Adult bone marrow-derived cells recruited during angiogenesis comprise precursors for periendothelial vascular mural cells - PubMed (original) (raw)
Adult bone marrow-derived cells recruited during angiogenesis comprise precursors for periendothelial vascular mural cells
Iiro Rajantie et al. Blood. 2004.
Abstract
Bone marrow (BM)-derived cells are thought to participate in the growth of blood vessels during postnatal vascular regeneration and tumor growth, a process previously attributed to stem and precursor cells differentiating to endothelial cells. We used multichannel laser scanning confocal microscopy of whole-mounted tissues to study angiogenesis in chimeric mice created by reconstituting C57BL mice with genetically marked syngeneic BM. We show that BM-derived endothelial cells do not significantly contribute to tumor- or cytokine-induced neoangiogenesis. Instead, BM-derived periendothelial vascular mural cells were persistently detected at sites of tumor- or vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis. Subpopulations of these cells expressed the pericyte-specific NG2 proteoglycan, or the hematopoietic markers CD11b and CD45, but did not detectably express the smooth muscle markers smooth muscle alpha-actin or desmin. Thus, the major contribution of the BM to angiogenic processes is not endothelial, but may come from progenitors for periendothelial vascular mural and hematopoietic effector cells.
Figures
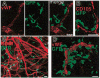
Figure 1. Periendothelial location of bone marrow–derived cells in angiogenic vessels
Angiogenesis was induced in the ears of mice that underwent BM transplantation by repeated subcutaneous VEGF protein injections (A) or by subcutaneous implantation of B16 melanoma (B-D). The tissues were studied by immunofluorescence microscopy (C) or by laser scanning confocal microscopy (A-B, D). (A-B) Vascular endothelial cells stained for von Willebrand factor (VWF, A) or CD105 (B) demonstrate the periendothelial location of the GFP+ BM-derived cells. Note that no GFP+ endothelial cells can be detected. (C) The abundant number and close association of BM-derived cells to endothelial cells (CD31 staining, red) can also be seen in the peritumoral area where larger arterioles with no apparent angiogenic activity are seen. (D) A 3-dimensional projection digitally reconstituted from stacks of confocal optical slices demonstrates the periendothelial location of the BM-derived GFP+ cells bordering the vascular endothelial cells expressing VWF (red). Bars represent 40 μm.
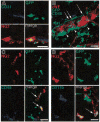
Figure 2. Subpopulations of periendothelial BM-derived vascular mural cells express the pericyte marker NG2 proteolygan and/or the hematopoietic markers CD45 or CD11b
Angiogenesis was induced in mice that underwent BM transplantation by subcutaneous implantation of B16 melanoma (A, C-D) or by repeated subcutaneous VEGF protein injections (B), and the tissues were analyzed by confocal microscopy. (A) Some of the BM-derived mural cells covering angiogenic blood vessel endothelium (CD31 staining, blue) express the pericyte marker NG2 (red). (B) A 3-dimensional projection demonstrates that BM-derived GFP+ periendothelial cells encompass both cells expressing CD45 (arrowheads) and cells with no CD45 immunoreactivity (arrows). (C-D) Similarly, BM-derived NG2+ cells also include cells that do not coexpress CD45 or CD11b (arrows). Bars represent 30 μm.
Similar articles
- Contribution of bone marrow-derived pericyte precursor cells to corneal vasculogenesis.
Ozerdem U, Alitalo K, Salven P, Li A. Ozerdem U, et al. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005 Oct;46(10):3502-6. doi: 10.1167/iovs.05-0309. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005. PMID: 16186326 Free PMC article. - Minor contribution of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitors to the vascularization of murine gliomas.
Machein MR, Renninger S, de Lima-Hahn E, Plate KH. Machein MR, et al. Brain Pathol. 2003 Oct;13(4):582-97. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2003.tb00487.x. Brain Pathol. 2003. PMID: 14655762 Free PMC article. - Bone marrow-derived circulating endothelial precursors do not contribute to vascular endothelium and are not needed for tumor growth.
Purhonen S, Palm J, Rossi D, Kaskenpää N, Rajantie I, Ylä-Herttuala S, Alitalo K, Weissman IL, Salven P. Purhonen S, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 May 6;105(18):6620-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0710516105. Epub 2008 Apr 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18443294 Free PMC article. - Biology and flow cytometry of proangiogenic hematopoietic progenitors cells.
Rose JA, Erzurum S, Asosingh K. Rose JA, et al. Cytometry A. 2015 Jan;87(1):5-19. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.22596. Epub 2014 Nov 21. Cytometry A. 2015. PMID: 25418030 Free PMC article. Review. - The emerging role of the bone marrow-derived stem cells in (therapeutic) angiogenesis.
Carmeliet P, Luttun A. Carmeliet P, et al. Thromb Haemost. 2001 Jul;86(1):289-97. Thromb Haemost. 2001. PMID: 11487017 Review.
Cited by
- Origins of the tumor microenvironment: quantitative assessment of adipose-derived and bone marrow-derived stroma.
Kidd S, Spaeth E, Watson K, Burks J, Lu H, Klopp A, Andreeff M, Marini FC. Kidd S, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e30563. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030563. Epub 2012 Feb 20. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22363446 Free PMC article. - Mesenchymal stem-like cells isolated from human esophageal carcinoma and adjacent non-cancerous tissues.
Hu J, Zhou Z, Shi S, Zhu X, Wang X, Zhang W, Hu S, Qian H, Xu W. Hu J, et al. Oncol Lett. 2013 Jan;5(1):179-184. doi: 10.3892/ol.2012.1003. Epub 2012 Oct 30. Oncol Lett. 2013. PMID: 23255916 Free PMC article. - Evidence for incorporation of bone marrow-derived endothelial cells into perfused blood vessels in tumors.
Duda DG, Cohen KS, Kozin SV, Perentes JY, Fukumura D, Scadden DT, Jain RK. Duda DG, et al. Blood. 2006 Apr 1;107(7):2774-6. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-08-3210. Epub 2005 Dec 8. Blood. 2006. PMID: 16339405 Free PMC article. - Regeneration of the vascular compartment.
Becher MU, Nickenig G, Werner N. Becher MU, et al. Herz. 2010 Aug;35(5):342-51. doi: 10.1007/s00059-010-3360-0. Herz. 2010. PMID: 20842474 Review. - Influence of adult mesenchymal stem cells on in vitro vascular formation.
Sorrell JM, Baber MA, Caplan AI. Sorrell JM, et al. Tissue Eng Part A. 2009 Jul;15(7):1751-61. doi: 10.1089/ten.tea.2008.0254. Tissue Eng Part A. 2009. PMID: 19196139 Free PMC article.
References
- Asahara T, Murohara T, Sullivan A, et al. Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for angiogenesis. Science. 1997;275:964–967. - PubMed
- Asahara T, Masuda H, Takahashi T, et al. Bone marrow origin of endothelial progenitor cells responsible for postnatal vasculogenesis in physiological and pathological neovascularization. Circ Res. 1999;85:221–228. - PubMed
- Crosby JR, Kaminski WE, Schatteman G, et al. Endothelial cells of hematopoietic origin make a significant contribution to adult blood vessel formation. Circ Res. 2000;87:728–730. - PubMed
- Lyden D, Hattori K, Dias S, et al. Impaired recruitment of bone-marrow-derived endothelial and hematopoietic precursor cells blocks tumor angiogenesis and growth. Nat Med. 2001;7:1194–1201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R03 HD044783-02/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R03 HD044783-03/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD037243/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD37243/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R03 HD044783-01/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous