Arabidopsis det2 is defective in the conversion of (24R)-24-methylcholest-4-En-3-one to (24R)-24-methyl-5alpha-cholestan-3-one in brassinosteroid biosynthesis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Arabidopsis det2 is defective in the conversion of (24R)-24-methylcholest-4-En-3-one to (24R)-24-methyl-5alpha-cholestan-3-one in brassinosteroid biosynthesis
T Noguchi et al. Plant Physiol. 1999 Jul.
Abstract
Previously, we have shown that the Arabidopsis det2 (deetiolated2) mutant is defective in the biosynthesis of brassinosteroids (BR) and that DET2 (a steroid 5alpha-reductase) acts early in the proposed BR biosynthetic pathway. In this paper we present further biochemical characterization of det2. We have undertaken metabolic experiments with 2H-labeled substrates of intermediates involved in the formation of campestanol from campesterol, and quantitative analysis of intermediates in Arabidopsis wild type and det2. The results of these studies indicate the early operating steps of BR biosynthesis as: campesterol --> 4-en-3beta-ol --> 4-en-3-one --> 3-one --> campestanol in Arabidopsis, with det2 deficient in the conversion of 4-en-3-one to 3-one. We have also detected these intermediates in the formation of campestanol from campesterol and their metabolic conversions using cultured cells of Catharanthus roseus. These studies confirmed the biosynthetic sequence of events from campesterol to campestanol as was found in Arabidopsis. As such, the originally proposed biosynthetic pathway should be modified.
Figures
Figure 1
Metabolism of 2H-labeled sterols in Arabidopsis (wild type and det2) and C. roseus (V208 cultured cells). ○, Substrate; •, metabolite; W, Arabidopsis wild type; d, Arabidopsis det2; and V, C. roseus V208 cultured cells. Values in parentheses indicate conversion rates.
Figure 2
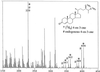
GC-MS analysis of 4-en-3-one fraction obtained from feeding [2H6]campesterol to the Arabidopsis wild type. *, Metabolite; #, endogenous.
Figure 3
GC-MS analysis of 4-en-3β-ol fraction obtained from feeding [2H6]campesterol to the Arabidopsis det2 mutant. *, Metabolite; #, endogenous.
Figure 4
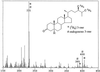
GC-MS analysis of 3-one fraction obtained from feeding [2H6]4-en-3-one to the Arabidopsis wild type. *, Metabolite; #, endogenous.
Figure 5
Proposed biosynthetic pathway for BL indicating the blocked step in the det2 mutant. Mevalonic acid.
References
- Altmann T. Recent advances in brassinosteroid molecular genetics. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 1998;1:378–383. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials