BAFF binds to the tumor necrosis factor receptor-like molecule B cell maturation antigen and is important for maintaining the peripheral B cell population - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2000 Jul 3;192(1):129-35.
doi: 10.1084/jem.192.1.129.
P Schneider, S L Kalled, L Wang, E A Lefevre, T G Cachero, F MacKay, S A Bixler, M Zafari, Z Y Liu, S A Woodcock, F Qian, M Batten, C Madry, Y Richard, C D Benjamin, J L Browning, A Tsapis, J Tschopp, C Ambrose
Affiliations
- PMID: 10880534
- PMCID: PMC1887706
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.192.1.129
BAFF binds to the tumor necrosis factor receptor-like molecule B cell maturation antigen and is important for maintaining the peripheral B cell population
J S Thompson et al. J Exp Med. 2000.
Abstract
The tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family member B cell activating factor (BAFF) binds B cells and enhances B cell receptor-triggered proliferation. We find that B cell maturation antigen (BCMA), a predicted member of the TNF receptor family expressed primarily in mature B cells, is a receptor for BAFF. Although BCMA was previously localized to the Golgi apparatus, BCMA was found to be expressed on the surface of transfected cells and tonsillar B cells. A soluble form of BCMA, which inhibited the binding of BAFF to a B cell line, induced a dramatic decrease in the number of peripheral B cells when administered in vivo. Moreover, culturing splenic cells in the presence of BAFF increased survival of a percentage of the B cells. These results are consistent with a role for BAFF in maintaining homeostasis of the B cell population.
Figures
Figure 1
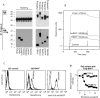
The extracellular domain of BCMA interacts with BAFF. (A) Human BCMA-Ig and various control TNFR-Ig molecules were mixed with Flag-tagged TNF ligands, immunoprecipitated (IP) with protein A Sepharose, and analyzed by Western blot (WB). Receptor-Ig is revealed with anti–human IgG (top), and coimmunoprecipitating ligands are detected using anti-Flag M2 antibody (bottom). α, anti-. (B) Interaction of BAFF with BCMA assayed by surface plasmon resonance (BIAcore). (C) BCMA-Ig binds stable 293 cell line expressing surface full-length BAFF. The wild-type 293 cells or a stable cell line expressing BAFF (reference 2) were stained with media containing similar amounts of BCMA-Ig, TNFR2-Ig, TRAILR2-Ig, or control media using PE-conjugated anti-hIgG1 (left and middle). The presence of surface BAFF was detected using an anti-hBAFF rat mAb, 43.9 (reference 2; right). (D) BCMA-Ig blocks BAFF binding to Raji cells. Various concentrations of either BCMA-Ig or LTβR-Ig were preincubated with Flag-BAFF, then added to Raji cells. BAFF binding was detected with the anti-Flag M2 antibody and analyzed by flow cytometry.
Figure 2
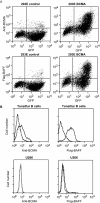
Cell surface expression of BCMA in transfected and primary cells. (A) 293E cells were cotransfected with expression vectors for green fluorescent protein (GFP) and full-length human BCMA or a control plasmid. Surface expression of BCMA was detected with either an anti-BCMA antibody (top) or Flag-BAFF (bottom). (B) Human tonsillar B cells and the U266 plasmocytic cell line were stained with either anti-BCMA, control rabbit antibody, or Flag-BAFF, and were analyzed by flow cytometry.
Figure 3
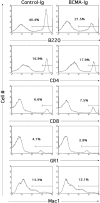
Administration of BCMA-Ig reduces the peripheral B cell population. Adult Balb/c mice were treated with four intraperitoneal injections of BCMA-Ig or control Ig over a period of 11 d. At day 19, splenic B220+ B cells, CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, and Gr1+ and Mac-1+ populations were analyzed by flow cytometry. A representative mouse from each group is shown.
Figure 4
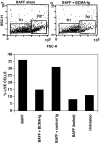
BAFF promotes the survival of splenocytes in vitro. (A) Forward (FSC) and side scatter (SSC) profiles of murine splenocytes in culture after 72 h in the presence or absence of BAFF. The R2 gate contains live cells (annexin V and propidium iodide negative). (B) Percentage of R2 cells surviving. BAFF concentration was 2 μg/ml, and fusion proteins were added at 10 μg/ml. This is a representative experiment of the assay done ∼10 times.
Similar articles
- B-cell maturation protein, which binds the tumor necrosis factor family members BAFF and APRIL, is dispensable for humoral immune responses.
Xu S, Lam KP. Xu S, et al. Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Jun;21(12):4067-74. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.12.4067-4074.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11359913 Free PMC article. - B cell maturation antigen, the receptor for a proliferation-inducing ligand and B cell-activating factor of the TNF family, induces antigen presentation in B cells.
Yang M, Hase H, Legarda-Addison D, Varughese L, Seed B, Ting AT. Yang M, et al. J Immunol. 2005 Sep 1;175(5):2814-24. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.5.2814. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16116167 - An essential role for BAFF in the normal development of B cells through a BCMA-independent pathway.
Schiemann B, Gommerman JL, Vora K, Cachero TG, Shulga-Morskaya S, Dobles M, Frew E, Scott ML. Schiemann B, et al. Science. 2001 Sep 14;293(5537):2111-4. doi: 10.1126/science.1061964. Epub 2001 Aug 16. Science. 2001. PMID: 11509691 - BAFF and the regulation of B cell survival.
Schneider P, Tschopp J. Schneider P, et al. Immunol Lett. 2003 Jul 3;88(1):57-62. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2478(03)00050-6. Immunol Lett. 2003. PMID: 12853163 Review. - Actions of BAFF in B cell maturation and its effects on the development of autoimmune disease.
Melchers F. Melchers F. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003 Nov;62 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):ii25-7. doi: 10.1136/ard.62.suppl_2.ii25. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003. PMID: 14532143 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- CNS Autoimmune Responses in BCMA-Deficient Mice Provide Insight for the Failure of Atacicept in MS.
Kumar G, Maria Z, Kohli U, Agasing A, Quinn JL, Ko RM, Zamvil SS, Axtell RC. Kumar G, et al. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2021 Mar 1;8(3):e973. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000973. Print 2021 May. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2021. PMID: 33649164 Free PMC article. - Current status of BAFF targeting immunotherapy in B-cell neoplasm.
Tagami N, Yuda J, Goto Y. Tagami N, et al. Int J Clin Oncol. 2024 Nov;29(11):1676-1683. doi: 10.1007/s10147-024-02611-2. Epub 2024 Sep 2. Int J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39222149 Free PMC article. Review. - BAFF selectively enhances the survival of plasmablasts generated from human memory B cells.
Avery DT, Kalled SL, Ellyard JI, Ambrose C, Bixler SA, Thien M, Brink R, Mackay F, Hodgkin PD, Tangye SG. Avery DT, et al. J Clin Invest. 2003 Jul;112(2):286-97. doi: 10.1172/JCI18025. J Clin Invest. 2003. PMID: 12865416 Free PMC article. - Targeting B Cell Maturation Antigen (BCMA) in Multiple Myeloma: Potential Uses of BCMA-Based Immunotherapy.
Cho SF, Anderson KC, Tai YT. Cho SF, et al. Front Immunol. 2018 Aug 10;9:1821. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01821. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30147690 Free PMC article. Review. - Replacing mouse BAFF with human BAFF does not improve B-cell maturation in hematopoietic humanized mice.
Lang J, Zhang B, Kelly M, Peterson JN, Barbee J, Freed BM, Di Santo JP, Matsuda JL, Torres RM, Pelanda R. Lang J, et al. Blood Adv. 2017 Dec 19;1(27):2729-2741. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2017010090. eCollection 2017 Dec 26. Blood Adv. 2017. PMID: 29296925 Free PMC article.
References
- Gravestein L.A., Borst J. Tumor necrosis factor receptor family members in the immune system. Semin. Immunol. 1998;10:423–434. - PubMed
- Shu H.-B., Hu W.-H., Johnson H. TALL-1 is a novel member of the TNF family that is down-regulated by mitogens. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1999;65:680–683. - PubMed
- Mukhopadhyay A., Ni J., Zhai Y., Yu G.-L., Aggarwal B.B. Identification and characterization of a novel cytokine, THANK, a TNF homologue that activates apoptosis, nuclear factor-κB, and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:15978–15981. - PubMed
- Moore P.A., Belvedere O., Orr A., Pieri K., LaFleur D.W., Feng P., Soppet D., Charters M., Gentz R., Parmelee D. BLySmember of the tumor necrosis factor family and B lymphocyte stimulator. Science. 1999;285:260–263. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials