Neurotrophins: roles in neuronal development and function - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Neurotrophins: roles in neuronal development and function
E J Huang et al. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2001.
Abstract
Neurotrophins regulate development, maintenance, and function of vertebrate nervous systems. Neurotrophins activate two different classes of receptors, the Trk family of receptor tyrosine kinases and p75NTR, a member of the TNF receptor superfamily. Through these, neurotrophins activate many signaling pathways, including those mediated by ras and members of the cdc-42/ras/rho G protein families, and the MAP kinase, PI-3 kinase, and Jun kinase cascades. During development, limiting amounts of neurotrophins function as survival factors to ensure a match between the number of surviving neurons and the requirement for appropriate target innervation. They also regulate cell fate decisions, axon growth, dendrite pruning, the patterning of innervation and the expression of proteins crucial for normal neuronal function, such as neurotransmitters and ion channels. These proteins also regulate many aspects of neural function. In the mature nervous system, they control synaptic function and synaptic plasticity, while continuing to modulate neuronal survival.
Figures
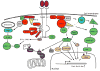
Figure 1
Schematic diagram of Trk receptor-mediated signal transduction pathways. Binding of neurotrophins to Trk receptors leads to the recruitment of proteins that interact with specific phosphotyrosine residues in the cytoplasmic domains of Trk receptors. These interactions lead to the activation of signaling pathways, such as the Ras, phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3k), and phospholipase C (PLC)-γ pathways, and ultimately result in activation of gene expression, neuronal survival, and neurite outgrowth (see text for detailed discussions and abbreviations). The nomenclature for tyrosine residues in the cytoplasmic domains of Trk receptors are based on the human sequence for TrkA. In this diagram, adaptor proteins are red, kinase green, small G proteins blue, and transcription factors brown.
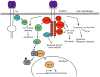
Figure 2
Schematic diagram of p75NTR-mediated signal transduction pathways. P75NTR interacts with proteins, including TRAF6, RhoA, NRAGE (neurotrophin receptor-interacting MAGE homologue), SC-1, and NRIF, and regulates gene expression, the cell cycle, apoptosis, mitogenic responses, and growth cone motility. Binding of neurotrophins to p75NTR has also been shown to activate the Jun kinase pathway, which can be inhibited by activation of the Ras-phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) pathway by Trk receptors. Similar to Figure 1, adaptor proteins are red, kinase green, small G proteins blue, and transcription factors brown. (See text for abbreviations.)
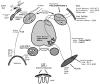
Figure 3
Summary of survival functions of neurotrophins in the peripheral nervous system. This diagram illustrates various components in the peripheral nervous system, including sensory ganglia, sympathetic ganglia, and enteric neurons. Only ligands or receptors with definitive loss of function phenotype are indicated in this figure. Ligands are indicated in italics and receptors are indicated in bold italics. (See text for abbreviations.)
Similar articles
- The biology of neurotrophins, signalling pathways, and functional peptide mimetics of neurotrophins and their receptors.
Skaper SD. Skaper SD. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2008 Feb;7(1):46-62. doi: 10.2174/187152708783885174. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2008. PMID: 18289031 Review. - Trk receptors: roles in neuronal signal transduction.
Huang EJ, Reichardt LF. Huang EJ, et al. Annu Rev Biochem. 2003;72:609-42. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.72.121801.161629. Epub 2003 Mar 27. Annu Rev Biochem. 2003. PMID: 12676795 Review. - Neurotrophins in cultured cells from periodontal tissues.
Kurihara H, Shinohara H, Yoshino H, Takeda K, Shiba H. Kurihara H, et al. J Periodontol. 2003 Jan;74(1):76-84. doi: 10.1902/jop.2003.74.1.76. J Periodontol. 2003. PMID: 12593600 Review. - The neurotrophin family of neurotrophic factors: an overview.
Skaper SD. Skaper SD. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;846:1-12. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-536-7_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22367796 Review. - Neurotrophic Factors: An Overview.
Skaper SD. Skaper SD. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1727:1-17. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7571-6_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29222769
Cited by
- Combination of Aβ clearance and neurotrophic factors as a potential treatment for Alzheimer's disease.
Lin LF, Liao MJ, Xue XY, Zhang W, Yan L, Cai L, Zhou XW, Zhou X, Luo HM. Lin LF, et al. Neurosci Bull. 2013 Feb;29(1):111-20. doi: 10.1007/s12264-012-1287-6. Epub 2012 Nov 21. Neurosci Bull. 2013. PMID: 23179066 Free PMC article. Review. - Blood Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) and Major Depression: Do We Have a Translational Perspective?
Arosio B, Guerini FR, Voshaar RCO, Aprahamian I. Arosio B, et al. Front Behav Neurosci. 2021 Feb 12;15:626906. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2021.626906. eCollection 2021. Front Behav Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33643008 Free PMC article. Review. - Porous Silicon Nanoparticles Targeted to the Extracellular Matrix for Therapeutic Protein Delivery in Traumatic Brain Injury.
Waggoner LE, Kang J, Zuidema JM, Vijayakumar S, Hurtado AA, Sailor MJ, Kwon EJ. Waggoner LE, et al. Bioconjug Chem. 2022 Sep 21;33(9):1685-1697. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.2c00305. Epub 2022 Aug 26. Bioconjug Chem. 2022. PMID: 36017941 Free PMC article. - A, B, C's of Trk Receptors and Their Ligands in Ocular Repair.
Gupta A, Galletti JG, Yu Z, Burgess K, de Paiva CS. Gupta A, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 15;23(22):14069. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214069. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430547 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Acheson A, Conover JC, Fandl JP, DeChiara TM, Russell M, et al. A BDNF autocrine loop in adult sensory neurons prevents cell death. Nature. 1995;374:450–53. - PubMed
- Agarwal ML, Taylor WR, Chernov MV, Chernova OB, Stark GR. The p53 network. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:1–4. - PubMed
- Airaksinen MS, Koltzenburg M, Lewin GR, Masu Y, Helbig C, et al. Specific subtypes of cutaneous mechanoreceptors require neurotrophin-3 following peripheral target innervation. Neuron. 1996;16:287–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous