IL-22: A critical mediator in mucosal host defense (original) (raw)
Abstract
IL-22 is an IL-10 family cytokine member that was recently discovered to be produced by Th17 cells. Current studies have revealed that IL-22 targets cells of the digestive, skin, and respiratory organ systems and plays an important role in mucosal immunity. The IL-22 receptor (IL-22R) is expressed exclusively in these tissues, thereby allowing the cytokine to mediate epithelial innate immunity in response to a variety of pathogens. Although recent studies have shown the importance of IL-22 in host defense against Gram-negative bacterial organisms (in gut and lung), there is evidence that IL-22 also plays a role in autoimmune disease, such as psoriasis. IL-22 therefore, not unlike other cytokines, has complex pro-inflammatory, anti-inflammatory, and autoimmune effects which continue to be under further investigation. This review will focus on what is known about IL-22 and its function in mucosal host defense.
Access this article
Subscribe and save
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime Subscribe now
Buy Now
Price excludes VAT (USA)
Tax calculation will be finalised during checkout.
Instant access to the full article PDF.
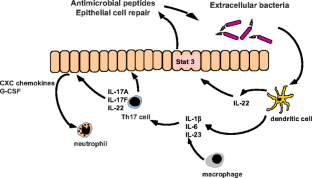
Fig. 1
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.
References
- Dumoutier et al (2000) Cloning and characterization of IL-10-related T cell derived inducible factor (IL-TIF), a novel cytokine structurally related to IL-10 and inducible by IL-9. J Immunol 164:1814–1819
CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Wolk K, Sabat R (2006) Interleukin-22: a novel T and NK cell-derived cytokine that regulates the biology of tissue cells. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 17:367–380
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Wolk X et al (2004) IL-22 increases the innate immunity of tissues. Immun 21:241–254
Article CAS Google Scholar - Wynn T (2005) Th17: a giant step from Th1 and Th2. Nat Immunol 6:1069–1070
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Betteli X et al (2007) Th17 cells in the circle of immunity and autoimmunity. Nat Immunol 8:345–350
Article Google Scholar - Liang X et al (2006) Interleukin 22 and IL-17 are coexpressed by Th17 cells and cooperatively enhance expression of antimicrobial peptides. J Exp Med 203:2271–2279
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Boniface X et al (2005) IL-22 inhibits epidermal differentiation and induces proinflammatory gene expression and migration of human keratinocytes. J Immunol 174:3695–3702
CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Wolk X et al (2006) IL-22 regulates the expression of genes responsible for antimicrobial defense, cellular differentiation, and mobility in keratinocytes: a potential role in psoriasis. Eur J Immunol 36:1309–1323
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Ma X et al (2008) IL-22 is required for Th17 cell-mediated pathology in a mouse model of psoriasis-like skin inflammation. J Clin Invest 118:597–607
CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Caproni X et al (2008) Serum levels of IL-17 and IL-22 are reduced by Etanercept, but not by Acitretin, in patients with psoriasis: a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Immunol. doi:10.1007/s10875-008-9233-0
- Nagalakshmi X et al (2004) Interleukin 22 activates STAT3 and induces IL-10 by colon epithelial cells. Int Immunopharmacol 4:679–691
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Brand X et al (2006) IL-22 is increased in active Crohn’s disease and promotes proinflammatory gene expression and intestinal epithelial cell migration. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 290:G827–G838
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Sugimoto X et al (2008) IL-22 ameliorates intestinal inflammation in a mouse model of ulcerative colitis. J Clin Invest 118:534–544
CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Zheng X et al (2008) Interleukin 22 mediates early host defense against attaching and effacing bacterial pathogens. Nat Med 14:282–289
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Whittington X et al (2004) IL-22: a potential immunomodulatory molecule in the lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 31:220–226
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Aujla X et al (2008) IL-22 mediates mucosal host defense against gram negative bacterial pneumonia. Nat Med 14:275–281
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Andoh X et al (2005) Interleukin-22, a member of the IL-10 subfamily, induces inflammatory responses in colonic subepithelial myofibroblasts. Gastroenterol 129:969–984
Article CAS Google Scholar - Cella X et al (2008) A human natural killer cell subset provides an innate source of IL-22 for mucosal immunity. Nat: Epub ahead of print
- Wolk X et al (2007) IL-22 induces lipopolysaccharide-binding protein in hepatocytes: a potential systemic role of IL-22 in Crohn’s disease. J Immunol 178:5973–5981
CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Zheng X et al (2007) Interleukin-22, a Th17 cytokine, mediates IL-23-induced dermal inflammation and acanthosis. Nat 445:648–651
Article CAS Google Scholar - Malmberg K, Ljunggren H (2009) Spotlight on IL-22-producing NK cell receptor expressing mucosal lymphocytes. Nat Immunol 10:11–12
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar - Sanos X et al (2009) RORγt and commensal microflora are required for the differentiation of mucosal interleukin 22-producing NKp46+ cells. Nat Immunol 10:83–91
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
- Division of Pulmonary Medicine, Allergy and Immunology, Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA, USA
S. J. Aujla & J. K. Kolls
Authors
- S. J. Aujla
- J. K. Kolls
Corresponding author
Correspondence toS. J. Aujla.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aujla, S.J., Kolls, J.K. IL-22: A critical mediator in mucosal host defense.J Mol Med 87, 451–454 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-009-0448-1
- Received: 10 November 2008
- Revised: 07 January 2009
- Accepted: 28 January 2009
- Published: 14 February 2009
- Issue Date: May 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-009-0448-1