The comparative RNA web (CRW) site: an online database of comparative sequence and structure information for ribosomal, intron, and other RNAs - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-3-2. Epub 2002 Jan 17.
Sankar Subramanian, Murray N Schnare, James R Collett, Lisa M D'Souza, Yushi Du, Brian Feng, Nan Lin, Lakshmi V Madabusi, Kirsten M Müller, Nupur Pande, Zhidi Shang, Nan Yu, Robin R Gutell
Affiliations
- PMID: 11869452
- PMCID: PMC65690
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-3-2
Comparative Study
The comparative RNA web (CRW) site: an online database of comparative sequence and structure information for ribosomal, intron, and other RNAs
Jamie J Cannone et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2002.
Erratum in
- BMC Bioinformatics. 2002 Jul;3(1):15
Abstract
Background: Comparative analysis of RNA sequences is the basis for the detailed and accurate predictions of RNA structure and the determination of phylogenetic relationships for organisms that span the entire phylogenetic tree. Underlying these accomplishments are very large, well-organized, and processed collections of RNA sequences. This data, starting with the sequences organized into a database management system and aligned to reveal their higher-order structure, and patterns of conservation and variation for organisms that span the phylogenetic tree, has been collected and analyzed. This type of information can be fundamental for and have an influence on the study of phylogenetic relationships, RNA structure, and the melding of these two fields.
Results: We have prepared a large web site that disseminates our comparative sequence and structure models and data. The four major types of comparative information and systems available for the three ribosomal RNAs (5S, 16S, and 23S rRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and two of the catalytic intron RNAs (group I and group II) are: (1) Current Comparative Structure Models; (2) Nucleotide Frequency and Conservation Information; (3) Sequence and Structure Data; and (4) Data Access Systems.
Conclusions: This online RNA sequence and structure information, the result of extensive analysis, interpretation, data collection, and computer program and web development, is accessible at our Comparative RNA Web (CRW) Site http://www.rna.icmb.utexas.edu. In the future, more data and information will be added to these existing categories, new categories will be developed, and additional RNAs will be studied and presented at the CRW Site.
Figures
Figure 1
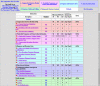
Introductory view of the CRW Site. The top frame divides the site into eight sections; the first four sections are the primary focus of this manuscript. The bottom frame contains the CRW Site's Table of Contents. Color-coding is used consistently throughout the CRW Site to help orient users.
Figure 2
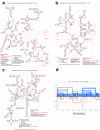
The most recent (November 1999) versions of the rRNA comparative structure models (see text for additional details). A. E. coli 23S rRNA, 5' half. B. E. coli 23S rRNA, 3' half. C. E. coli 16S rRNA. D. The "histogram" format for the E. coli 16S rRNA.
Figure 3
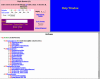
RDBMS (Standard) search form.
Figure 4
RDBMS (PhyloBrowser) basic phylogenetic search screen, showing two additional levels of phylogeny.
Figure 5
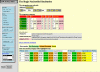
Analysis of the Bacterial 16S and 23S rRNA structure models using the "RNA Structure Query System." The entire system (selection frame and results) is shown with the results for the distribution of single nucleotides, sorted in order of decreasing prevalence in unpaired regions.
Similar articles
- 5SRNAdb: an information resource for 5S ribosomal RNAs.
Szymanski M, Zielezinski A, Barciszewski J, Erdmann VA, Karlowski WM. Szymanski M, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jan 4;44(D1):D180-3. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1081. Epub 2015 Oct 20. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 26490961 Free PMC article. - Sequence and structural conservation in RNA ribose zippers.
Tamura M, Holbrook SR. Tamura M, et al. J Mol Biol. 2002 Jul 12;320(3):455-74. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(02)00515-6. J Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 12096903 - Bacterial phylogeny based on 16S and 23S rRNA sequence analysis.
Ludwig W, Schleifer KH. Ludwig W, et al. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1994 Oct;15(2-3):155-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.1994.tb00132.x. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1994. PMID: 7524576 Review. - The nucleotide sequence of 5 S ribosomal RNA from Vibrio marinus.
MacDonell MT, Colwell RR. MacDonell MT, et al. Microbiol Sci. 1984 Dec;1(9):229-31. Microbiol Sci. 1984. PMID: 6086080 Review.
Cited by
- DHX36 binding induces RNA structurome remodeling and regulates RNA abundance via m6A reader YTHDF1.
Zhang Y, Zhao J, Chen X, Qiao Y, Kang J, Guo X, Yang F, Lyu K, Ding Y, Zhao Y, Sun H, Kwok CK, Wang H. Zhang Y, et al. Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 15;15(1):9890. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54000-y. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39543097 Free PMC article. - Sturnidae sensu lato Mitogenomics: Novel Insights into Codon Aversion, Selection, and Phylogeny.
Han S, Ding H, Peng H, Dai C, Zhang S, Yang J, Gao J, Kan X. Han S, et al. Animals (Basel). 2024 Sep 26;14(19):2777. doi: 10.3390/ani14192777. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39409726 Free PMC article. - The point mutation A1387G in the 16S rRNA gene confers aminoglycoside resistance in Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli.
Zarske M, Werckenthin C, Golz JC, Stingl K. Zarske M, et al. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2024 Nov 6;68(11):e0083324. doi: 10.1128/aac.00833-24. Epub 2024 Oct 15. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2024. PMID: 39404347 Free PMC article. - Discovery and Quantification of Long-Range RNA Base Pairs in Coronavirus Genomes with SEARCH-MaP and SEISMIC-RNA.
Allan MF, Aruda J, Plung JS, Grote SL, des Taillades YJM, de Lajarte AA, Bathe M, Rouskin S. Allan MF, et al. Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 7:rs.3.rs-4814547. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4814547/v1. Res Sq. 2024. PMID: 39149495 Free PMC article. Preprint. - LinearAlifold: Linear-time consensus structure prediction for RNA alignments.
Malik A, Zhang L, Gautam M, Dai N, Li S, Zhang H, Mathews DH, Huang L. Malik A, et al. J Mol Biol. 2024 Sep 1;436(17):168694. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2024.168694. Epub 2024 Jul 4. J Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38971557
References
- Darwin C. Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life. First edition, 1859; second edition, 1860; third edition, 1861; fourth edition, 1866; fifth edition, 1869; sixth and final edition, 1872.
- Woese CR, Magrum LJ, Fox GE. Archaebacteria. J Mol Evol. 1978;11:245–251. - PubMed
- Holley RW, Apgar J, Everett GA, Madison JT, Marquisee M, Merrill SH, Penswick JR, Zamir A. Structure of a ribonucleic acid. Science. 1965;147:1462–1465. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources