Genetic characterization of the Klebsiella pneumoniae waa gene cluster, involved in core lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Genetic characterization of the Klebsiella pneumoniae waa gene cluster, involved in core lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis
M Regué et al. J Bacteriol. 2001 Jun.
Abstract
A recombinant cosmid containing genes involved in Klebsiella pneumoniae C3 core lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis was identified by its ability to confer bacteriocin 28b resistance to Escherichia coli K-12. The recombinant cosmid contains 12 genes, the whole waa gene cluster, flanked by kbl and coaD genes, as was found in E. coli K-12. PCR amplification analysis showed that this cluster is conserved in representative K. pneumoniae strains. Partial nucleotide sequence determination showed that the same genes and gene order are found in K. pneumoniae subsp. ozaenae, for which the core chemical structure is known. Complementation analysis of known waa mutants from E. coli K-12 and/or Salmonella enterica led to the identification of genes involved in biosynthesis of the inner core backbone that are shared by these three members of the Enterobacteriaceae. K. pneumoniae orf10 mutants showed a two-log-fold reduction in a mice virulence assay and a strong decrease in capsule amount. Analysis of a constructed K. pneumoniae waaE deletion mutant suggests that the WaaE protein is involved in the transfer of the branch beta-D-Glc to the O-4 position of L-glycero-D-manno-heptose I, a feature shared by K. pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, and Yersinia enterocolitica.
Figures
FIG. 1
Comparative structure of the chemotype Rc core LPS of E. coli and S. enterica (A) (20) versus K. pneumoniae strain RFK-11 (B) (43, 45). In K. pneumoniae RFK-11 (O8−:K−), only two Kdo_p_ residues were detected (42). In K. pneumoniae R20 (O1−:K20−), a Glc_p_N residue substituted with a tetraglycan of α-1,2-linked
d
-_glycero_-
d
-_manno_-heptopyranose was found instead of Glc_p_ll (44). Dashed arrows denote modifications that are either nonstoichiometric or are confined to a particular core LPS type. P, phosphate; PPEtn, ethanolamine pyrophosphate.
FIG. 2
Physical map of plasmids used in this study. Plasmids conferring high- and low-level bacteriocin 28b resistance on E. coli NM554 are denoted by asterisks and underlined letters, respectively. The right-side _Bgl_II site corresponds to the junction between the insert and vector cosmid in recombinant cosmid pNUR8.
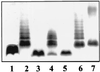
FIG. 3
E. coli NM554 harboring plasmids pNUR8 (lane 1), pNUR5 (lane 3), vector pLA2917 (lane 2), pBG3 (lane 4), pBG1 (lane 5), pNUC4 (lane 6), and pBG2 (lane 7). Similar results were obtained using the E. coli DH5α background.
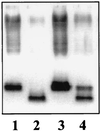
FIG. 4
SDS-Tricine-PAGE analysis of LPS from S. enterica serovar Typhimurium SA1377 (_waaC_630) (lane 1), SA1377 (pB1) (lane 2), SA1377 (pBG1) (lane 3), SA1377 (pGEMT-WaaC) (lane 4), SL3789 (waaF511) (lane 5), SL3789 (pB1) (lane 6), and SL3789 (pGEMT-WaaF) (lane 7).
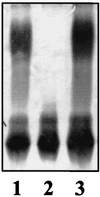
FIG. 5
SDS-PAGE analysis of LPS from K. pneumoniae 52145 (wild type) (lane 1), NC20 (waaL) (lane 2), and NC20 (pGEMT-WaaL).
FIG. 6
SDS-Tricine-PAGE analysis of LPS from K. pneumoniae 52145 (wild type) (lane 1), NC16 (waaE) (lane 2), NC16 (pGEMT-WaaE) (lane 3), and NC16 (pGLU) (lane 4).
Similar articles
- The inner-core lipopolysaccharide biosynthetic waaE gene: function and genetic distribution among some Enterobacteriaceae.
Izquierdo L, Abitiu N, Coderch N, Hita B, Merino S, Gavin R, Tomás JM, Regué M. Izquierdo L, et al. Microbiology (Reading). 2002 Nov;148(Pt 11):3485-3496. doi: 10.1099/00221287-148-11-3485. Microbiology (Reading). 2002. PMID: 12427940 - A second galacturonic acid transferase is required for core lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis and complete capsule association with the cell surface in Klebsiella pneumoniae.
Fresno S, Jiménez N, Canals R, Merino S, Corsaro MM, Lanzetta R, Parrilli M, Pieretti G, Regué M, Tomás JM. Fresno S, et al. J Bacteriol. 2007 Feb;189(3):1128-37. doi: 10.1128/JB.01489-06. Epub 2006 Dec 1. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17142396 Free PMC article. - [Research advances in the virulence factors of Klebsiella pneumoniae--A review].
Kang Y, Tian P, Tan T. Kang Y, et al. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2015 Oct 4;55(10):1245-52. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2015. PMID: 26939452 Review. Chinese. - Nucleotide sequence of rmpB, a Klebsiella pneumoniae gene that positively controls, colanic biosynthesis in Escherichia coli.
Vasselon T, Sansonetti PJ, Nassif X. Vasselon T, et al. Res Microbiol. 1991 Jan;142(1):47-54. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(91)90096-s. Res Microbiol. 1991. PMID: 2068379 Review.
Cited by
- The transcriptional regulator Fur modulates the expression of uge, a gene essential for the core lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis in Klebsiella pneumoniae.
Muner JJ, de Oliveira PAA, Baboghlian J, Moura SC, de Andrade AG, de Oliveira MM, Campos YF, Mançano ASF, Siqueira NMG, Pacheco T, Ferraz LFC. Muner JJ, et al. BMC Microbiol. 2024 Jul 27;24(1):279. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03418-x. BMC Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39061004 Free PMC article. - Designing phage cocktails to combat the emergence of bacteriophage-resistant mutants in multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae.
Yoo S, Lee K-M, Kim N, Vu TN, Abadie R, Yong D. Yoo S, et al. Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Jan 11;12(1):e0125823. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01258-23. Epub 2023 Nov 29. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38018985 Free PMC article. - Construction and application of the conditionally essential gene knockdown library in Klebsiella pneumoniae to screen potential antimicrobial targets and virulence genes via Mobile-CRISPRi-seq.
Zhu Q, Lin Q, Jiang Y, Chen S, Tian J, Yang S, Li Y, Li M, Wang Y, Shen C, Meng S, Yang L, Feng Y, Qu J. Zhu Q, et al. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023 Oct 31;89(10):e0095623. doi: 10.1128/aem.00956-23. Epub 2023 Oct 10. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37815340 Free PMC article. - Novel Virulence Factors Deciphering Klebsiella pneumoniae KpC4 Infect Maize as a Crossing-Kingdom Pathogen: An Emerging Environmental Threat.
Huang M, He P, He P, Wu Y, Munir S, He Y. Huang M, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 15;23(24):16005. doi: 10.3390/ijms232416005. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555647 Free PMC article. - High-Throughput Screen for Inhibitors of Klebsiella pneumoniae Virulence Using a Tetrahymena pyriformis Co-Culture Surrogate Host Model.
Woods AL, Parker D, Glick MM, Peng Y, Lenoir F, Mulligan E, Yu V, Piizzi G, Lister T, Lilly MD, Dzink-Fox J, Jansen JM, Ryder NS, Dean CR, Smith TM. Woods AL, et al. ACS Omega. 2022 Feb 1;7(6):5401-5414. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c06633. eCollection 2022 Feb 15. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 35187355 Free PMC article.
References
- Allen A G, Maskell D J. The identification, cloning and mutagenesis of a genetic locus required for lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis in Bordetella pertussis. Mol Microbiol. 1996;19:37–52. - PubMed
- Altschul S F, Gish W, Miller W, Myers E W, Lipman D. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous