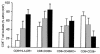Weak anti-HIV CD8(+) T-cell effector activity in HIV primary infection - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 1999 Nov;104(10):1431-9.
doi: 10.1172/JCI7162.
M Dupuis, J C Deschemin, C Goujard, C Deveau, L Meyer, N Ngo, C Rouzioux, J G Guillet, J F Delfraissy, M Sinet, A Venet
Affiliations
- PMID: 10562305
- PMCID: PMC409838
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI7162
Weak anti-HIV CD8(+) T-cell effector activity in HIV primary infection
M Dalod et al. J Clin Invest. 1999 Nov.
Abstract
HIV-specific CD8(+) T cells play a major role in the control of virus during HIV primary infection (PI) but do not completely prevent viral replication. We used IFN-gamma enzyme-linked immunospot assay and intracellular staining to characterize the ex vivo CD8(+) T-cell responses to a large variety of HIV epitopic peptides in 24 subjects with early HIV PI. We observed HIV-specific responses in 71% of subjects. Gag and Nef peptides were more frequently recognized than Env and Pol peptides. The number of peptides recognized was low (median 2, range 0-6). In contrast, a much broader response was observed in 30 asymptomatic subjects with chronic infection: all were responders with a median of 5 peptides recognized (range 1-13). The frequency of HIV-specific CD8(+) T cells among PBMC for a given peptide was of the same order of magnitude in both groups. The proportion of HIV-specific CD8(+)CD28(-) terminally differentiated T cells was much lower in PI than at the chronic stage of infection. The weakness of the immune response during HIV PI could partially account for the failure to control HIV. These findings have potential importance for defining immunotherapeutic strategies and establishing the goals for effective vaccination.
Figures
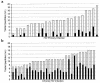
Figure 1
Comparison of anti-HIV CD8+ T-cell responses of HIV-infected subjects in PI (a) and during chronic infection (b). The Y axis represents the numbers of tested peptides; black bars show numbers of recognized peptides; and white bars show numbers of peptides not recognized. Each bar on the X axis represents the data obtained for 1 individual.
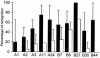
Figure 2
Comparison of the frequencies of anti-HIV CD8+ T-cell responses for different HLA restriction elements. The mean percentages (and standard deviation) of viral epitopic peptides recognized are shown for each HLA restriction element for HIV-infected individuals during PI (open bars) or chronic infection (filled bars).
Figure 3
Level of CD8+ T-cell activation in peripheral blood. Bars represent percentages (±SD) of CD8+HLA-DR+, CD8+CD38+, CD8+CD45RO+, and CD8+CD28+ in PBMC of HIV-infected subjects during PI (gray bars) and chronic infection (black bars) as compared with control HIV-seronegative individuals (white bars).
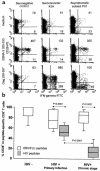
Figure 4
Comparison of the proportion of CD8+CD28+ T cells specific for HIV or other viral peptides among CD8+ T cells. (a) Representative experiments from 3 HLA-B8–expressing individuals where PBMC were incubated in medium alone or stimulated with peptides EBNA-3 325-333 derived from EBV and Gag 259-267 from HIV-1. IFN-γ intracellular production (x axis) and CD28 expression (y axis) were analyzed on gated CD8+ T lymphocytes. 200,000 events were acquired for subject KJA and 400,000 for the other individuals. Absolute numbers of events are indicated in the right quadrants of each dot-plot. (b) Boxes representing the fraction of CD8+ CD28+ T cells (25th–75th percentile) specific for HIV peptides (gray boxes) or for influenza or EBV peptides (white boxes) in subjects with PI (n = 14) or chronic HIV infection (n = 14), and seronegative controls (n = 4).
Similar articles
- Cytolytic T lymphocytes (CTLs) from HIV-1 subtype C-infected Indian patients recognize CTL epitopes from a conserved immunodominant region of HIV-1 Gag and Nef.
Thakar MR, Bhonge LS, Lakhashe SK, Shankarkumar U, Sane SS, Kulkarni SS, Mahajan BA, Paranjape RS. Thakar MR, et al. J Infect Dis. 2005 Sep 1;192(5):749-59. doi: 10.1086/432547. Epub 2005 Jul 27. J Infect Dis. 2005. PMID: 16088824 - Poor recognition of HIV-1 Nef protein by CD8 T cells from HIV-1-infected children: impact of age.
Buseyne F, Scott-Algara D, Corre B, Porrot F, Monchatre E, Bellal N, Burgard M, Rouzioux C, Blanche S, Rivière Y. Buseyne F, et al. Virology. 2006 Oct 25;354(2):271-9. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.07.014. Epub 2006 Aug 10. Virology. 2006. PMID: 16904156 - Terminally differentiated CD8 cells in HIV-infected children: HIV-GAG/POL specificity and IFN-γ production.
Delbeck D, Siepermann M, Feyen O, Wirth S, Baumann U, Wintergerst U, Oette M, Adam R, Jetzek-Zader M, Niehues T. Delbeck D, et al. Klin Padiatr. 2011 Jul;223(4):214-20. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1269917. Epub 2011 Apr 6. Klin Padiatr. 2011. PMID: 21472637 - Viral Inhibitory Activity of CD8+ T Cells in HIV Infection.
Pannus P, Vanham G. Pannus P, et al. AIDS Rev. 2019;21(3):115-125. doi: 10.24875/AIDSRev.19000068. AIDS Rev. 2019. PMID: 31532399 Review. - Therapeutic role of CD8+ T cells in HIV-1 infection: targets and suppressors of viral replication.
Meireles-de-Souza LR, Shattock RJ. Meireles-de-Souza LR, et al. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2005 Mar;5(3):321-32. doi: 10.1517/14712598.5.3.321. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2005. PMID: 15833070 Review.
Cited by
- Dynamic correlation between CTL response and viral load in primary human immunodeficiency virus-1 infected Koreans.
Kim GJ, Lee HS, Hong KJ, Kim SS. Kim GJ, et al. Virol J. 2010 Sep 16;7:239. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-7-239. Virol J. 2010. PMID: 20846412 Free PMC article. - Changes in function of HIV-specific T-cell responses with increasing time from infection.
Ndongala ML, Kamya P, Boulet S, Peretz Y, Rouleau D, Tremblay C, Leblanc R, Côté P, Baril JG, Thomas R, Vézina S, Boulassel MR, Routy JP, Sékaly RP, Bernard NF. Ndongala ML, et al. Viral Immunol. 2010 Apr;23(2):159-68. doi: 10.1089/vim.2009.0084. Viral Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20373996 Free PMC article. - HLA Alleles Associated with Delayed Progression to AIDS Contribute Strongly to the Initial CD8(+) T Cell Response against HIV-1.
Altfeld M, Kalife ET, Qi Y, Streeck H, Lichterfeld M, Johnston MN, Burgett N, Swartz ME, Yang A, Alter G, Yu XG, Meier A, Rockstroh JK, Allen TM, Jessen H, Rosenberg ES, Carrington M, Walker BD. Altfeld M, et al. PLoS Med. 2006 Oct;3(10):e403. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0030403. PLoS Med. 2006. PMID: 17076553 Free PMC article. - Influence of dominant HIV-1 epitopes on HLA-A3/peptide complex formation.
Racape J, Connan F, Hoebeke J, Choppin J, Guillet JG. Racape J, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Nov 28;103(48):18208-13. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0609029103. Epub 2006 Nov 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 17116886 Free PMC article. - Living in a house of cards: re-evaluating CD8+ T-cell immune correlates against HIV.
Makedonas G, Betts MR. Makedonas G, et al. Immunol Rev. 2011 Jan;239(1):109-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2010.00968.x. Immunol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21198668 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Pantaleo G, Graziosi C, Fauci AS. Virologic and immunologic events in primary HIV infection. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1997;18:257–266. - PubMed
- Kahn JO, Walker BD. Acute human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:33–39. - PubMed
- Schmitz JE, et al. Control of viremia in simian immunodeficiency virus infection by CD8+ lymphocytes. Science. 1999;283:857–860. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous