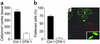CD4(+) T cells specific to a glomerular basement membrane antigen mediate glomerulonephritis - PubMed (original) (raw)
CD4(+) T cells specific to a glomerular basement membrane antigen mediate glomerulonephritis
Jean Wu et al. J Clin Invest. 2002 Feb.
Abstract
Ab-mediated mechanisms have been considered the major causes of glomerulonephritis (GN). However, recent studies suggest that T cells may be more important in mediating GN. To investigate the effects of antigen-specific CD4(+) T cells, we generated Th1 cell lines specific for this antigen from rats that had been immunized with a recombinant form of the glomerular basement membrane (GBM) antigen, Col4alpha3NC1. Upon the transfer of in vitro-activated T cell lines to pertussis toxin-primed, naive syngeneic rats, the recipients developed severe proteinuria/albuminuria, which plateaued after approximately 35 days. Although no IgG binding to GBM or C3 deposition could be detected by immunofluorescence, five out of eleven rats exhibited severe GN, as judged by the formation of characteristic crescent-shaped lesions in the glomeruli, whereas the others exhibited modest GN. Thus Col4alpha3NC1-specific T cells directly initiated glomerular injury in the recipients. One notable difference from GN induced by active immunization was a T cell infiltration in the renal interstitium, which affected some tubules. We therefore injected fluorescence-labeled Col4alpha3NC1-specific into naive rats, and we found that they were enriched 4.5-fold in the kidney cortex relative to nonspecific control T cells 24 hours later. Many of the T cells were located in the Bowman's space and had a flattened shape, suggesting that the primary target for the T cells was in or adjacent to the Bowman's capsule.
Figures
Figure 1
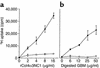
Antigen specificities of a T cell line generated from rCol4α3NC1-immunized rat. (a) An rCol4α3NC1 T cell line (filled circles) or T cells from CFA-immunized rat (open circles) were incubated with different concentrations of rCol4α3NC1 (x axis) in the presence of irradiated syngeneic thymocytes. The proliferation of T cells was measured as uptake of 3H (Δcpm, y axis). (b) T cells’ responses to digested rat GBM.
Figure 2
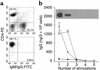
Cellular composition of rCol4α3NC1-specific T cell lines. (a) Flow cytometry analysis of whole lymphocytes from rCol4α3NC1-immunized rats (top panel) and a T cell line (bottom panel). (b) Rat IgG concentration in the supernatants of two Col4α3NC1 T cell lines (open circles and squares) and one control CFA T cell line (filled circles) collected after each stimulation (x axis). Ab activities to rCol4α3NC1 in the supernatants from a Col4α3NC1 T cell line, determined by Western blot analysis, are shown (inset).
Figure 3
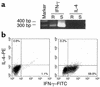
Cytokine profiles in an rCol4α3NC1-specific T cell line. (a) RT-PCR detection of rat INF-γ/IL-4 expressions at rest (R) or after rCol4α3NC1 stimulation (S). DNA size markers are shown at the left. (b) Flow cytometry analyses on cells from a Col4α3NC1-specific T cell line at rest (left panel) or stimulated by mitogens (right panel) after intracellular stain with anti–rat IFN-γ and IL-4 Ab’s.
Figure 4
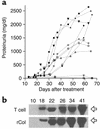
Proteinuria and albuminuria development in the rCol4α3NC1-specific T cell recipients. (a) Urine samples were collected as indicated (x axis) in 11 T cell recipients, and proteinuria was measured (y axis). Filled symbols, rats with severe GN; open symbols, modest GN; dashed lines, normal kidney. (b) Urine samples from a representative T cell recipient (T cell) with severe GN and a rat immunized with rCol4α3NC1 (rCol) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Arrows at right indicate serum albumin.
Figure 5
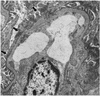
Development of GN in the rCol4α3NC1-specific T cell recipients. (a) Histology shows a glomerulus with fibrin deposition and crescent formation. Adjacent to the glomerulus is a mononuclear infiltrate. Focal tubules are dilated and contain intensely eosinophilic material consistent with protein. (b) Immunoperoxidase staining shows CD3+ T cells (brown in color) in mononuclear cell infiltrate surrounding a glomerulus with crescentic lesion. (c) Immunofluorescence stain show CD11b/c+ monocytes/macrophages (red) clustered in the Bowman’s space of an affected glomerulus. GBM and TBM are counterstained green by FITC-labeled SR-6. Arrowheads outline the basement membrane of the Bowman’s capsule.
Figure 6
EM micrograph shows segmental effacement of visceral epithelial cell (podocytes) foot processes (arrows) in an rCol4α3NC1-specific T cell recipient.
Figure 7
Direct immunofluorescence of Ab on serial frozen sections of kidney from an rCol4α3NC1 T cell recipient. (a) Section stained with FITC-labeled anti-rat IgM Ab. Crescent-shaped fluorescence staining is visible. (b) Section stained with Ab to rat IgG (negative). (c) Counterstaining by methylene blue illustrates fibrin in a crescentic lesion in glomerulus.
Figure 8
Tracing CFDA-SE–labeled T cells in kidney cortex by fluorescent microscopy. (a and b) rCol4α3NC1-specific T cells or CFA T cells were transferred into naive recipients. The labeled cells were counted in serial frozen sections of the kidney cortex 24 hours later, and labeled cell density was calculated (a). Elongated cells are expressed as a percentage of all labeled cells (b). (c) Fluorescent microscopy illustrates an elongated rCol4α3NC1-specific cell (green) in the Bowman’s capsule. GBM is stained red by PE-labeled SR-13. The tubules (T) with background are visible. Inset: high power of two elongated, labeled T cells.
Comment in
- What sensitized cells just might be doing in glomerulonephritis.
Bolton WK. Bolton WK. J Clin Invest. 2002 Mar;109(6):713-4. doi: 10.1172/JCI15285. J Clin Invest. 2002. PMID: 11901177 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
- The evolution of crescentic nephritis and alveolar haemorrhage following induction of autoimmunity to glomerular basement membrane in an experimental model of Goodpasture's disease.
Reynolds J, Moss J, Duda MA, Smith J, Karkar AM, Macherla V, Shore I, Evans DJ, Woodrow DF, Pusey CD. Reynolds J, et al. J Pathol. 2003 May;200(1):118-29. doi: 10.1002/path.1336. J Pathol. 2003. PMID: 12692850 - T-cell epitope of alpha3 chain of type IV collagen induces severe glomerulonephritis.
Wu J, Borillo J, Glass WF, Hicks J, Ou CN, Lou YH. Wu J, et al. Kidney Int. 2003 Oct;64(4):1292-301. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00227.x. Kidney Int. 2003. PMID: 12969147 - Spontaneous recovery from early glomerular inflammation is associated with resistance to anti-GBM glomerulonephritis: tolerance and autoimmune tissue injury.
Robertson J, Wu J, Arends J, Zhou C, Adrogue HE, Chan JT, Lou Y. Robertson J, et al. J Autoimmun. 2008 Jun;30(4):246-56. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2007.10.004. Epub 2007 Nov 28. J Autoimmun. 2008. PMID: 18054199 Free PMC article. - Anti-GBM glomerulonephritis: a T cell-mediated autoimmune disease?
Lou YH. Lou YH. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2004 Mar-Apr;52(2):96-103. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2004. PMID: 15179323 Review. - Crescentic glomerulonephritis--a manifestation of a nephritogenic Th1 response?
Kitching AR, Holdsworth SR, Tipping PG. Kitching AR, et al. Histol Histopathol. 2000 Jul;15(3):993-1003. doi: 10.14670/HH-15.993. Histol Histopathol. 2000. PMID: 10963141 Review.
Cited by
- Protein A immunoadsorption for anti-glomerular basement membrane nephritis.
Liu C, Li X, Yang Y, Zhao Y, Zhang L. Liu C, et al. Heliyon. 2024 Jul 23;10(15):e35049. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35049. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39157406 Free PMC article. - Pembrolizumab-Induced Anti-GBM Glomerulonephritis: A Case Report.
El Yamani N, Cote G, Riopel J, Marcoux N, Mac-Way F, Philibert D, Agharazii M. El Yamani N, et al. Kidney Med. 2023 May 30;5(8):100682. doi: 10.1016/j.xkme.2023.100682. eCollection 2023 Aug. Kidney Med. 2023. PMID: 37415622 Free PMC article. - Atypical Anti-Glomerular Basement Membrane Disease.
Bharati J, Yang Y, Sharma P, Jhaveri KD. Bharati J, et al. Kidney Int Rep. 2023 Mar 21;8(6):1151-1161. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2023.03.010. eCollection 2023 Jun. Kidney Int Rep. 2023. PMID: 37284681 Free PMC article. Review. - Atypical Antiglomerular Basement Membrane Nephritis Following Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor.
Javaugue V, Watson MJ, Fervenza FC, Nasr SH. Javaugue V, et al. Kidney Int Rep. 2022 May 3;7(8):1913-1916. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2022.04.089. eCollection 2022 Aug. Kidney Int Rep. 2022. PMID: 35967108 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
- Wilson, C.B. 1996. Renal response to immunologic glomerular injury. In The kidney. Volume 2. B.M. Brennen, editor. W.B. Saunders Co. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA. 1263–1349.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous