The KEGG resource for deciphering the genome - PubMed (original) (raw)
The KEGG resource for deciphering the genome
Minoru Kanehisa et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004.
Abstract
A grand challenge in the post-genomic era is a complete computer representation of the cell and the organism, which will enable computational prediction of higher-level complexity of cellular processes and organism behavior from genomic information. Toward this end we have been developing a knowledge-based approach for network prediction, which is to predict, given a complete set of genes in the genome, the protein interaction networks that are responsible for various cellular processes. KEGG at http://www.genome.ad.jp/kegg/ is the reference knowledge base that integrates current knowledge on molecular interaction networks such as pathways and complexes (PATHWAY database), information about genes and proteins generated by genome projects (GENES/SSDB/KO databases) and information about biochemical compounds and reactions (COMPOUND/GLYCAN/REACTION databases). These three types of database actually represent three graph objects, called the protein network, the gene universe and the chemical universe. New efforts are being made to abstract knowledge, both computationally and manually, about ortholog clusters in the KO (KEGG Orthology) database, and to collect and analyze carbohydrate structures in the GLYCAN database.
Figures
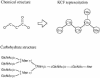
Figure 1
Chemical compound structures in the COMPOUND database and carbohydrate structures in the GLYCAN database are graph objects, where the nodes are either atoms or monosaccharides and the edges are covalent bonds. For the purpose of chemical structure comparison, the chemical structure is converted to the KCF (KEGG Chemical Function) representation where the same atoms are distinguished by their environments.
References
- Kanehisa M. and Bork,P. (2003) Bioinformatics in the post-sequence era. Nature Genet., 33, 305–310. - PubMed
- Hattori M., Okuno,Y., Goto,S. and Kanehisa,M. (2003) Development of a chemical structure comparison method for integrated analysis of chemical and genomic information in the metabolic pathways. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 125, 11853–11865. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials