Enhancer RNAs participate in androgen receptor-driven looping that selectively enhances gene activation (original) (raw)
Significance
We report that enhancer RNAs (eRNAs), a class of long noncoding RNAs, participate in the androgen receptor (AR)-dependent looping complex that enhances spatial communication of distal enhancers and target promoters, leading to transcriptional activation events. Furthermore, our data show that KLK3 eRNA (KLK3e) selectively enhances the gene expression of AR-regulated genes, and provide evidence for a positive regulatory loop in which AR-dependent transcription is modulated by an intermediate eRNA. These findings may translate into improved RNA-based therapy (eRNA suppression) to enhance the durability of androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) and prediction of the efficacy of ADT by measuring the enhancer-derived activity (eRNA expression) in prostate tumors.
Keywords: KLK3e/AR/Med1 complex, chromosomal looping
Abstract
The androgen receptor (AR) is a key factor that regulates the behavior and fate of prostate cancer cells. The AR-regulated network is activated when AR binds enhancer elements and modulates specific enhancer–promoter looping. Kallikrein-related peptidase 3 (KLK3), which codes for prostate-specific antigen (PSA), is a well-known AR-regulated gene and its upstream enhancers produce bidirectional enhancer RNAs (eRNAs), termed KLK3e. Here, we demonstrate that KLK3e facilitates the spatial interaction of the KLK3 enhancer and the KLK2 promoter and enhances long-distance KLK2 transcriptional activation. KLK3e carries the core enhancer element derived from the androgen response element III (ARE III), which is required for the interaction of AR and Mediator 1 (Med1). Furthermore, we show that KLK3e processes RNA-dependent enhancer activity depending on the integrity of core enhancer elements. The transcription of KLK3e was detectable and its expression is significantly correlated with KLK3 (_R_2 = 0.6213, P < 5 × 10−11) and KLK2 (_R_2 = 0.5893, P < 5 × 10−10) in human prostate tissues. Interestingly, RNAi silencing of KLK3e resulted in a modest negative effect on prostate cancer cell proliferation. Accordingly, we report that an androgen-induced eRNA scaffolds the AR-associated protein complex that modulates chromosomal architecture and selectively enhances AR-dependent gene expression.
Androgens and the androgen receptor (AR) play pivotal roles not only in the development of the normal prostate gland but also in the growth and progression of prostate cancer (PCa) (1–4). Androgens exert their biological and physiological effects through activating AR transcriptional activity. AR, a transcription factor, recruits ligand-dependent transcriptional machinery that activates a tissue-specific transcriptional program involved in development and differentiation (4–6). In PCa cells, AR occupies numerous gene loci to activate transcripts mediating critical cellular activities, such as energy and metabolism (5). AR activation and reactivation are essential for PCa development and tumor recurrence (7).
One unanticipated observation that emerged from multiple global studies of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) occupancy was that Pol II binds to a large number of intergenic AR-bound enhancers marked by histone H3 lysine 4 monomethylation (H3K4me1) and lysine 27 acetylation (H3K27ac) and produces enhancer-derived long noncoding RNAs (eRNAs) (8–11). Although eRNAs are bidirectional and nonpolyadenylated, their induction correlates with the induction of adjacent exon-coding genes (9). The activity of eRNAs was shown to augment the expression of not only neighboring but also intrachromosomally distant genes to convey enhancer-dependent transcription (12, 13). Recently, the 5′-GRO-seq data have revealed that sequence-specific transcription factors and eRNA transcripts are required for transfer of full enhancer activity to a target promoter (14). Moreover, eRNAs have been shown to configure a chromatin state that facilitate transcription factors binding on the target promoters at defined genomic loci (15).
Mechanistically, eRNAs have been shown to associate with the cohesin complex at estrogen receptor binding sites and contribute to gene activation by stabilizing estrogen receptor-α (ER-α)/eRNA-induced enhancer-promoter looping (16, 17). In addition, ncRNA-activating (ncRNA-a), a class of enhancer-like RNAs, has been shown to interact with the Mediator complex that enhances transcription in a _cis_-mediated mechanism (18), highlighting an RNA-dependent functional effect. Therefore, we hypothesized that eRNAs facilitates spatial communication of enhancers and promoters, thereby enhancing transcriptional activation events. Here, we report that the Kallikrein-related peptidase 3 (KLK3) enhancer, one of the strongest AR-bound enhancers in prostate cancer cells, produces KLK3 eRNA (KLK3e), which impacts androgen-induced gene activation. This work reveals that KLK3e selectively enhances AR-regulated gene expression through its collaboration with the AR-dependent looping complex. Thus, our findings provide evidence for a positive regulatory loop in which the AR-regulated network is modulated by an intermediate eRNA.
Results
The KLK3 Enhancer Produces eRNA (KLK3e).
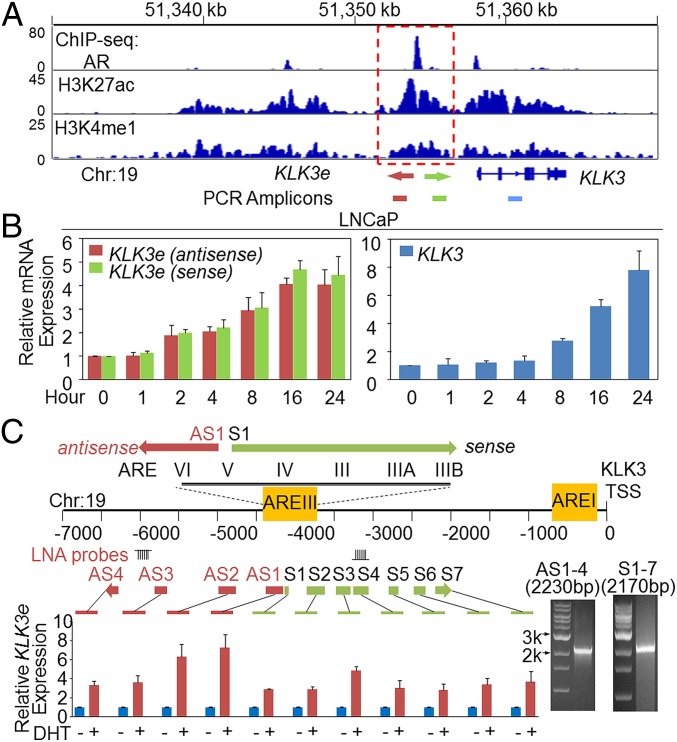
We compiled recently established genomic datasets (19) and showed that the KLK3 enhancer, also defined as the androgen response element III (ARE III) (20), was marked by AR, H3K27ac, and H3K4me1, implying that this region is transcriptionally active (Fig. 1_A_). In fact, the transcription of KLK3 eRNA (KLK3e) was demonstrated by GRO-seq data (10) and confirmed by our reverse transcription–quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) analyses in androgen-dependent LNCaP and VCaP, and androgen-independent LNCaP-abl cells (21) (Fig. 1_B_ and Fig. S1 A and B). The expression of KLK3e was induced within the first hour of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) exposure and its expression level gradually increased in a time-dependent manner, resembling the expression of mature KLK3 in both LNCaP and VCaP cells; in contrast, although transcription at the KLK3 locus remains active in androgen-independent LNCaP-abl, androgens (DHT) did not stimulate their mRNA expression to a comparable magnitude as those in parental LNCaP cells (Fig. S1_B_). Next, we investigated the impact of AR antagonist, bicalutamide, on the expression of KLK3e. The expression of KLK3e and KLK3 was induced upon DHT stimulation and blocked by bicalutamide (Fig. S1_C_), revealing that ligand-dependent eRNA synthesis takes place in association with target mRNA transcription. Taken together, our findings are consistent with the previous report that there is a high correlation of activity-dependent induction between eRNAs and adjacent coding mRNAs (9).
Fig. 1.
The KLK3 enhancer produces lncRNAs. (A) The chromatin status in the vicinity of KLK3. ChIP-seq datasets of AR, H3K27ac, and H3K4me1 (19). (B) RT-qPCR analyses of expression of antisense KLK3 eRNA (red bar), sense KLK3 eRNA (green bar), and mature KLK3 (blue bar) upon DHT (10 nM) treatment in a time-dependent manner in LNCaP cells. (C, Upper) A diagram of functional ARE positions that are relative to the KLK3 transcription starting site (TSS) adapted from ref. 20. (Lower) RT-qPCR analyses of the expression of segments of KLK3e with DHT (10 nM) treatment in LNCaP cells. The regions of LNA probes against the antisense and sense KLK3e were as indicated. Primer sets for qPCR were designed to specifically target either antisense (primers AS1–AS4) or sense strand (primer S1–S7) of KLK3e as shown. The right electrophoresis images show the PCR products of antisense (2,230 bp) and sense (2,170 bp) KLK3e. All data analyzed by RT-qPCR were normalized to the expression level in vehicle (−). Data are shown as mean ± SD (n ≥ 3).
Although multiple studies have identified different eRNA species from mammalian enhancers, the precise mapping of eRNAs has not been described. Because eRNAs produced from these intergenic enhancers are low at steady state (9) and estimated at fewer than 100 copies per cell (17), we enriched cellular RNAs by depleting rRNAs before reverse transcription. PCR primer sets against the antisense (AS1–AS4) and sense (S1–S7) of KLK3e were designed based on the GRO-seq and genomic datasets (10, 19). As shown in Fig. 1_C_, the transcription of bidirectional KLK3e was captured; whereas, no robust DHT-induced transcription was detectable beyond AS4 and S7. We performed primer-extension PCR assay to connect shorter fragments (Fig. S1_D_) and further showed PCR products for the antisense (2,230 bp) and sense (2,170 bp) of KLK3e (Fig. 1_C_ and cDNA sequences available in SI Experimental Procedures). To distinguish whether the eRNA at KLK3 enhancer are polyadenylated or not, we performed reverse transcription using random hexamer primers and 3′-RACE (poly-T) adapter from the same RNA materials. As shown in Fig. S1_E_, the expression of AS4 and S7 was substantially induced by DHT treatment, suggesting that the poly-A tail was added to the 3′-end of antisense and sense KLK3e. In contrast, S1 showed less DHT-stimulated expression in the poly-T priming compared with random hexamer primed cDNA. These data suggest that this locus produces a mixture of RNA species; some of them are polyadenylated, whereas others may be actively undergoing synthesis of polyadenylation, but we cannot totally exclude the existence of those species without poly-A tails. To detect the size of the mature eRNA at this loci, we customized double DIG-labeled probes using locked nucleic acids (LNA) (Exiqon). Northern analysis revealed that a major form (∼2.5 kb) and a minor form (∼1.7 kb) of sense KLK3e were produced upon DHT induction, whereas no signal was detected at the antisense strand (Fig. S1_F_), suggesting that the expression of antisense strand may be lower than the levels that can be detected by the LNA probe (Fig. S1_F_). Collectively, this suggests that the sense strand (S1–S7) KLK3e, a ∼2.2-kb transcript, is polyadenylated and yields a ∼2.5-kb transcript shown in Northern analysis. Although the antisense KLK3e can be polyadenylated and detected by qPCR, its expression may be substantially lower than the sense strand and cannot be detected by Northern analysis under the same experimental settings, indicating that the sense strand KLK3e is the dominant species.
The Regulatory Function of KLK3e on the Kallikrein Locus.
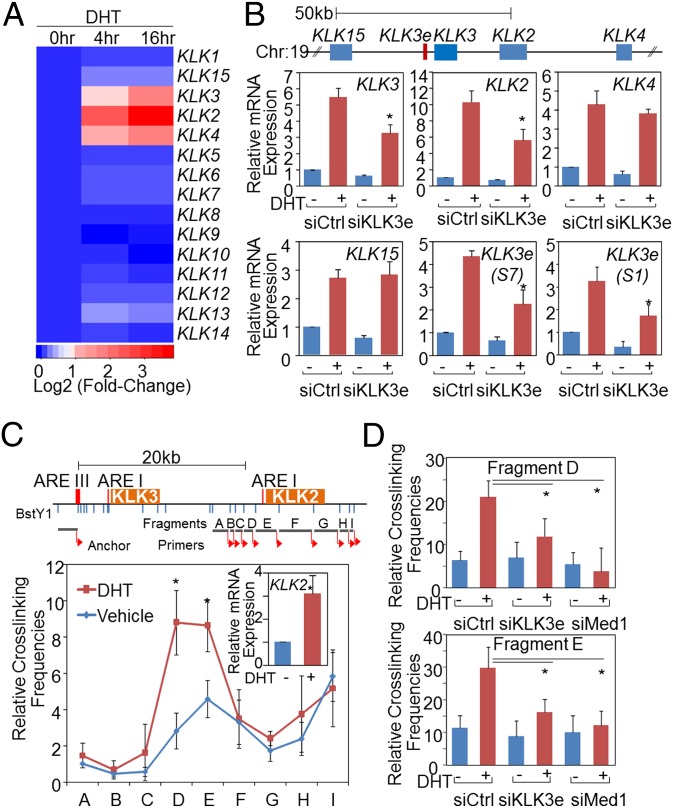
To investigate the potential function of eRNAs in transcriptional regulation, short interfering RNAs (siRNAs) targeting KLK3e (siKLK3e) were designed on the basis of KLK3e mapping. Results obtained from distinct sets of siRNAs against the sense strand of KLK3e showed that siKLK3e specifically targeted sense KLK3e and significantly impeded DHT-induced KLK3 expression in both LNCaP and VCaP cells but had a minimal impact on LNCaP-abl cells (Fig. 2_B_ and Fig. S2 A–E), consistent with the notion that ligand-activated eRNAs are important for nearby gene activation (13, 17). Considering that KLK15, 2, and 4 were adjacent to KLK3 and androgen-responsive (Fig. 2_A_), we examined whether KLK3e impacted transcription of these KLKs. Interestingly, knocking down of sense KLK3e significantly inhibited the expression of KLK2, whereas other KLKs remained unchanged (Fig. 2_B_). We also investigated the effect of antisense KLK3e on the regulation of target gene expression. RNAi silencing of the antisense of KLK3e showed a marginal inhibitory effect on KLK3 and KLK2 gene expression (Fig. S2_F_). Despite the presence of bidirectional KLK3e transcription, data from siRNA to KLK3e and Northern analysis showed that the sense strand of KLK3e is the dominant transcript with functional effects on the expression of KLK3 and distant KLK2. Thus, we chose the sense KLK3e and continued to study its RNA-dependent enhancer activity.
Fig. 2.
The regulatory function of KLK3e on the KLK locus. (A) A heat map of the KLK transcripts upon 4 and 16 h of DHT exposure in LNCaP cells (21). Genes are listed as their order in the kallikrein loci from centromere (Top) to telomere (Bottom). (B, Upper) Schematic drawing indicates the relative position of AR-regulated KLK genes and KLK3e on the chromosome 19. (Lower) LNCaP cells were treated with vehicle (−) or DHT (10 nM) and 50 nM of nonsilencing control (siCtrl) or KLK3e siRNA (siKLK3e); lowercase “e” denoted as eRNA. Efficacy and effects of KLK3e depletion on KLK genes were assessed by RT-qPCR. (C, Upper) Schematic graph shows the KLK3/2 gene loci. (Lower) LNCaP cells were treated with vehicle or DHT for 4 h. KLK2 mRNA expression was assessed by RT-qPCR (Inset). The relative cross-linking frequency between the anchor region (ARE III) and distal fragments (shaded bars) was determined by qPCR and normalized to the control region (fragment A). (D) The relative cross-linking frequency between the anchor region D and E region was determined by qPCR and normalized to the A region. All data analyzed by RT-qPCR or qPCR were normalized to the expression level in vehicle and are shown as mean ± SD (n ≥ 3), and *P < 0.05.
Because the induction of eRNA is strongly correlated with the enhancer looping to target gene promoters (13, 16, 17), it is possible that the KLK3 enhancer element is able to interact with the KLK2 promoter. To address this, we used the chromosome conformation capture (3C) assay to study the spatial interaction of the KLK3/2 loci. It should be noted that the KLK2 promoter contains an ARE I that shares over 80% sequence homology with the ARE I in the KLK3 promoter (20). Indeed, DHT induces KLK2 transcription and the interaction between the anchor and fragment D and E by twofold to threefold (Fig. 2_C_). Amplified PCR of anchor-fragment D (105 bp) and anchor-fragment E (115 bp) was confirmed by DNA sequencing (Fig. S2 G and H), suggesting that the KLK3 enhancer interacts with the KLK2 promoter to mediate distal KLK2 gene activation.
To study the mechanism of KLK3e-mediated transcriptional events, we looked for KLK3e interacting partners by asking whether KLK3e interacts with AR, because KLK3e carries the core enhancer element. We conducted AR-directed RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) coupled with qPCR using primer sets targeting the core enhancer element at 5′-end (S1), middle segment (S4), and 3′-end (S7) of the sense KLK3e. Our results show a specific DHT-induced interaction between AR and S1 (Fig. S2_I_), suggesting that AR relies on the core enhancer element of KLK3e. Because Med1 has been shown to directly interact with AR and is involved in the chromosomal interaction of enhancer–promoter looping (22, 23), we next asked whether Med1 participates in the observed eRNA functions. RIP analysis revealed a strong androgen-stimulated interaction of S1 and Med1 (Fig. S2_J_), comparable to the interaction of KLK3e and AR. Conversely, the antisense KLK3e (AS1) exhibited modest interaction with AR and Med1 (Fig. S2_K_), implying that the enhancer function of these two KLK3e species is determined by the levels of interaction with the AR–Med1 complex.
To investigate the potential role of KLK3e in the KLK3/2 loci, we next used 3C-qPCR to assess the interaction of the anchor-fragment D/E regions in KLK3e-depleted cells. Silencing of KLK3e impaired KLK2 gene expression and the interaction of the KLK2 promoter and the KLK3 enhancer (Fig. 2_D_). Suppression of Med1 also substantially reduced the interaction of the KLK3/2 loci (Fig. 2_D_ and Fig. S2_L_), supporting a pivotal role of Med1 in mediating this long-range chromatin looping (18, 22). Hence, our results demonstrate that both KLK3e and Med1 are involved in maintaining the spatial interaction between an enhancer and a target promoter.
The KLK3e/AR/Med1 Ribonucleoprotein Complex Transcriptionally Regulates Target Promoters.
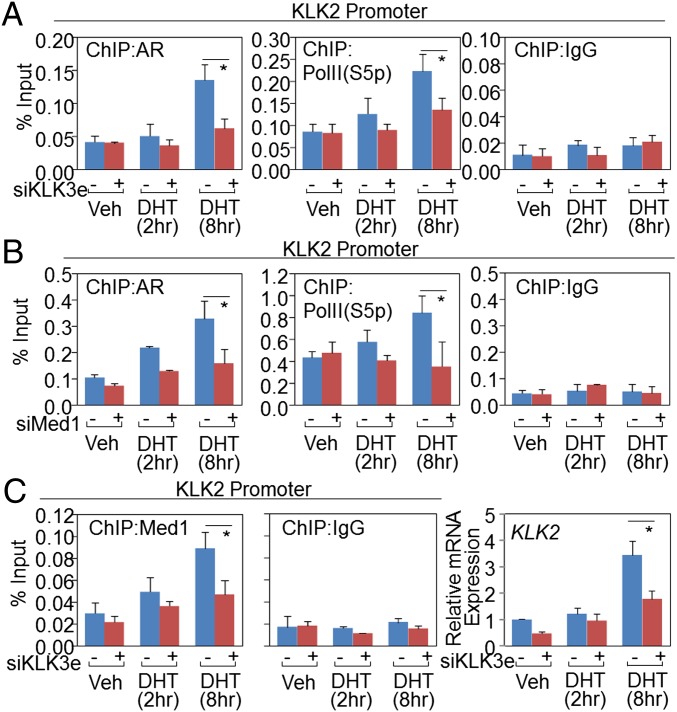
To ensure that the endogenous KLK3e plays a functional role on its target promoters, we performed chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) using antibodies against AR and activated RNA polymerase II (Pol II S5p) in KLK3e-depleted cells. These analyses demonstrated that depletion of KLK3e inhibited AR binding and Pol II activation at the KLK2 promoter, consistent with the reduction of gene expression of KLK2 (Fig. 3_A_). Next, we examined the regulatory effect of Med1 on the target promoters. As expected, knockdown of Med1 significantly reduced AR occupancy and Pol II activation at the KLK2 promoter (Fig. 3_B_). Whether KLK3e collaborates with Med1 and functionally affects transcription of the KLK2 promoter is unclear. Depletion KLK3e resulted in decrease of Med1 binding to the promoters of KLK2 (Fig. 3_C_). In addition, the effect of siKLK3e and siMed1 on the gene expression of KLK2 and Med1 was shown in Fig. S3_A_. Altogether, our data suggest that KLK3e cooperates with Med1 to enhance KLK2 gene expression. It should be noted that the actions of AR, Med1, and Pol II at the KLK3 promoter were comparable to those at the KLK2 promoter (Fig. S3 B–D), implying that the regulatory function of KLK3e at the KLK3/2 promoters may act through the same AR-dependent ribonucleoprotein complex.
Fig. 3.
The KLK3e/AR/Med1 ribonucleoprotein complex transcriptionally regulates target promoters. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) of AR or Med1 or activated Pol II (S5p) was performed in KLK3e- or Med1-depleted LNCaP cells with or without DHT (10 nM) for 2 or 8 h. (A–C) qPCR was conducted to measure the action of AR, Pol II (S5p), and Med1 at the KLK2 promoter. Data are shown as mean ± SD (n ≥ 3) and *P < 0.05.
Interestingly, silencing of KLK3e did not affect the action of AR and Pol II on the KLK3 enhancer (Fig. S3_E_), suggesting that the biogenesis of KLK3e takes place after ligand-activated AR was recruited to the enhancer. Although depletion of Med1 blocked AR binding and Pol II activation on the KLK3 enhancer, the expression of KLK3e was not significantly affected, implying that residual Med1-associated module may be sufficient for KLK3e production (Fig. S3_F_). Collectively, our data show the mechanism by which KLK3e forms a functional complex with AR and Med1 to promote transcription, supporting the findings that transfer of full enhancer activity to a target promoter depends on enhancer-bound transcription factors and enhancer-derived RNA transcripts (14).
The Core Enhancer Element Renders KLK3e RNA-Dependent Enhancer Activity.
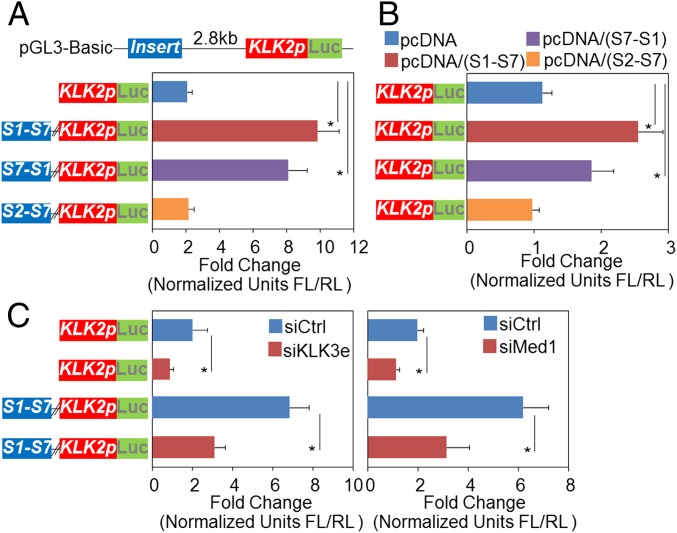
To validate the enhancer function of KLK3e, we used a luciferase reporter assay to quantitatively measure AR transcriptional activity. Although inclusion of KLK3e (S1–S7) or flipped (S7–S1) sequences markedly increased KLK2 promoter activity by fourfold to fivefold, this effect was abolished when ARE III sequences were deleted (S2–S7) (Fig. 4_A_), confirming the importance of the enhancer integrity and their orientational independency (17, 24).
Fig. 4.
The core enhancer element renders KLK3e RNA-dependent enhancer activity. (A, Upper) Schematic representation shows the insertion in KLK2 promoter driven luciferase reporter. (Lower) Reporter assay analyses were performed with or without insertion of full-length (S1–S7), flipped (S7–S1), and ARE deleted (S2–S7) of sense KLK3e. (B) Reporter analysis of cotransfecting the reporter with independent overexpressing vector as indicated. (C) The effects of siKLK3e (Left) or siMed1 (Right) on the KLK2 promoter-driven Luciferase activity. Luciferase activity was measured in the presence of DHT (10 nM) for 24 h. All data shown are mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments. *P < 0.05; firefly luciferase/Renilla luciferase (FL/RL).
The expression of the KLK3e from the luciferase reporter was validated by RT-PCR (Fig. S4_A_), indicating that AREs have the capacity to produce eRNAs. We next asked whether the KLK3e transcript alone is adequate for this transcriptional enhancement. For this purpose, we performed a cotransfection study based on reporters together with CMV-driven sense KLK3e constructs. As shown, the full-length (S1–S7) and flipped (S7–S1) KLK3e increased luciferase expression by 2- ∼ 2.5-fold, whereas ARE deletion (S2–S7) failed to enhance promoter activity (Fig. 4_B_). Furthermore, antisense KLK3e (AS1–AS4) was unable to induce luciferase expression as sense KLK3e (S1–S7) did (Fig. S4 B and C), again arguing that the sense KLK3e is the functional long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) rather than the antisense strand. To examine whether AR is required for the action of KLK3e, we conducted experiments in AR-negative COS-7 cells and confirmed that the activity of KLK3e depends on the availability of ligand-activated AR (Fig. S4 D and E). Altogether, these data show that the core enhancer elements are essential for the enhancer activity of KLK3e and that ectopic KLK3e induces the promoter activity on a luciferase reporter, implying a transregulatory activation mediated by KLK3e.
As a complementary approach, we also addressed whether the observed luciferase expression is mediated through endogenous KLK3e. RNAi silencing of KLK3e significantly reduced luciferase activity in the reporters with or without KLK3e insertion (Fig. 4_C_, Left), showing that KLK3e is required for the enhancement of DHT-induced activation. When KLK3e was ectopically expressed, it restored the luciferase expression inhibited by KLK3e suppression (Fig. S4_F_). Most importantly, the luciferase activity in the reporter with KLK3e insertion was reduced by ∼50% in Med1-depleted cells (Fig. 4_C_, Right), suggesting that Med1 facilitates KLK3e-dependent transcription. Notably, ncRNA-a has been shown to mediate long-range transcriptional activation through its association with the Med1 complex (18). In summary, our results strongly suggest that KLK3e forms a functional complex with AR and Med1 that facilitates the association of AR-bound enhancers with promoters of target genes, resulting in transcriptional activation.
KLK3 eRNA Selectively Enhances AR-Regulated Gene Expression.
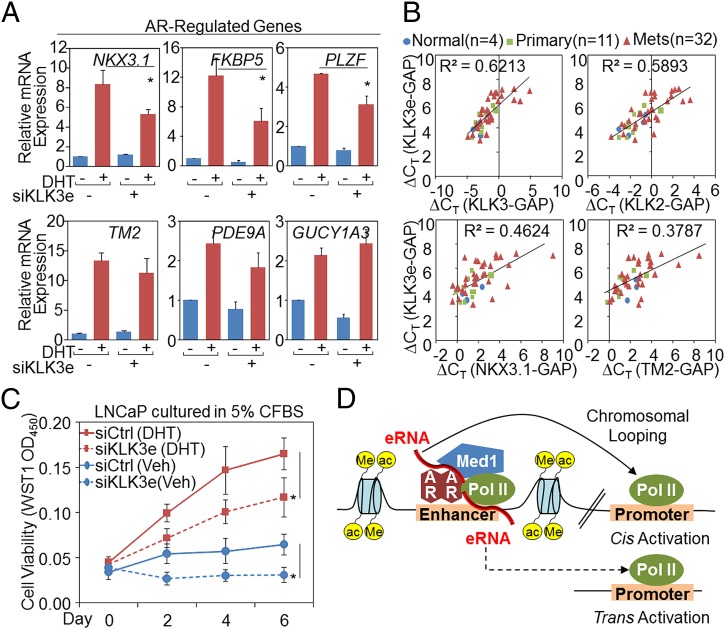
To explore the potential effect of KLK3e beyond the KLK locus, we measured the expression of canonical androgen-regulated genes in KLK3e-depleted cells. Suppression of KLK3e decreased the expression of NKX3.1, FKBP5, and PLZF, whereas the expression of TMPRSS2, PDE9A, and GUCY1A3 was not affected (Fig. 5_A_). Additionally, we observed a comparable KLK3e-mediated inhibition of NXK3.1 gene expression in VCaP cells (Fig. S2_D_). Moreover, we showed the expression eRNAs at upstream of NKX3.1, FKBP5, PLZF was induced by DHT but not affected by KLK3e siRNA knockdown (Fig. S5_A_), suggesting that the KLK3e siRNA does not interfere with the transcription of eRNAs found at the enhancers of NKX3.1, FKBP5, and PLZF. Although eRNA-mediated trans effects are likely to be relatively infrequent or quantitatively small (17), our data show that KLK3e selectively regulates the expression of AR-regulated genes that do not reside on the same chromosome, implying a transregulatory function of KLK3e on AR-dependent gene expression.
Fig. 5.
KLK3e selectively enhances AR-regulated gene expression. (A) LNCaP cells were treated with vehicle or DHT (10 nM) and/or siCtrl or siKLK3e. The effect of siKLK3e on AR-regulated gene expression was determined by RT-qPCR. (B) Correlation between KLK3e (S1) and target gene expression in vivo. All data were normalized for GAPDH by the differences in threshold cycles (∆_C_T) from the normal human prostate gland (n = 4), primary (n = 11) and metastatic (n = 32) prostate tumors (25). (C) LNCaP cells were cultured in 5% charcoal/dextran-treated FBS (C-FBS) medium, followed by siRNA knockdown of scrambled control (siCtrl) or KLK3e (siKLK3e) with ethanol (veh) or DHT (10 nM) treatment. Cell growth was measured by WST1 assay. Data represent mean ± SD (n ≥ 3), and *P < 0.05. (D) A proposed model for functional activities of the eRNA/AR/Med1 complex in DHT-induced cis (solid line) and potential trans (dish line) gene activation events.
We further assessed the regulatory role of KLK3e and Med1 on the promoter of NKX3.1 and TMPRSS2 to mechanistically validate our above findings in the KLK loci. Although depletion of KLK3e significantly reduced the enrichment of AR and Pol II S5p at the NKX3.1 promoter (Fig. S5_B_, Upper), the action of these factors at the TMPRSS2 promoter was unaffected (Fig. S5_B_, Lower). In contrast, Med1 knockdown considerably blocked both AR occupancy and Pol II activity at both the NKX3.1 and TMPRSS2 promoters (Fig. S5_C_). These results demonstrate that KLK3e selectively enhances gene expression, whereas Med1 has a more general effect on the regulation of AR-dependent transcription. Most importantly, KLK3e depletion reduced Med1 recruitment to the promoter of NKX3.1, not TMPRSS2 (Fig. S5 D and E), revealing that this eRNA/AR/Med1 complex may possess a degree of specificity in the AR-dependent transcriptional machinery. Furthermore, we evaluated the gene expression from the normal human prostate gland (n = 4), primary (n = 11) and metastatic (n = 32) human prostate tumors (25), and showed that the correlation (_R_2) of KLK3e (S1) with KLK3, KLK2, NKX3.1, and TMPRSS2 was 0.6213 (P < 5 × 10−11), 0.5893 (P < 5 × 10−10), 0.4624 (P < 2 × 10−7), and 0.3787 (P < 5 × 10−6), respectively. In addition, the expression the KLK3 and KLK2 was the most correlated (_R_2 = 0.8361, P < 3 × 10−16) (Fig. 5_B_ and Fig. S5_F_). Collectively, these in vivo data indicate that the transcription of KLK3e was detectable and its presence correlates with KLK3/2 gene expression. We noted less of a correlation between KLK3e expression and those genes in trans, and the correlation was stronger with NKX3.1 than TMPRSS2, consistent with our in vitro data, although these data do not prove a direct effect in vivo of KLK3e on the transcription of these genes. Next, we investigated the biological effect of KLK3e siRNA on LNCaP cells and showed that KLK3e depletion significantly compromised cell growth in the presence and absence of exogenous androgens (Fig. 5_C_). Although this negative effect is modest, we postulate that suppression of multiple eRNAs produced from distinct enhancer elements may synergetically block the AR transcriptional program. Thus, substantial efforts are needed to fully characterize the transcriptional and biological functions of other significant androgen-induced eRNAs in the future.
Discussion
We demonstrate that bidirectional KLK3e was produced from one of the strongest AR-bound enhancers (ARE III) and its expression pattern resembles KLK3 in prostate cancer cell lines (Fig. 1 and Fig. S1), in agreement with the previous report that a high correlation of activity-dependent induction exists between eRNAs and adjacent coding mRNAs (9). Suppression of KLK3e exclusively reduces gene expression of KLK3 and KLK2, not other KLK family members and that KLK3e facilitates the assembly of the transcriptional apparatus at the promoters during gene activation events. This classifies KLK3e as a family of functional lncRNA involved in enhancing long-distance gene transcription.
Whether eRNAs function as molecular bridges that mediate spatial interactions of distal enhancers and target promoters, or directly configure a chromatin state that facilitate transcription factor binding at the target promoters is unclear. Recently, chromatin isolation by RNA purification coupled with deep sequencing was deployed to interrogate the nature of RNA and DNA interaction in a genome-wide scale (26). Rosenfeld and colleagues (17) used this methodology to identify potential sites where estrogen-induced FOXC1 eRNA localizes in the genome. Although FOXC1 eRNA is specifically enriched in a small fraction of genomic loci, there were no known estrogen-regulated genes found adjacent to these RNA/DNA binding sites (17), implying that the functional effect of eRNAs on target genes may not completely rely on nucleotide base pairing. In this report, we demonstrate that KLK3e mediates chromosomal looping of KLK3/2 loci and confirmed in a heterologous reporter assay that KLK3e cooperates with AR and Med1 to enhance KLK2 promoter activity through the core enhancer element (ARE III). The state of KLK3e and KLK3/2 was further validated in human prostate tissues (n = 47) and showed that the expression of KLK3e significantly correlates with KLK3 (_R_2 = 0.6213, p < 5 × 10−11) and KLK2 (_R_2 = 0.5893, p < 5 × 10−10), implying that KLK3e may coordinate the transcription of KLK3/2 (Fig. 5_B_). However, we do not completely understand how KLK-associated eRNAs are regulated in castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC), although it is well accepted that the AR-mediated transcriptional program remains active. This observation can be explained by the activity of other nuclear receptors, because the core sequence of ARE can be also be recognized by glucocorticoid receptor (GR), progesterone receptor (PR), and mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) (27). More importantly, it has been shown that AR inhibition resulted in GR up-regulation in a subset of prostate cancer cells supporting a mechanism of bypassing AR blockade via an alternative nuclear receptor in CRPC (28). Thus, it is possible that GR, PR, or MR may mediate the expression of KLK3e, KLK3, and KLK2, attributing to adaptive or compensatory effects generated during CRPC development.
In view of the regulatory potential of lncRNAs on gene regulation in trans (29–31), eRNAs may be part of coactivator complexes and regulatory factors that participate in the transcriptional regulatory network. Although the entire circuitry of AR-dependent genes is unlikely controlled by a single eRNA, presumably, there are more androgen-induced eRNAs, and there could be redundancy in their enhancer activity. It is conceivable that multiple eRNAs produced from distinct enhancer elements tether with their own transcriptional modules that operate simultaneously to initiate an accurate and a rapid transcriptional program. Therefore, we propose that an eRNA may function as a scaffold that guides an AR-associated protein complex to target chromatin and selectively enhances DHT-stimulated transcription either intrachromosomally (cis activity) or interchromosomally (trans activity). This positive regulatory loop may provide new insight into RNA-dependent functional effects on the regulation of lineage- or tissue-specific gene expression.
Although androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) is designed to block the androgen signaling pathway and is the standard treatment for advanced prostate cancer, this study may help us to understand how androgen ADT influences the activity of AR-bound enhancers through altered expression of eRNAs. In addition, the differential eRNA expression patterns observed may be predictive markers of ADT efficacy for individual prostate cancer patients. More importantly, eRNAs may represent new targets that when suppressed may improve the therapeutic durability of ADT.
Experimental Procedures
ChIP Assay.
ChIP experiments were performed as previously described (19) with some modifications. Briefly, 10 million cells were used per IP. Cells were fixed with 1% formaldehyde solution. DNA was sonicated and subjected to immunoprecipitation with antibodies against androgen receptor (N-20X; Santa Cruz Biotechnology), Med1/TRAP220 (A300-793A; Bethyl Laboratories), RNA Polymerase II (p-Ser5) (ab5131; Abcam), or nonspecific IgG. DNA was purified and analyzed by qPCR. The primers for qPCR are provided in SI Experimental Procedures.
RIP Assay.
RIP experiments were performed as described previously with some modification (31). Briefly, 10 million cells were used per IP. Cells were fixed in 0.3% formaldehyde solution. Total chromatin and RNAs were sonicated and subjected to immunoprecipitation with the same AR and Med1 antibodies used in ChIP experiments. Immunoprecipitated RNAs were isolated using TRIzol LS reagent, followed by cDNA synthesis. The primers for qPCR are provided in SI Experimental Procedures.
3C Assay.
The 3C assay was performed as previously described with some modifications (32). After DHT (10 nM) treatment, LNCaP cells were fixed with 1% formaldehyde. Cell pellets were lysed and resuspended in restriction buffer for BstY1 and 0.1% SDS for 10 min at 65 °C. Triton X-100 was added to a final concentration of 1.8% followed by overnight digestion of BstY1 (1,500 U per 107 cells) at 37 °C. DNA ligation was performed for 4 d at 16 °C. The ligated samples were reverse cross-linked with proteinase K at 65 °C overnight, followed by phenol/chloroform extraction and EtOH precipitation. The primers for qPCR are provided in SI Experimental Procedures.
Additional experimental procedures and methods are listed in SI Experimental Procedures.
Supplementary Material
Supporting Information
Acknowledgments
We extend our gratitude to Dr. Changmeng Cai for his contributions in experimental and technical assistance, suggestions, and critical reading of the manuscript. The work from the laboratory of P.W.K. was supported by the Prostate Specialized Program of Research Excellence (P50CA090381) and Department of Defense Postdoctoral Training Award W81XWH-13-1-0383. S.P.B. was supported by National Institutes of Health Grant P01 CA163227 and Department of Defense Grant W81XWH-11-1-0295.
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
This article is a PNAS Direct Submission.
References
- 1.Heinlein CA, Chang C. Androgen receptor in prostate cancer. Endocr Rev. 2004;25(2):276–308. doi: 10.1210/er.2002-0032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Knudsen KE, Penning TM. Partners in crime: Deregulation of AR activity and androgen synthesis in prostate cancer. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2010;21(5):315–324. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2010.01.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Nelson PS. Molecular states underlying androgen receptor activation: A framework for therapeutics targeting androgen signaling in prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(6):644–646. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.39.1300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hendriksen PJM, et al. Evolution of the androgen receptor pathway during progression of prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2006;66(10):5012–5020. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Massie CE, et al. The androgen receptor fuels prostate cancer by regulating central metabolism and biosynthesis. EMBO J. 2011;30(13):2719–2733. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Baek SH, et al. Ligand-specific allosteric regulation of coactivator functions of androgen receptor in prostate cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103(9):3100–3105. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0510842103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Yuan X, Balk SP. Mechanisms mediating androgen receptor reactivation after castration. Urol Oncol. 2009;27(1):36–41. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2008.03.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.De Santa F, et al. A large fraction of extragenic RNA pol II transcription sites overlap enhancers. PLoS Biol. 2010;8(5):e1000384. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kim T-K, et al. Widespread transcription at neuronal activity-regulated enhancers. Nature. 2010;465(7295):182–187. doi: 10.1038/nature09033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wang D, et al. Reprogramming transcription by distinct classes of enhancers functionally defined by eRNA. Nature. 2011;474(7351):390–394. doi: 10.1038/nature10006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ørom UA, Shiekhattar R. Long noncoding RNAs usher in a new era in the biology of enhancers. Cell. 2013;154(6):1190–1193. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.08.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ørom UA, et al. Long noncoding RNAs with enhancer-like function in human cells. Cell. 2010;143(1):46–58. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.09.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Melo CA, et al. eRNAs are required for p53-dependent enhancer activity and gene transcription. Mol Cell. 2013;49(3):524–535. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.11.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lam MT, et al. Rev-Erbs repress macrophage gene expression by inhibiting enhancer-directed transcription. Nature. 2013;498(7455):511–515. doi: 10.1038/nature12209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mousavi K, et al. eRNAs promote transcription by establishing chromatin accessibility at defined genomic loci. Mol Cell. 2013;51(5):606–617. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.07.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hah N, Murakami S, Nagari A, Danko CG, Kraus WL. Enhancer transcripts mark active estrogen receptor binding sites. Genome Res. 2013;23(8):1210–1223. doi: 10.1101/gr.152306.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Li W, et al. Functional roles of enhancer RNAs for oestrogen-dependent transcriptional activation. Nature. 2013;498(7455):516–520. doi: 10.1038/nature12210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lai F, et al. Activating RNAs associate with Mediator to enhance chromatin architecture and transcription. Nature. 2013;494(7438):497–501. doi: 10.1038/nature11884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Yu J, et al. An integrated network of androgen receptor, polycomb, and TMPRSS2-ERG gene fusions in prostate cancer progression. Cancer Cell. 2010;17(5):443–454. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2010.03.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lawrence MG, Lai J, Clements JA. Kallikreins on steroids: Structure, function, and hormonal regulation of prostate-specific antigen and the extended kallikrein locus. Endocr Rev. 2010;31(4):407–446. doi: 10.1210/er.2009-0034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wang Q, et al. Androgen receptor regulates a distinct transcription program in androgen-independent prostate cancer. Cell. 2009;138(2):245–256. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.04.056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Chen Z, et al. Phospho-MED1-enhanced UBE2C locus looping drives castration-resistant prostate cancer growth. EMBO J. 2011;30(12):2405–2419. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Jin F, Claessens F, Fondell JD. Regulation of androgen receptor-dependent transcription by coactivator MED1 is mediated through a newly discovered noncanonical binding motif. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(2):858–870. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.304519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kong S, Bohl D, Li C, Tuan D. Transcription of the HS2 enhancer toward a cis-linked gene is independent of the orientation, position, and distance of the enhancer relative to the gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1997;17(7):3955–3965. doi: 10.1128/mcb.17.7.3955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Stanbrough M, et al. Increased expression of genes converting adrenal androgens to testosterone in androgen-independent prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2006;66(5):2815–2825. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Chu C, Qu K, Zhong FL, Artandi SE, Chang HY. Genomic maps of long noncoding RNA occupancy reveal principles of RNA-chromatin interactions. Mol Cell. 2011;44(4):667–678. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.08.027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kim H-J, Park YI, Dong M-S. Comparison of prostate cancer cell lines for androgen receptor-mediated reporter gene assays. Toxicol In Vitro. 2006;20(7):1159–1167. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2006.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Arora VK, et al. Glucocorticoid receptor confers resistance to antiandrogens by bypassing androgen receptor blockade. Cell. 2013;155(6):1309–1322. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.11.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Rinn JL, et al. Functional demarcation of active and silent chromatin domains in human HOX loci by noncoding RNAs. Cell. 2007;129(7):1311–1323. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.05.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Prensner JR, et al. Transcriptome sequencing across a prostate cancer cohort identifies PCAT-1, an unannotated lincRNA implicated in disease progression. Nat Biotechnol. 2011;29(8):742–749. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Yang L, et al. lncRNA-dependent mechanisms of androgen-receptor-regulated gene activation programs. Nature. 2013;500(7464):598–602. doi: 10.1038/nature12451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Li Q, et al. Integrative eQTL-based analyses reveal the biology of breast cancer risk loci. Cell. 2013;152(3):633–641. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.12.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supporting Information