer enrichment statistics and compare them with our LIBD Human DLPFC Visium dataset.
If you are interested in running this web application locally, you can do so thanks to the spatialLIBD R/Bioconductor package that powers this web application as shown below.
Run this web application locally
spatialLIBD::run_app()
You will have more control about the length of the
session and memory usage.
You could also use this function to visualize your
own data given some requirements described
in detail in the package vignette documentation
at http://research.libd.org/spatialLIBD/.
Shiny website mirrors
- Main shiny application website(note that the link must have a trailing slash
/for it to work) - Shinyapps This version has less RAM memory but is typically deployed using the latest version of
spatialLIBD.
Introductory material
If you prefer to watch a video overview of the HumanPilot project, check the following journal club presentation of the main results.
You might also be interested in the explainer video and companion blog postas well as the original Feb 29, 2020 blog postfrom when we first made this project public.
R/Bioconductor package
The spatialLIBD package contains functions for:
- Accessing the spatial transcriptomics data from the LIBD Human Pilot project (code on GitHub) generated with the Visium platform from 10x Genomics. The data is retrieved fromBioconductor’s
ExperimentHub. - Visualizing the spot-level spatial gene expression data and clusters.
- Inspecting the data interactively either on your computer or throughspatial.libd.org/spatialLIBD/.
For more details, please check the documentation website or the Bioconductor package landing pagehere.
Installation instructions
Get the latest stable R release fromCRAN. Then install spatialLIBD using from Bioconductor the following code:
if (!requireNamespace("BiocManager", quietly = TRUE)) { install.packages("BiocManager") }
BiocManager::install("spatialLIBD")
If you want to use the development version of spatialLIBD, you will need to use the R version corresponding to the current Bioconductor-devel branch as described in more detail on theBioconductor website. Then you can install spatialLIBD from GitHub using the following command.
BiocManager::install("LieberInstitute/spatialLIBD")
Access the data
Through the spatialLIBD package you can access the processed data in it’s final R format. However, we also provide a table of links so you can download the raw data we received from 10x Genomics.
Processed data
Using spatialLIBD you can access the Human DLPFC spatial transcriptomics data from the 10x Genomics Visium platform. For example, this is the code you can use to access the layer-level data. For more details, check the help file for fetch_data().
Load the package
library("spatialLIBD")
Download the spot-level data
spe <- fetch_data(type = "spe")
This is a SpatialExperiment object
spe #> class: SpatialExperiment #> dim: 33538 47681 #> metadata(0): #> assays(2): counts logcounts #> rownames(33538): ENSG00000243485 ENSG00000237613 ... ENSG00000277475 #> ENSG00000268674 #> rowData names(9): source type ... gene_search is_top_hvg #> colnames(47681): AAACAACGAATAGTTC-1 AAACAAGTATCTCCCA-1 ... #> TTGTTTCCATACAACT-1 TTGTTTGTGTAAATTC-1 #> colData names(69): sample_id Cluster ... array_row array_col #> reducedDimNames(6): PCA TSNE_perplexity50 ... TSNE_perplexity80 #> UMAP_neighbors15 #> mainExpName: NULL #> altExpNames(0): #> spatialCoords names(2) : pxl_col_in_fullres pxl_row_in_fullres #> imgData names(4): sample_id image_id data scaleFactor
Note the memory size
lobstr::obj_size(spe) #> 2.04 GB
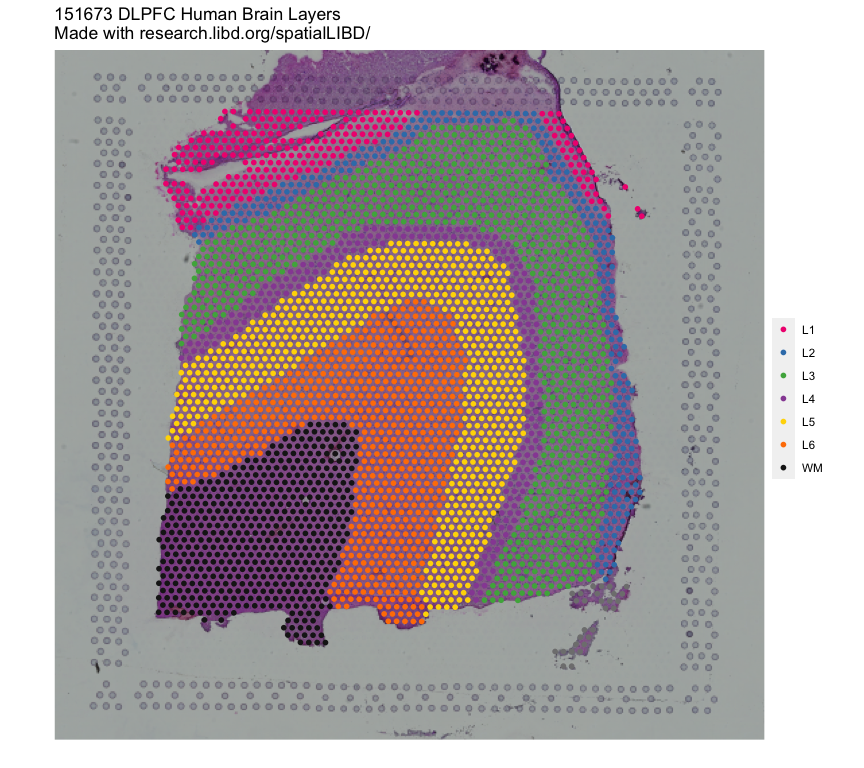
Remake the logo image with histology information
vis_clus( spe = spe, clustervar = "spatialLIBD", sampleid = "151673", colors = libd_layer_colors, ... = " DLPFC Human Brain Layers\nMade with research.libd.org/spatialLIBD/" )
Raw data
You can access all the raw data throughGlobus (jhpce#HumanPilot10x). Furthermore, below you can find the links to the raw data we received from 10x Genomics.
| SampleID | h5_filtered | h5_raw | image_full | image_hi | image_lo | loupe | HTML_report |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 151507 | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | GitHub |
| 151508 | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | GitHub |
| 151509 | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | GitHub |
| 151510 | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | GitHub |
| 151669 | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | GitHub |
| 151670 | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | GitHub |
| 151671 | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | GitHub |
| 151672 | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | GitHub |
| 151673 | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | GitHub |
| 151674 | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | GitHub |
| 151675 | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | GitHub |
| 151676 | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | AWS | GitHub |
Citation
Below is the citation output from using citation('spatialLIBD') in R. Please run this yourself to check for any updates on how to citespatialLIBD.
citation('spatialLIBD') #> To cite package 'spatialLIBD' in publications use: #> #> Pardo B, Spangler A, Weber LM, Hicks SC, Jaffe AE, Martinowich K, #> Maynard KR, Collado-Torres L (2022). "spatialLIBD: an R/Bioconductor #> package to visualize spatially-resolved transcriptomics data." BMC #> Genomics. doi:10.1186/s12864-022-08601-w #> https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-022-08601-w, #> https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-022-08601-w. #> #> Maynard KR, Collado-Torres L, Weber LM, Uytingco C, Barry BK, #> Williams SR, II JLC, Tran MN, Besich Z, Tippani M, Chew J, Yin Y, #> Kleinman JE, Hyde TM, Rao N, Hicks SC, Martinowich K, Jaffe AE #> (2021). "Transcriptome-scale spatial gene expression in the human #> dorsolateral prefrontal cortex." Nature Neuroscience. #> doi:10.1038/s41593-020-00787-0 #> https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-020-00787-0, #> https://www.nature.com/articles/s41593-020-00787-0. #> #> Huuki-Myers LA, Spangler A, Eagles NJ, Montgomergy KD, Kwon SH, Guo #> B, Grant-Peters M, Divecha HR, Tippani M, Sriworarat C, Nguyen AB, #> Ravichandran P, Tran MN, Seyedian A, Consortium P, Hyde TM, Kleinman #> JE, Battle A, Page SC, Ryten M, Hicks SC, Martinowich K, #> Collado-Torres L, Maynard KR (2024). "A data-driven single-cell and #> spatial transcriptomic map of the human prefrontal cortex." #> Science. doi:10.1126/science.adh1938 #> https://doi.org/10.1126/science.adh1938, #> https://doi.org/10.1126/science.adh1938. #> #> Kwon SH, Parthiban S, Tippani M, Divecha HR, Eagles NJ, Lobana JS, #> Williams SR, Mark M, Bharadwaj RA, Kleinman JE, Hyde TM, Page SC, #> Hicks SC, Martinowich K, Maynard KR, Collado-Torres L (2023). #> "Influence of Alzheimer’s disease related neuropathology on local #> microenvironment gene expression in the human inferior temporal #> cortex." GEN Biotechnology. doi:10.1089/genbio.2023.0019 #> https://doi.org/10.1089/genbio.2023.0019, #> https://doi.org/10.1089/genbio.2023.0019. #> #> To see these entries in BibTeX format, use 'print(, #> bibtex=TRUE)', 'toBibtex(.)', or set #> 'options(citation.bibtex.max=999)'.
HumanPilot code
Re-shaping your data to our structure
As described in the spatialLIBD vignette, you can see the scripts in this repository for re-shaping your data to look like ours. That is.
reorganize_folder.Ravailableherere-organizes the raw data we were sent by 10x Genomics.Layer_Notebook.Ravailableherereads in the Visium data and builds a list ofRangeSummarizedExperiment()objects from_SummarizedExperiment_, one per sample (image) that is eventually saved asHuman_DLPFC_Visium_processedData_rseList.rda.convert_sce.Ravailableherereads inHuman_DLPFC_Visium_processedData_rseList.rdaand builds an initialsceobject with image data undermetadata(sce)$imagewhich is a single data.frame. Subsetting doesn’t automatically subset the image, so you have to do it yourself when plotting as is done bysce_image_clus_p()andsce_image_gene_p(). Having the data from all images in a single object allows you to use the spot-level data from all images to compute clusters and do other similar analyses to the ones you would do with sc/snRNA-seq data. The script creates theHuman_DLPFC_Visium_processedData_sce.Rdatafile.sce_scran.Ravailableherethen uses scran to read inHuman_DLPFC_Visium_processedData_sce.Rdata, compute the highly variable genes (stored in our finalsceobject atrowData(sce)$is_top_hvg), perform dimensionality reduction (PCA, TSNE, UMAP) and identify clusters using the data from all images. The resulting data is then stored asHuman_DLPFC_Visium_processedData_sce_scran.Rdataand is the main object used throughout our analysis code(Maynard, Collado-Torres, Weber, Uytingco et al., 2021).make-data_spatialLIBD.Ravailable in the source version ofspatialLIBDand online hereis the script that reads inHuman_DLPFC_Visium_processedData_sce_scran.Rdataas well as some other outputs from our analysis and combines them into the finalsceandsce_layerobjects provided by_spatialLIBD_ (Pardo, Spangler, Weber, Hicks et al., 2022). This script simplifies some operations in order to simplify the code behind the_shiny_ application provided by_spatialLIBD_.
10X directory
Contains some of the raw files provided by 10X. Given their size, we only included the small ones here. ## Analysis directory
The README.md was the one we initially prepared for our collaborators at an early stage of the project. That README file described some of our initial explorations using packages such as_scran,zinbwave_ and other approaches such as using k-means with X/Y spatial information. These analyses were not used for our manuscript beyond creating the sceobject we previously described.
The 10x Genomics file structure is replicated insideHistology where we saved the image segmentation analysis output to estimate the number of cells per spot. This involved running some histology image segmentation softwareand the counting code that requires our file structure (sgeID input).
The main layer-level analysis code is located atLayer_Guesses, for examplelayer_specificity.R is the R script for pseudo-bulking the spot-level data to create the layer-level data. The spatialLIBD layer annotation files are saved in the First_Round andSecond_Round directories which you can upload to the shiny web application.
We also include directories with code for processing external datasets such as he_layers,allen_data,hafner_vglut.
We would like to highlight that a lot of the plotting code and functionality from these scripts has been implemented in_spatialLIBD_which would make a lot of our analysis simpler. Finally, for reproducibility purposes we included the R session information in many of our R scripts. Although in general we used R 3.6.1 and 3.6.2 with Bioconductor release 3.10.
outputs directory
Contains outputs from the different unsupervised, semi-supervised, known gene marker based and other clustering results. The analysis code that generates these CSV files is located inside R Markdown files at theAnalysis directory such asSpatialDE_clustering.Rmd.
Bibliography
[1] K. R. Maynard, L. Collado-Torres, L. M. Weber, C. Uytingco, et al. “Transcriptome-scale spatial gene expression in the human dorsolateral prefrontal cortex”. In: Nature Neuroscience (2021). DOI: 10.1038/s41593-020-00787-0.https://www.nature.com/articles/s41593-020-00787-0.
[2] B. Pardo, A. Spangler, L. M. Weber, S. C. Hicks, et al. “spatialLIBD: an R/Bioconductor package to visualize spatially-resolved transcriptomics data”. In: BMC Genomics (2022). DOI: 10.1186/s12864-022-08601-w.https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-022-08601-w.
Internal
- JHPCE location:
/dcs04/lieber/lcolladotor/with10x_LIBD001/HumanPilot - Main
sceR object file:/dcs04/lieber/lcolladotor/with10x_LIBD001/HumanPilot/Analysis/Human_DLPFC_Visium_processedData_sce_scran.Rdata.