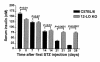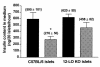Resistance to type 1 diabetes induction in 12-lipoxygenase knockout mice - PubMed (original) (raw)
Resistance to type 1 diabetes induction in 12-lipoxygenase knockout mice
D Bleich et al. J Clin Invest. 1999.
Abstract
Leukocyte 12-lipoxygenase (12-LO) gene expression in pancreatic beta cells is upregulated by cytotoxic cytokines like IL-1beta. Recent studies have demonstrated that 12-LO inhibitors can prevent glutamate-induced neuronal cell death when intracellular glutathione stores are depleted. Therefore, 12-LO pathway inhibition may prevent beta-cell cytotoxicity. To evaluate the role of 12-LO gene expression in immune-mediated islet destruction, we used 12-LO knockout (12-LO KO) mice. Male homozygous 12-LO KO mice and control C57BL/6 mice received 5 consecutive daily injections of low-dose streptozotocin to induce immune-mediated diabetes. Fasting serum glucose and insulin levels were measured at 7-day intervals, and the mice were followed up for 28 days. 12-LO KO mice were highly resistant to diabetes development compared with control mice and had higher serum insulin levels on day 28. Isolated pancreatic islets were treated with IL-1beta, TNF-alpha, and IFN-gamma for 18 hours. Glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in cytokine-treated islets from C57/BL6 mice decreased 54% from that of untreated islets. In marked contrast, the same cytokine mix led to only a 26% decrease in islets from 12-LO KO mice. Furthermore, cytokine-induced 12-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (12-HETE) production was absent in 12-LO KO islets but present in C57/BL6 islets. Isolated peritoneal macrophages were stimulated for 48 hours with IFN-gamma + LPS and compared for nitrate/nitrite generation. 12-LO KO macrophages generated 50% less nitrate/nitrite when compared with C57BL/6 macrophages. In summary, elimination of leukocyte 12-LO in mice ameliorates low dose streptozotocin-induced diabetes by increasing islet resistance to cytokines and decreasing macrophage production of nitric oxide.
Figures
Figure 1
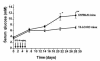
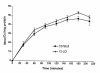
Serum glucose levels in low dose STZ–treated 12-LO KO and C57BL/6 mice. Eight 12-LO KO and 12 C57BL/6 mice received 40 mg/kg of STZ for 5 consecutive days as shown. The mean fasting serum glucose ± SEM for each group of mice is shown at each time point. 12-LO KO mice were significantly more resistant to STZ-induced diabetes than C57BL/6 control mice. *P = 0.01 vs. 12-LO KO. **P = 0.003 vs. 12-LO KO.
Figure 2
Serum insulin levels in low dose STZ–treated 12-LO KO and C57BL/6 mice. 12-LO KO mice demonstrated a 45% decrease in insulin levels from day 0 to day 28, whereas C57BL/6 mice had a 90% decrease in insulin levels after low-dose STZ treatment. A statistically significant difference in insulin levels between 12-LO KO and C57BL/6 mice is seen on days 21 and 28.
Figure 3
Differential effect of cytokines on 12-HETE production in C57BL/6 and 12-LO KO islets. C57BL/6 islets demonstrated a 2.5-fold increase in 12-HETE production in the presence of cytokines, whereas 12-HETE production in 12-LO KO islets was unchanged. The number in parenthesis represents the number of experiments performed for each condition. *P < 0.05 vs. C57BL/6 islets.
Figure 4
Basal and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in 12-LO KO and C57BL/6 islets. Islet preparations were assessed for basal and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion as described in Methods. 12-LO KO islets secreted 102 ± 2 ng insulin/20 islets/h in the basal state and 620 ± 50 ng insulin/20 islets/h when stimulated with 17 mM glucose. In comparison, C57BL/6 islets secreted 102 ± 4 ng insulin/20 islets/h in the basal state and 595 ± 101 ng insulin/20 islets/h when stimulated with 17 mM glucose. The number in parenthesis represents the number of experiments performed for each condition.
Figure 5
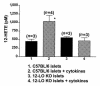
Effect of cytokine treatment on glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in 12-LO KO and C57BL/6 islets. Isolated islets were subjected to high-dose cytokine treatment as shown. Filled bars represent 17 mM glucose stimulation; hatched bars represent cytokine treatment (0.5 ng/mL IL-1β + 30 ng/mL TNF-α + 30 ng/mL IFN-γ) plus 17 mM glucose stimulation. Cytokine treatment decreased glucose-stimulated insulin secretion by 26% and 54% in 12-LO KO and C57BL/6 islets, respectively. Shown is 1 representative experiment in triplicate out of 3 separate experiments. *P < 0.03 vs. C57BL/6 glucose-stimulated islets.
Figure 6
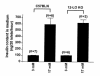
Nitrate/nitrite determination in 12-LO KO and C57BL/6 peritoneal macrophages. Peritoneal macrophages were purified as described in Methods and stimulated with LPS (2 μg/mL) + IFN-γ (100 ng/mL) for 48 hours. We used Griess reagent to measure total medium nitrate/nitrite as an estimate of NO production. As shown, 12-LO KO macrophages generated ∼50% of the NO of C57BL/6 macrophages under the conditions described. Six individual experiments were performed with macrophages isolated from both strains of mice. *P < 0.0001 vs. C57BL/6 macrophages.
Figure 7
Generation of superoxide by 12-LO KO and C57BL/6 macrophages. Purified macrophages were treated with PMA (50 ng/mL), and superoxide generation was measured by monitoring the reduction of ferricytochrome c to ferrocytochrome_c_ at 550 λ over time. As shown, no difference was observed in superoxide generation. Eight individual experiments were performed with macrophages isolated from both strains of mice.
Similar articles
- Interleukin-18 mRNA, but not interleukin-18 receptor mRNA, is constitutively expressed in islet beta-cells and up-regulated by interferon-gamma.
Hong TP, Andersen NA, Nielsen K, Karlsen AE, Fantuzzi G, Eizirik DL, Dinarello CA, Mandrup-Poulsen T. Hong TP, et al. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2000 Jun;11(2):193-205. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2000. PMID: 10903798 - Induction of cyclooxygenase-2 gene in pancreatic beta-cells by 12-lipoxygenase pathway product 12-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid.
Han X, Chen S, Sun Y, Nadler JL, Bleich D. Han X, et al. Mol Endocrinol. 2002 Sep;16(9):2145-54. doi: 10.1210/me.2001-0300. Mol Endocrinol. 2002. PMID: 12198250 - Nitric oxide mediates cytokine-induced inhibition of insulin secretion by human islets of Langerhans.
Corbett JA, Sweetland MA, Wang JL, Lancaster JR Jr, McDaniel ML. Corbett JA, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1731-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1731. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993. PMID: 8383325 Free PMC article. - The role of 12-lipoxygenase in pancreatic -cells (Review).
Bleich D, Chen S, Gu JL, Nadler JL. Bleich D, et al. Int J Mol Med. 1998 Jan;1(1):265-72. Int J Mol Med. 1998. PMID: 9852229 Review. - Effector mechanisms in low-dose streptozotocin-induced diabetes.
Lukić ML, Stosić-Grujicić S, Shahin A. Lukić ML, et al. Dev Immunol. 1998;6(1-2):119-28. doi: 10.1155/1998/92198. Dev Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9716913 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Group VIA Phospholipase A2 (iPLA2β) Modulates Bcl-x 5'-Splice Site Selection and Suppresses Anti-apoptotic Bcl-x(L) in β-Cells.
Barbour SE, Nguyen PT, Park M, Emani B, Lei X, Kambalapalli M, Shultz JC, Wijesinghe D, Chalfant CE, Ramanadham S. Barbour SE, et al. J Biol Chem. 2015 Apr 24;290(17):11021-31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.648956. Epub 2015 Mar 11. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25762722 Free PMC article. - Minireview: 12-Lipoxygenase and Islet β-Cell Dysfunction in Diabetes.
Tersey SA, Bolanis E, Holman TR, Maloney DJ, Nadler JL, Mirmira RG. Tersey SA, et al. Mol Endocrinol. 2015 Jun;29(6):791-800. doi: 10.1210/me.2015-1041. Epub 2015 Mar 24. Mol Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25803446 Free PMC article. Review. - 12/15-Lipoxygenase signaling in the endoplasmic reticulum stress response.
Cole BK, Kuhn NS, Green-Mitchell SM, Leone KA, Raab RM, Nadler JL, Chakrabarti SK. Cole BK, et al. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Mar 15;302(6):E654-65. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00373.2011. Epub 2012 Jan 3. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22215650 Free PMC article. - Elimination of negative feedback control mechanisms along the insulin signaling pathway improves beta-cell function under stress.
Gurevitch D, Boura-Halfon S, Isaac R, Shahaf G, Alberstein M, Ronen D, Lewis EC, Zick Y. Gurevitch D, et al. Diabetes. 2010 Sep;59(9):2188-97. doi: 10.2337/db09-0890. Epub 2010 Jun 14. Diabetes. 2010. PMID: 20547979 Free PMC article. - Role of uncoupling protein UCP2 in cell-mediated immunity: how macrophage-mediated insulitis is accelerated in a model of autoimmune diabetes.
Emre Y, Hurtaud C, Karaca M, Nubel T, Zavala F, Ricquier D. Emre Y, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Nov 27;104(48):19085-90. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0709557104. Epub 2007 Nov 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 18006654 Free PMC article.
References
- Bleich D, Chen S, Gu J-L, Nadler JL. The role of 12-lipoxygenase in pancreatic β-cells. Int J Mol Med. 1998;1:265–272. - PubMed
- Turk J, Colca J, Kotagal N, McDaniel M. Arachidonic acid metabolism in isolated pancreatic islets. I. Identification and quantitation of lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase products. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984;794:110–124. - PubMed
- Turk J, Colca J, McDaniel M. Arachidonic acid metabolism in isolated pancreatic islets. III. Effects of exogenous lipoxygenase products and inhibitors on insulin secretion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984;834:23–36. - PubMed
- Turk J, et al. Arachidonic acid metabolism in isolated pancreatic islets. IV. Negative ion mass spectrometric quantitation of monooxygenase product synthesis by liver and islets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985;835:1–17. - PubMed
- Turk J, Wolf BA, Easom RA, Hughes JH, McDaniel ML. Arachidonic acid metabolism in isolated pancreatic islets. V. The enantiomeric composition of 12-hydroxy-(5,8,10,14)-eicosatetraenoic acid indicates synthesis by a 12-lipoxygenase rather than monooxygenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989;1001:16–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials