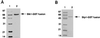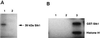Characterization of a Hank's type serine/threonine kinase and serine/threonine phosphoprotein phosphatase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa - PubMed (original) (raw)
Characterization of a Hank's type serine/threonine kinase and serine/threonine phosphoprotein phosphatase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
S Mukhopadhyay et al. J Bacteriol. 1999 Nov.
Abstract
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an opportunistic pathogen that causes infections in eye, urinary tract, burn, and immunocompromised patients. We have cloned and characterized a serine/threonine (Ser/Thr) kinase and its cognate phosphoprotein phosphatase. By using oligonucleotides from the conserved regions of Ser/Thr kinases of mycobacteria, an 800-bp probe was used to screen P. aeruginosa PAO1 genomic library. A 20-kb cosmid clone was isolated, from which a 4.5-kb DNA with two open reading frames (ORFs) were subcloned. ORF1 was shown to encode Ser/Thr phosphatase (Stp1), which belongs to the PP2C family of phosphatases. Overlapping with the stp1 ORF, an ORF encoding Hank's type Ser/Thr kinase was identified. Both ORFs were cloned in pGEX-4T1 and expressed in Escherichia coli. The overexpressed proteins were purified by glutathione-Sepharose 4B affinity chromatography and were biochemically characterized. The Stk1 kinase is 39 kDa and undergoes autophosphorylation and can phosphorylate eukaryotic histone H1. A site-directed Stk1 (K86A) mutant was shown to be incapable of autophosphorylation. A two-dimensional phosphoamino acid analysis of Stk1 revealed strong phosphorylation at a threonine residue and weak phosphorylation at a serine residue. The Stp1 phosphatase is 27 kDa and is an Mn(2+)-, but not a Ca(2+)- or a Mg(2+)-, dependent Ser/Thr phosphatase. Its activity is inhibited by EDTA and NaF, but not by okadaic acid, and is similar to that of PP2C phosphatase.
Figures
FIG. 1
Genetic organization of the Ser/Thr phosphatase (stp1) and Ser/Thr kinase (stk1) of P. aeruginosa PAO1. A 4.5-kb _Eco_RI fragment encodes two overlapping ORFs, stp1 and stk1. The stp1 ORF is 726 bp and encodes a Ser/Thr phosphatase belonging to the PP2C family. The stk1 ORF is 987 bp and encodes a Hank’s type Ser/Thr kinase. Upstream of stp1 is an ORF with sequence similarity to the L. pneumophila icmF gene. A search of the P. aeruginosa genome database indicated the presence of yet another ORF with very little intervening sequence, suggesting that stp1 and stk1 genes might be a part of a regulon.
FIG. 2
(A) Amino acid sequence alignment of P. aeruginosa (P.a) Stk1 with M. tuberculosis (M.t), S. coelicolor (S.c), and M. xanthus (M.x) kinases. The conserved residues are indicated by the asterisk, and various motifs described in the text are marked. (B) Amino acid sequence alignment of P. aeruginosa (P.a) Stp1 with M. tuberculosis (M.t) and B. subtilis (B.s) phosphatases. The conserved residues are indicated by the asterisk, and various motifs described in the text are marked.
FIG. 3
(A) Purification of the P. aeruginosa Stk1 as a GST fusion in E. coli. Lanes 1, molecular mass standards; 2, Stk1-GST fusion protein (67 kDa). (B) Purification of the P. aeruginosa Stp1 as a GST fusion in E. coli. Lanes 1, molecular mass standards; 2, Stp1-GST fusion protein (53 kDa).
FIG. 4
(A) Autophosphorylation of the purified Stk1 (wild-type) and Stk1 (K86A) mutant proteins by using [γ-32P]ATP. First, 2 μg of the purified kinase and the K86A mutant protein were incubated with [γ-32P]ATP in TMD buffer for 10 min before being loaded onto an SDS–12.5% PAGE gel. A 39-kDa phosphorylated band was observed in lane 1 (wild-type Stk1), whereas no such phosphorylated band was observed with the mutant protein (lane 2). (B) Phosphorylation of the histone H1 protein by Stk1. A total of 2 μg of histone H1 was incubated with 2 μg of the GST-Stk1 for 10 min. The reaction mixture was analyzed on an SDS–12% PAGE gel and autoradiographed. Lane 1, boiled Stk1 plus histone H1 plus [γ-32P]ATP; lane 2, histone H1 plus [γ-32P]ATP; lane 3, Stk1 plus histone H1 plus [γ-32P]ATP.
FIG. 5
(A) Phosphoamino acid analysis of the purified Ser/Thr kinase, Stk1, from P. aeruginosa. Stk1 was expressed in E. coli and purified as a T7-tag fusion protein. The kinase was autophosphorylated and two-dimensional phosphoamino acid analysis was performed as described in Materials and Methods. Threonine is strongly phosphorylated, and serine is weakly phosphorylated, whereas tyrosine is not phosphorylated at all. (B) Ninhydrin staining of the TLC plate showing the relative positions of the phosphoamino acids.
FIG. 6
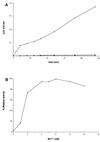
(A) Effect of divalent cations on the Stp1 activity as determined by pNPP hydrolysis. Symbols: Mn++ (□), Ca++ (■), Mg++ (⧫). (B) Effect of manganese ion concentration on the Stp1 activity as determined by pNPP hydrolysis.
FIG. 7
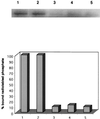
Activity of the purified P. aeruginosa Stp1 phosphatase overexpressed in E. coli. Phosphorylated casein was treated with the purified Stp1, and the dephosphorylated casein protein was analyzed by SDS–12.5% PAGE. Lane 1, phosphorylated casein (unboiled); lane 2, phosphorylated casein (boiled); lanes 3, 4, and 5, phosphorylated casein incubated with the purified Stp1 phosphatase for 30, 60, and 90 min, respectively. The radioactivities were measured by a phosphorimager, and the percent bound radioactivities are depicted below.
FIG. 8
RT-PCR analysis showing the contranscription of stp1 and stk1 genes from P. aeruginosa PAO1. Lanes: A, DNA markers (kilobases); B, primer combination 1 and 2; C, primer combination 3 and 4; D, primer combination 7 and 4; E, primer combination 1 and 5; F, primer combination 1 and 6; G, primer combination 3 and 8. All of the PCR products were of the expected sizes, and there was no amplification of the cDNA when primers 3 and 8 were used (control).
FIG. 9
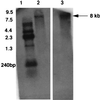
Northern blot analysis of the stp1 and stk1 genes from P. aeruginosa. Lanes: 1, RNA markers; 2, RNA probed with stp1 gene; 3, RNA probed with the stk1 gene.
Similar articles
- Identification of two eukaryote-like serine/threonine kinases encoded by Chlamydia trachomatis serovar L2 and characterization of interacting partners of Pkn1.
Verma A, Maurelli AT. Verma A, et al. Infect Immun. 2003 Oct;71(10):5772-84. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.10.5772-5784.2003. Infect Immun. 2003. PMID: 14500499 Free PMC article. - Identification and Biochemical Characterization of a Novel Protein Phosphatase 2C-Like Ser/Thr Phosphatase in Escherichia coli.
Rajagopalan K, Dworkin J, Nagle E. Rajagopalan K, et al. J Bacteriol. 2018 Aug 24;200(18):e00225-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00225-18. Print 2018 Sep 15. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 29967116 Free PMC article. - Survey, analysis and genetic organization of genes encoding eukaryotic-like signaling proteins on a cyanobacterial genome.
Zhang CC, Gonzalez L, Phalip V. Zhang CC, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998 Aug 15;26(16):3619-25. doi: 10.1093/nar/26.16.3619. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998. PMID: 9685474 Free PMC article. Review. - The serine, threonine, and/or tyrosine-specific protein kinases and protein phosphatases of prokaryotic organisms: a family portrait.
Shi L, Potts M, Kennelly PJ. Shi L, et al. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1998 Oct;22(4):229-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.1998.tb00369.x. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1998. PMID: 9862122 Review.
Cited by
- Regulatory interactions of a virulence-associated serine/threonine phosphatase-kinase pair in Bacillus anthracis.
Shakir SM, Bryant KM, Larabee JL, Hamm EE, Lovchik J, Lyons CR, Ballard JD. Shakir SM, et al. J Bacteriol. 2010 Jan;192(2):400-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.01221-09. Epub 2009 Nov 13. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 19915022 Free PMC article. - Impacts of Ser/Thr Protein Kinase Stk1 on the Proteome, Twitching Motility, and Competitive Advantage in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Zhu X, Feng C, Zhou L, Li Z, Zhang Y, Pan J. Zhu X, et al. Front Microbiol. 2021 Sep 22;12:738690. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.738690. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34733256 Free PMC article. - Dimerization of the RamC morphogenetic protein of Streptomyces coelicolor.
Hudson ME, Nodwell JR. Hudson ME, et al. J Bacteriol. 2004 Mar;186(5):1330-6. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.5.1330-1336.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 14973038 Free PMC article. - Quorum sensing regulation of the two hcp alleles in Vibrio cholerae O1 strains.
Ishikawa T, Rompikuntal PK, Lindmark B, Milton DL, Wai SN. Ishikawa T, et al. PLoS One. 2009 Aug 24;4(8):e6734. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006734. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19701456 Free PMC article. - Modulation of cell wall structure and antimicrobial susceptibility by a Staphylococcus aureus eukaryote-like serine/threonine kinase and phosphatase.
Beltramini AM, Mukhopadhyay CD, Pancholi V. Beltramini AM, et al. Infect Immun. 2009 Apr;77(4):1406-16. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01499-08. Epub 2009 Feb 2. Infect Immun. 2009. PMID: 19188361 Free PMC article.
References
- Bettina C B, Sadosky A B, Shuman H A. The Legionella pneumophilia icm locus: a set of genes required for intracellular multiplication in macrophages. Mol Microbiol. 1994;14:797–808. - PubMed
- Boyle J W, Geer P V D, Hunter T. Phosphopeptide mapping and phosphoaminoacid analysis by two-dimensional separation on thin-layer cellulose plates. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:110–149. - PubMed
- Cole S T, Brosch R, Parkhill J, Garnier T, Churcher C, Harris D, Gordon S V, Eiglmeier K, Gas S, Barry III C E, Tekaia F, Badcock K, Basham D, Brown D, Chillingworth T, Connor R, Davies R, Devlin K, Feltwell T, Gentles S, Hamlin N, Holroyd S, Hornsby T, Jagels K, Krogh A, McLean J, Moule S, Murphy L, Oliver K, Osborne J, Rajandream M-A, Rogers J, Rutter S, Seeger K, Skelton J, Squares R, Squares S, Sulston J E, Taylor K, Whitehead S, Barrell B G. Deciphering the biology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from the complete genome sequence. Nature. 1998;393:537–544. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous