Mortality in relation to smoking: 50 years' observations on male British doctors - PubMed (original) (raw)
Mortality in relation to smoking: 50 years' observations on male British doctors
Richard Doll et al. BMJ. 2004.
Abstract
Objective: To compare the hazards of cigarette smoking in men who formed their habits at different periods, and the extent of the reduction in risk when cigarette smoking is stopped at different ages.
Design: Prospective study that has continued from 1951 to 2001.
Setting: United Kingdom.
Participants: 34 439 male British doctors. Information about their smoking habits was obtained in 1951, and periodically thereafter; cause specific mortality was monitored for 50 years.
Main outcome measures: Overall mortality by smoking habit, considering separately men born in different periods.
Results: The excess mortality associated with smoking chiefly involved vascular, neoplastic, and respiratory diseases that can be caused by smoking. Men born in 1900-1930 who smoked only cigarettes and continued smoking died on average about 10 years younger than lifelong non-smokers. Cessation at age 60, 50, 40, or 30 years gained, respectively, about 3, 6, 9, or 10 years of life expectancy. The excess mortality associated with cigarette smoking was less for men born in the 19th century and was greatest for men born in the 1920s. The cigarette smoker versus non-smoker probabilities of dying in middle age (35-69) were 42% nu 24% (a twofold death rate ratio) for those born in 1900-1909, but were 43% nu 15% (a threefold death rate ratio) for those born in the 1920s. At older ages, the cigarette smoker versus non-smoker probabilities of surviving from age 70 to 90 were 10% nu 12% at the death rates of the 1950s (that is, among men born around the 1870s) but were 7% nu 33% (again a threefold death rate ratio) at the death rates of the 1990s (that is, among men born around the 1910s).
Conclusion: A substantial progressive decrease in the mortality rates among non-smokers over the past half century (due to prevention and improved treatment of disease) has been wholly outweighed, among cigarette smokers, by a progressive increase in the smoker nu non-smoker death rate ratio due to earlier and more intensive use of cigarettes. Among the men born around 1920, prolonged cigarette smoking from early adult life tripled age specific mortality rates, but cessation at age 50 halved the hazard, and cessation at age 30 avoided almost all of it.
Figures
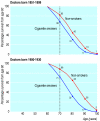
Fig 1
Survival from age 60 for continuing cigarette smokers and lifelong non-smokers among UK male doctors born 1851-1899 (median 1889) and 1900-1930 (median 1915), with percentages alive at each decade of age
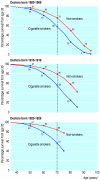
Fig 2
Survival from age 35 for continuing cigarette smokers and lifelong non-smokers among UK male doctors born 1900-1909, 1910-1919, and 1920-1929, with percentages alive at each decade of age
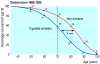
Fig 3
Survival from age 35 for continuing cigarette smokers and lifelong non-smokers among UK male doctors born 1900-1930, with percentages alive at each decade of age
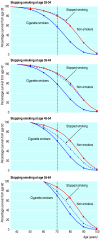
Fig 4
Effects on survival of stopping smoking cigarettes at age 25-34 (effect from age 35), age 35-44 (effect from age 40), age 45-54 (effect from age 50), and age 55-64 (effect from age 60)
Comment in
- New insights from the British doctors study.
Stampfer M. Stampfer M. BMJ. 2004 Jun 26;328(7455):1507. doi: 10.1136/bmj.328.7455.1507. BMJ. 2004. PMID: 15217842 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Contrasting male and female trends in tobacco-attributed mortality in China: evidence from successive nationwide prospective cohort studies.
Chen Z, Peto R, Zhou M, Iona A, Smith M, Yang L, Guo Y, Chen Y, Bian Z, Lancaster G, Sherliker P, Pang S, Wang H, Su H, Wu M, Wu X, Chen J, Collins R, Li L; China Kadoorie Biobank (CKB) collaborative group. Chen Z, et al. Lancet. 2015 Oct 10;386(10002):1447-56. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00340-2. Lancet. 2015. PMID: 26466050 Free PMC article. Review. - Mortality in relation to smoking: 40 years' observations on male British doctors.
Doll R, Peto R, Wheatley K, Gray R, Sutherland I. Doll R, et al. BMJ. 1994 Oct 8;309(6959):901-11. doi: 10.1136/bmj.309.6959.901. BMJ. 1994. PMID: 7755693 Free PMC article. - Smoking, smoking cessation, and lung cancer in the UK since 1950: combination of national statistics with two case-control studies.
Peto R, Darby S, Deo H, Silcocks P, Whitley E, Doll R. Peto R, et al. BMJ. 2000 Aug 5;321(7257):323-9. doi: 10.1136/bmj.321.7257.323. BMJ. 2000. PMID: 10926586 Free PMC article. - The 21st century hazards of smoking and benefits of stopping: a prospective study of one million women in the UK.
Pirie K, Peto R, Reeves GK, Green J, Beral V; Million Women Study Collaborators. Pirie K, et al. Lancet. 2013 Jan 12;381(9861):133-41. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61720-6. Epub 2012 Oct 27. Lancet. 2013. PMID: 23107252 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Factors associated with smoking in immigrants from non-western to western countries - what role does acculturation play? A systematic review.
Reiss K, Lehnhardt J, Razum O. Reiss K, et al. Tob Induc Dis. 2015 Apr 16;13(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s12971-015-0036-9. eCollection 2015. Tob Induc Dis. 2015. PMID: 25908932 Free PMC article. - A pre-post pilot study of a brief, web-based intervention to engage disadvantaged smokers into cessation treatment.
Brunette MF, Gunn W, Alvarez H, Finn PC, Geiger P, Ferron JC, McHugo GJ. Brunette MF, et al. Addict Sci Clin Pract. 2015 Feb 1;10(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s13722-015-0026-5. Addict Sci Clin Pract. 2015. PMID: 25638283 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Comparison of the characteristics of long-term users of electronic cigarettes versus nicotine replacement therapy: A cross-sectional survey of English ex-smokers and current smokers.
Nelson VA, Goniewicz ML, Beard E, Brown J, Sheals K, West R, Shahab L. Nelson VA, et al. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2015 Aug 1;153:300-5. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2015.05.005. Epub 2015 May 18. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2015. PMID: 26026493 Free PMC article. - Phenotypic age mediates effects of Life's Essential 8 on reduced mortality risk in US adults.
Zhao Y, Yang H, Jiao R, Wang Y, Xiao M, Song M, Yu H, Liao C, Pang Y, Gao W, Huang T, Yu C, Lv J, Li S, Qi L, Li L, Sun D. Zhao Y, et al. Precis Clin Med. 2024 Sep 16;7(3):pbae019. doi: 10.1093/pcmedi/pbae019. eCollection 2024 Sep. Precis Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39309670 Free PMC article. - Number of components of the metabolic syndrome; smoking and inflammatory markers.
Kawada T, Otsuka T, Endo T, Kon Y. Kawada T, et al. Int J Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Winter;11(1):23-6. doi: 10.5812/ijem.8403. Epub 2012 Dec 21. Int J Endocrinol Metab. 2013. PMID: 23853616 Free PMC article.
References
- Müller FH. Tabakmissbrauch und lungencarcinoma. Zeitschrift Krebsforsch 1939;49: 57-85.
- Schairer E, Schöniger E. Lungenkrebs und Tabakverbrauch. Zeitschrift Krebsforsch 1943;54: 261-69.
- Wassink WF. Onstaansvoorwasrden voor Longkanker. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 1948;92: 3732-47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous