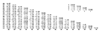RSEARCH: finding homologs of single structured RNA sequences - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
RSEARCH: finding homologs of single structured RNA sequences
Robert J Klein et al. BMC Bioinformatics. 2003.
Abstract
Background: For many RNA molecules, secondary structure rather than primary sequence is the evolutionarily conserved feature. No programs have yet been published that allow searching a sequence database for homologs of a single RNA molecule on the basis of secondary structure.
Results: We have developed a program, RSEARCH, that takes a single RNA sequence with its secondary structure and utilizes a local alignment algorithm to search a database for homologous RNAs. For this purpose, we have developed a series of base pair and single nucleotide substitution matrices for RNA sequences called RIBOSUM matrices. RSEARCH reports the statistical confidence for each hit as well as the structural alignment of the hit. We show several examples in which RSEARCH outperforms the primary sequence search programs BLAST and SSEARCH. The primary drawback of the program is that it is slow. The C code for RSEARCH is freely available from our lab's website.
Conclusion: RSEARCH outperforms primary sequence programs in finding homologs of structured RNA sequences.
Figures
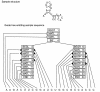
Figure 1
An example SCFG architecture. The sequence at the top folds into the specified secondary structure. At the bottom, the nodal architecture of the model that would produce this sequence is shown. Shaded triangles represent base pair emitting nodes, and point to the base pair they emit. Open triangles represent single nucleotide emitting nodes, and point to the nucleotide they emit.
Figure 2
The two classes of local alignment. Each example shows how the nodal guide tree best aligns to the target sequence. At the bottom is the RSEARCH output for the alignment. On the left is an example of begin locality, while on the right is an example of end locality. The numbers next to the query sequence represent positions relative to the entire query; the numbers next to the target sequence represent positions relative to the subsequence defined in the "Target =" line.
Figure 3
The RIBOSUM85-60 matrix. The 16 × 16 matrix is used to get scores for aligning base pairs. The 4 × 4 matrix is used to get scores for aligning single-stranded regions. Positive scores are shaded.
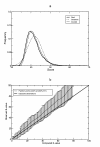
Figure 4
RSEARCH statistics, a Distribution of scores for a search against random sequences. We searched a database of 10,000 random sequences of 10,000 nucleotides each with a GC composition of 50% using the precursor to the C. elegans miRNA mir-40 as the query [60]. We took the best score found for each of the 10,000 sequences in the database and plotted their distribution. We then calculated the mean and standard deviation and plotted the Gaussian distribution for those values. We also calculated K and λ for the Gumbel distribution and plotted that distribution. b Average observed number of hits with E-value less than a cutoff versus reported E-value for searches of various RNase P queries against database of Archaeal genomes. E-values were computed using partition points of 40% and 60% G+C content.
Similar articles
- Complexes with truncated RNAs from the large domain of Archaeoglobus fulgidus signal recognition particle.
Bhuiyan SH, Pakhomova ON, Hinck AP, Zwieb C. Bhuiyan SH, et al. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2001 May 1;198(2):105-10. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2001.tb10626.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2001. PMID: 11430398 - RScan: fast searching structural similarities for structured RNAs in large databases.
Xue C, Liu GP. Xue C, et al. BMC Genomics. 2007 Jul 31;8:257. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-257. BMC Genomics. 2007. PMID: 17663795 Free PMC article. - Computational analysis of RNAs.
Eddy SR. Eddy SR. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:117-28. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.003. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381287 - Structural basis for activation of an archaeal ribonuclease P RNA by protein cofactors.
Kimura M. Kimura M. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2017 Sep;81(9):1670-1680. doi: 10.1080/09168451.2017.1353404. Epub 2017 Jul 17. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28715256 Review. - Computational identification of functional RNA homologs in metagenomic data.
Nawrocki EP, Eddy SR. Nawrocki EP, et al. RNA Biol. 2013 Jul;10(7):1170-9. doi: 10.4161/rna.25038. Epub 2013 May 20. RNA Biol. 2013. PMID: 23722291 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Predicting pseudoknotted structures across two RNA sequences.
Sperschneider J, Datta A, Wise MJ. Sperschneider J, et al. Bioinformatics. 2012 Dec 1;28(23):3058-65. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts575. Epub 2012 Oct 8. Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 23044552 Free PMC article. - QRNAstruct: a method for extracting secondary structural features of RNA via regression with biological activity.
Terai G, Asai K. Terai G, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Jul 22;50(13):e73. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac220. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35390152 Free PMC article. - Fast pairwise structural RNA alignments by pruning of the dynamical programming matrix.
Havgaard JH, Torarinsson E, Gorodkin J. Havgaard JH, et al. PLoS Comput Biol. 2007 Oct;3(10):1896-908. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.0030193. Epub 2007 Aug 20. PLoS Comput Biol. 2007. PMID: 17937495 Free PMC article. - Identification of 22 candidate structured RNAs in bacteria using the CMfinder comparative genomics pipeline.
Weinberg Z, Barrick JE, Yao Z, Roth A, Kim JN, Gore J, Wang JX, Lee ER, Block KF, Sudarsan N, Neph S, Tompa M, Ruzzo WL, Breaker RR. Weinberg Z, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(14):4809-19. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm487. Epub 2007 Jul 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17621584 Free PMC article. - Efficient alignment of RNAs with pseudoknots using sequence alignment constraints.
Yoon BJ. Yoon BJ. EURASIP J Bioinform Syst Biol. 2009;2009(1):491074. doi: 10.1155/2009/491074. Epub 2009 Apr 14. EURASIP J Bioinform Syst Biol. 2009. PMID: 19390684 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous