Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) tat induces nitric-oxide synthase in human astroglia - PubMed (original) (raw)
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) tat induces nitric-oxide synthase in human astroglia
Xiaojuan Liu et al. J Biol Chem. 2002.
Abstract
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection is known to cause neuronal injury and dementia in a significant proportion of patients. However, the mechanism by which HIV-1 mediates its deleterious effects in the brain is poorly defined. The present study was undertaken to investigate the effect of the HIV-1 tat gene on the expression of inducible nitric-oxide synthase (iNOS) in human U373MG astroglial cells and primary astroglia. Expression of the tat gene as RSV-tat but not that of the CAT gene as RSV-CAT in U373MG astroglial cells led to the induction of NO production and the expression of iNOS protein and mRNA. Induction of NO production by recombinant HIV-1 Tat protein and inhibition of RSV-tat-induced NO production by anti-Tat antibodies suggest that RSV-tat-induced production of NO is dependent on Tat and that Tat is secreted from RSV-tat-transfected astroglia. Similar to U373MG astroglial cells, RSV-tat also induced the production of NO in human primary astroglia. The induction of human iNOS promoter-derived luciferase activity by the expression of RSV-tat suggests that RSV-tat induces the transcription of iNOS. To understand the mechanism of induction of iNOS, we investigated the role of NF-kappaB and C/EBPbeta, transcription factors responsible for the induction of iNOS. Activation of NF-kappaB as well as C/EBPbeta by RSV-tat, stimulation of RSV-tat-induced production of NO by the wild type of p65 and C/EBPbeta, and inhibition of RSV-tat-induced production of NO by deltap65, a dominant-negative mutant of p65, and deltaC/EBPbeta, a dominant-negative mutant of C/EBPbeta, suggest that RSV-tat induces iNOS through the activation of NF-kappaB and C/EBPbeta. In addition, we show that extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) but not that p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) is involved in RSV-tat induced production of NO. Interestingly, PD98059, an inhibitor of the ERK pathway, and deltaERK2, a dominant-negative mutant of ERK2, inhibited RSV-tat-induced production of NO through the inhibition of C/EBPbeta but not that of NF-kappaB. This study illustrates a novel role for HIV-1 tat in inducing the expression of iNOS in human astrocytes that may participate in the pathogenesis of HIV-associated dementia.
Figures
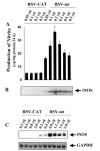
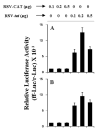
Fig. 1. Expression of RSV-tat induces the production of NO and the expression of iNOS protein in human U373MG astroglial cells
Cells plated at 50–60% confluence in 6-well plates were transfected with different amounts of either RSV-CAT or RSV-tat using LipofectAMINE Plus (Invitrogen) as described under “Materials and Methods.” After 24 h of transfection, cells were incubated under serum-free conditions. A, after 24 h of incubation, supernatants were used for nitrite assay. Data are the mean ± S.D. of three different experiments. B, cell homogenates were electrophoresed, transferred onto nitrocellulose membrane, and immunoblotted with antibodies against mouse macrophage iNOS as mentioned under “Materials and Methods.” C, cells plated at 50–60% confluence in 100-mm dishes were transfected with different amounts of either RSV-CAT or RSV-tat. After 24 h of transfection, cells were incubated under serum-free conditions. After 24 h of incubation, cells were taken out directly by adding Ultraspec-II RNA reagent (Biotecx Laboratories Inc.) to the plates for isolation of total RNA, and Northern blot analysis for iNOS mRNA was carried out as described under “Materials and Methods.”
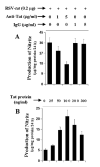
Fig. 2. Expression of RSV-tat induces the production of NO through the secretion of tat in human U373MG astroglial cells
A, cells plated in 6-well plates were transfected with 0.2 _μ_g of RSV-tat. After 24 h of transfection, cells were incubated under serum-free conditions in the presence of different concentrations of anti-Tat antibodies and control IgG. After 24 h of incubation, supernatants were used for nitrite assay. Data are the mean ± S.D. of three different experiments. B, cells were treated with different concentrations of recombinant HIV-1 Tat protein under serum-free conditions. After 24 h, supernatants were used for nitrite assay. Data are the mean ± S.D. of three different experiments.
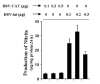
Fig. 3. Expression of RSV-tat induces the production of NO in human primary astroglia
Cells plated at 50–60% confluence in 6-well plates were transfected with different amounts of either RSV-CAT or RSV-tat. After 24 h of transfection, cells were incubated under serum-free conditions. After 24 h of incubation, supernatants were used for nitrite assay. Data are the mean ± S.D. of three different experiments.
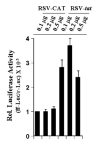
Fig. 4. Expression of RSV-tat induces iNOS promoter-derived luciferase activity in human U373MG astroglial cells
Cells plated in 6-well plates were cotransfected with 0.5 _μ_g of phiNOS(7.2)Luc (a construct containing the human iNOS promoter fused to the luciferase gene) and different amounts of either RSV-CAT or RSV-tat. All transfections also included 50 ng/_μ_g pRL-TK (as transfection efficiency control). After 24 h of transfection, cells were incubated under serum-free conditions for 18 h. Firefly (ff-Luc) and Renilla (r-Luc) luciferase activities were obtained by analyzing total cell extract as described under “Materials and Methods.” Data are the mean ± S.D. of three different experiments.
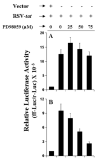
Fig. 5. Expression of RSV-tat induces activation of NF-κ_B and C/EBP_β in human U373MG astroglial cells
Cells plated in 6-well plates were cotransfected with 0.5 _μ_g of either pBIIX-Luc (A) or pC/ EBP_β_-Luc (B) and different amounts of either RSV-CAT or RSV-tat. All transfections also included 50 ng/_μ_g pRL-TK. After 24 h of transfection, cells were incubated under serum-free conditions for 18 h. Firefly (ff-Luc) and Renilla (r-Luc) luciferase activities were obtained by analyzing total cell extract. Data are the mean ± S.D. of three different experiments.
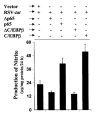
Fig. 6. Effect of wild-type p65 and C/EBP_β_ and dominant-negative mutants of p65 (Δp65) and C/EBP_β_ (ΔC/EBP_β_) on RSV-_tat_-induced production of NO in human U373MG astroglial cells
Cells plated in 6-well plates were cotransfected with 0.2 μ_g of RSV-tat and 0.5 μ_g of an empty vector, p65, C/EBP_β, Δp65, or ΔC/EBP_β. After 24 h of transfection, cells were incubated under serum-free conditions for another 24 h. Supernatants were used for the nitrite assay. Data are the mean ± S.D. of three different experiments.
Fig. 7. Expression of RSV-tat induces activation of ERK in human U373MG astroglial cells
Cells were transfected with different amounts of RSV-tat. After 24 h of transfection, cells were incubated under serum-free conditions. After 18 h of incubation, activities of ERK and p38 MAPK were assayed as described under “Materials and Methods.”
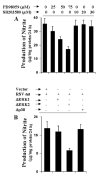
Fig. 8. Role of ERK and p38 MAPK in RSV-_tat_-induced NO production in human U373MG astroglial cells
A, cells were transfected with 0.2 _μ_g of RSV-tat. After 24 h of transfection, cells were incubated under serum-free conditions in the presence or absence of different concentrations of PD98059 and SB203580. After 24 h of incubation, supernatants were used for the nitrite assay. Data are the mean ± S.D. of three different experiments. B, cells were cotransfected with 0.2 _μ_g of RSV-tat and 0.5 _μ_g of either an empty vector or ΔERK1, ΔERK2, or Δp38. After 24 h of transfection, cells were incubated under serum-free conditions for another 24 h. Supernatants were used for the nitrite assay. Data are the mean ± S.D. of three different experiments.
Fig. 9. Effect of PD98059 on RSV-_tat_-induced activation of NF-κ_B and C/EBP_β in human U373MG astroglial cells
Cells plated in 6-well plates were cotransfected with 0.2 _μ_g of RSV-tat and 0.5 _μ_g of either pBIIX-Luc (A) or pC/EBP_β_-Luc (B). All transfections also included 50 ng/_μ_g pRL-TK. After 24 h of transfection, cells were incubated in the presence or absence of different concentrations of PD98059 under serum-free conditions for 18 h. Firefly (ff-Luc) and Renilla (r-Luc) luciferase activities were obtained by analyzing total cell extract. Data are the mean ± S.D. of three different experiments.
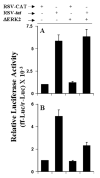
Fig. 10. Effect of ΔERK2, the dominant-negative mutant of ERK2, on RSV-_tat_-induced activation of NF-κ_B and C/EBP_β in human U373MG astroglial cells
Cells were cotransfected with 0.2 _μ_g of RSV-tat, 0.5 _μ_g of either an empty vector or ΔERK2, and 0.5 _μ_g of either pBIIX-Luc (A) or pC/EBP_β_-Luc (B). After 24 h of transfection, cells were incubated under serum-free conditions for 18 h. Firefly (ff-Luc) and Renilla (r-Luc) luciferase activities were obtained by analyzing total cell extract. Data are the mean ± S.D. of three different experiments.
Similar articles
- Role of protein kinase R in double-stranded RNA-induced expression of nitric oxide synthase in human astroglia.
Auch CJ, Saha RN, Sheikh FG, Liu X, Jacobs BL, Pahan K. Auch CJ, et al. FEBS Lett. 2004 Apr 9;563(1-3):223-8. doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(04)00302-3. FEBS Lett. 2004. PMID: 15063753 Free PMC article. - Ligation of CD40 stimulates the induction of nitric-oxide synthase in microglial cells.
Jana M, Liu X, Koka S, Ghosh S, Petro TM, Pahan K. Jana M, et al. J Biol Chem. 2001 Nov 30;276(48):44527-33. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M106771200. Epub 2001 Sep 10. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11551948 Free PMC article. - Role of mitogen-activated protein kinases in inducible nitric oxide synthase and TNFalpha expression in human fetal astrocytes.
Hua LL, Zhao ML, Cosenza M, Kim MO, Huang H, Tanowitz HB, Brosnan CF, Lee SC. Hua LL, et al. J Neuroimmunol. 2002 May;126(1-2):180-9. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(02)00055-3. J Neuroimmunol. 2002. PMID: 12020969 - Gemfibrozil, a lipid-lowering drug, inhibits the induction of nitric-oxide synthase in human astrocytes.
Pahan K, Jana M, Liu X, Taylor BS, Wood C, Fischer SM. Pahan K, et al. J Biol Chem. 2002 Nov 29;277(48):45984-91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M200250200. Epub 2002 Sep 18. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12244038 Free PMC article. - Transactivator of Transcription (Tat)-Induced Neuroinflammation as a Key Pathway in Neuronal Dysfunction: A Scoping Review.
Muvenda T, Williams AA, Williams ME. Muvenda T, et al. Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Nov;61(11):9320-9346. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04173-w. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38627350 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Expression of substance P, neurokinin-1 receptor and immune markers in the brains of individuals with HIV-associated neuropathology.
Spitsin S, Stevens KE, Douglas SD. Spitsin S, et al. J Neurol Sci. 2013 Nov 15;334(1-2):18-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2013.07.008. Epub 2013 Aug 2. J Neurol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23916293 Free PMC article. - Differential involvement of p38 and JNK MAP kinases in HIV-1 Tat and gp120-induced apoptosis and neurite degeneration in striatal neurons.
Singh IN, El-Hage N, Campbell ME, Lutz SE, Knapp PE, Nath A, Hauser KF. Singh IN, et al. Neuroscience. 2005;135(3):781-90. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.05.028. Epub 2005 Aug 19. Neuroscience. 2005. PMID: 16111829 Free PMC article. - Growth hormone releasing hormone induces the expression of nitric oxide synthase.
Barabutis N, Siejka A, Schally AV. Barabutis N, et al. J Cell Mol Med. 2011 May;15(5):1148-55. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01096.x. Epub 2010 May 26. J Cell Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 20518847 Free PMC article. - Tumor necrosis factor-alpha at the crossroads of neuronal life and death during HIV-associated dementia.
Saha RN, Pahan K. Saha RN, et al. J Neurochem. 2003 Sep;86(5):1057-71. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.01942.x. J Neurochem. 2003. PMID: 12911614 Free PMC article. Review. - Role of very-late antigen-4 (VLA-4) in myelin basic protein-primed T cell contact-induced expression of proinflammatory cytokines in microglial cells.
Dasgupta S, Jana M, Liu X, Pahan K. Dasgupta S, et al. J Biol Chem. 2003 Jun 20;278(25):22424-31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M301789200. Epub 2003 Apr 10. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12690109 Free PMC article.
References
- Bagasra O, Lavi E, Bobroski L, Khalili K, Pestaner JB, Pomerantz RJ. AIDS. 1996;10:573–585. - PubMed
- Glass JD, Johnson RT. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1996;19:1–26. - PubMed
- Tornatore C, Chandra R, Berger JR, Major EO. Neurology. 1994;44:481–487. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P20-RR15635/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS039940-01A1/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS039940/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS39940/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- CA76958/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR015635/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous