Germline p53 mutations in a cohort with childhood sarcoma: sex differences in cancer risk - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
doi: 10.1086/374567. Epub 2003 Feb 27.
Affiliations
- PMID: 12610779
- PMCID: PMC1180359
- DOI: 10.1086/374567
Comparative Study
Germline p53 mutations in a cohort with childhood sarcoma: sex differences in cancer risk
Shih-Jen Hwang et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2003 Apr.
Abstract
To characterize cancer risk in heterozygous p53 mutation carriers, we analyzed cancer incidence in 56 germline p53 mutation carriers and 3,201 noncarriers from 107 kindreds ascertained through patients with childhood soft-tissue sarcoma who were treated at the University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center. We systematically followed members in these kindreds for cancer incidence for >20 years and evaluated their p53 gene status. We found seven kindreds with germline p53 mutations that include both missense and truncation mutation types. Kaplan-Meier analysis showed similar cancer risks between 21 missense and 35 truncation p53 mutation carriers (log-rank chi(2)=0.04; P=.84). We found a significantly higher cancer risk in female carriers than in male carriers (log-rank chi(2)=12.1; P<.001), a difference not explained by an excess of sex-specific cancer. The calculated standardized incidence ratio (SIR) showed that mutation carriers had a risk for all types of cancer that was much higher than that for the general population (SIR = 41.1; 95% confidence interval [CI] 29.9-55.0) whereas noncarriers had a risk for all types of cancer that was similar to that in the general population (SIR = 0.9; 95% CI 0.8-1.0). The calculated SIRs showed a >100-fold higher risk of sarcoma, female breast cancer, and hematologic malignancies for the p53 mutation carriers and agreed with the findings of an earlier segregation analysis based on the same cohort. These results quantitatively illustrated the spectrum of cancer risk in germline p53 mutation carriers and will provide valuable reference for the evaluation and treatment of patients with cancer.
Figures
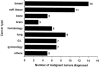
Figure 1
Number of site-specific cancers for 56 germline p53 mutation carriers. Eleven carriers did not have cancer at the time of last contact. A total of 67 malignant neoplasms were diagnosed for the 45 carriers (excluded probands). The “hematology” group comprises four leukemia and two multiple myeloma; the “gynecology” group comprises four ovarian cancers, two prostate cancers, and one testicular cancer; and the “others” group comprises three head and neck tumors, one melanoma, and one thyroid cancer. G.I. = gastrointestinal.
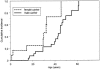
Figure 2
Kaplan-Meier estimated cumulative incidence of all types of cancer—in 56 germline p53 mutation carriers (excluding probands) identified in a cohort with childhood sarcoma. Ages shown are the time between birth and first-cancer diagnosis, for those with cancer, and the time between birth and either last contact or death, for those without cancer. Among these 56 carriers, 21 carry missense mutations, and 35 carry truncation mutations.
Figure 3
Kaplan-Meier estimated cumulative incidence for all types of cancer—in 27 male and 29 female germline p53 mutation carriers. Ages shown are the time between birth and first-cancer diagnosis, for those with cancer, and the time between birth and either last contact or death, for those without cancer.
Figure 4
Kaplan-Meier estimated cumulative incidence for all types of cancer—in 27 male and 12 female germline p53 mutation carriers. Cases of breast, ovarian, and prostate cancer were excluded here. Ages shown are the time between birth and first-cancer diagnosis, for those with cancer, and the time between birth and either last contact or death, for those without cancer.
References
Electronic-Database Information
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for LFS and p53) - PubMed
References
- Birch JM, Alston RD, McNally RJ, Evans DG, Kelsey AM, Harris M, Eden OB, Varley JM (2001) Relative frequency and morphology of cancers in carriers of germline TP53 mutations. Oncogene 20:4621–4628 - PubMed
- Birch JM, Blair V, Kelsey AM, Evans DG, Harris M, Tricker KJ, Varley JM (1998) Cancer phenotype correlates with constitutional TP53 genotype in families with the Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Oncogene 17:1061–1068 - PubMed
- Blagosklonny MV (2000) p53 from complexity to simplicity: mutant p53 stabilization, gain-of-function, and dominant-negative effect. FASEB J 14:1901–1907 - PubMed
- Bondy ML, Lustbader ED, Strom SS, Strong LC (1992) Segregation analysis of 159 soft tissue sarcoma kindreds: comparison of fixed and sequential sampling schemes. Genet Epidemiol 9:291–304 - PubMed
- Bougeard G, Limacher JM, Martin C, Charbonnier F, Killian A, Delattre O, Longy M, Jonveaux P, Fricker JP, Stoppa-Lyonnet D, Flaman JM, Frebourg T (2001) Detection of 11 germline inactivating TP53 mutations and absence of TP63 and HCHK2 mutations in 17 French families with Li-Fraumeni or Li-Fraumeni-like syndrome. J Med Genet 38:253–257 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous