Human ganglion cells express the alpha-2 adrenergic receptor: relevance to neuroprotection - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Human ganglion cells express the alpha-2 adrenergic receptor: relevance to neuroprotection
F B Kalapesi et al. Br J Ophthalmol. 2005 Jun.
Abstract
Background/aim: Alpha-2alpha adrenergic receptor (alpha(2)-AR) agonists are thought to be neuroprotective, preventing retinal ganglion cell death independent of pressure reduction. Previous studies have identified alpha(2)-ARs in rat retina. The authors aimed to demonstrate the presence and localisation of alpha(2)-ARs in human and rat retina and on the rat retinal ganglion cell line, RGC-5.
Methods: Seven postmortem human and three postmortem rat eyes were paraformaldehyde fixed and frozen. RGC-5 cells were also paraformaldehyde fixed. The expression of alpha(2A)-ARs was determined by antibody immunofluorescence.
Results: alpha(2A)-AR expression was identified in the human retina, on ganglion cells, and cells in the inner and outer nuclear layers (INL, ONL). Differential alpha(2A)-AR staining patterns in the INL and ONL suggest a further restriction to as yet unidentified neuronal subclasses. The RGC-5 cell line also expressed alpha(2A)-ARs in undifferentiated cells and an increased expression upon fully differentiated cells.
Conclusion: alpha(2)-AR agonists in addition to their pressure lowering effects in the eye, may act directly upon retinal neurons, including retinal ganglion cells. The presence of alpha(2)-ARs on the RGC-5 cell line allows future investigation of these possible direct effects using in vitro glaucoma model systems.
Figures
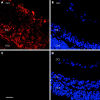
Figure 1
α2A-AR expression in the rat retina. Confocal images of rat retina labelled with α2A-AR antibody throughout retinal layers. (A) Shows positive immunostaining for the α2A-AR on retinal ganglion cells, cells in the inner nuclear layer (INL) and less so, but also on the membrane of outer nuclear layer (ONL) cells. (C) A retina control with secondary antibody alone showing no non-specific staining. (B) and (D) are equivalent to (A) and (C) retinal sections, respectively, showing Hoechst nuclear counterstaining. All images are taken with the ×63 objective, (C) shows 25 μm scale bar. GCL, ganglion cell layer.
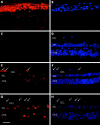
Figure 2
α2A-AR expression in the human cornea and retina. Confocal images of human eye labelled with α2A-AR antibody in cornea and retinal layers. (A), (E), and (G) Immunostained with α2A-AR antibody and (C) with chicken IgY alone. (B), (F), (H), and (D) Corresponding Hoechst nuclear counterstaining. (A) The positive control, is human corneal epithelium showing specific strong staining for the 2AR. (C) A retina control with chicken IgY alone showing no non-specific staining. (E) and (G) Staining of two different human retinas with positive retinal ganglion cells (arrows) and variable staining in inner (INL) and outer nuclear layers (ONL). Between different retinas, there was some variability in overall intensity but a similar pattern of staining. All images are taken with the ×63 objective. (G) Shows 25 μm scale bar. GCL, ganglion cell layer.
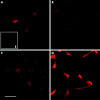
Figure 3
α2A-AR expression in the rat retinal ganglion cell line, RGC-5. Confocal images of rat retinal ganglion cell line RGC-5 labelled with α2A-AR antibody. (A) Undifferentiated RGC-5 cells have low, though positive, level of α2A-AR expression. (B-D) 3, 5, and 7 days, respectively, of RGC-5 differentiation, showing positive α2A-AR expression, with maximum expression at 7 days of differentiation. (E) (inset) RGC-5 cells with chicken IgY alone showing no non-specific staining. Identical staining and confocal imaging conditions used for all images. All images ×40 objective. (C) Shows 25 μm scale bar.
Similar articles
- Alpha2 adrenergic modulation of NMDA receptor function as a major mechanism of RGC protection in experimental glaucoma and retinal excitotoxicity.
Dong CJ, Guo Y, Agey P, Wheeler L, Hare WA. Dong CJ, et al. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008 Oct;49(10):4515-22. doi: 10.1167/iovs.08-2078. Epub 2008 Jun 19. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008. PMID: 18566471 - Comparison of the neuroprotective effects of adrenoceptor drugs in retinal cell culture and intact retina.
Baptiste DC, Hartwick AT, Jollimore CA, Baldridge WH, Chauhan BC, Tremblay F, Kelly ME. Baptiste DC, et al. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002 Aug;43(8):2666-76. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002. PMID: 12147601 - Role of nonfeminizing estrogen analogues in neuroprotection of rat retinal ganglion cells against glutamate-induced cytotoxicity.
Kumar DM, Perez E, Cai ZY, Aoun P, Brun-Zinkernagel AM, Covey DF, Simpkins JW, Agarwal N. Kumar DM, et al. Free Radic Biol Med. 2005 May 1;38(9):1152-63. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.12.007. Free Radic Biol Med. 2005. PMID: 15808412 - Role of alpha-2 agonists in neuroprotection.
Wheeler L, WoldeMussie E, Lai R. Wheeler L, et al. Surv Ophthalmol. 2003 Apr;48 Suppl 1:S47-51. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6257(03)00004-3. Surv Ophthalmol. 2003. PMID: 12852434 Review. - A forensic path to RGC-5 cell line identification: lessons learned.
Krishnamoorthy RR, Clark AF, Daudt D, Vishwanatha JK, Yorio T. Krishnamoorthy RR, et al. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013 Aug 23;54(8):5712-9. doi: 10.1167/iovs.13-12085. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013. PMID: 23975727 Review.
Cited by
- The Role of Retinal Ganglion Cell Structure and Function in Glaucoma.
Feng KM, Tsung TH, Chen YH, Lu DW. Feng KM, et al. Cells. 2023 Dec 8;12(24):2797. doi: 10.3390/cells12242797. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38132117 Free PMC article. Review. - Adrenoceptors in the Eye - Physiological and Pathophysiological Relevance.
Ruan Y, Buonfiglio F, Gericke A. Ruan Y, et al. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2024;285:453-505. doi: 10.1007/164_2023_702. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38082203 Review. - Ocular Distribution of Brimonidine and Brinzolamide after Topical Instillation of a 0.1% Brimonidine Tartrate and 1% Brinzolamide Fixed-Combination Ophthalmic Suspension: An Interventional Study.
Orii Y, Kunikane E, Yamada Y, Morioka M, Iwasaki K, Arimura S, Mizuno A, Inatani M. Orii Y, et al. J Clin Med. 2023 Jun 21;12(13):4175. doi: 10.3390/jcm12134175. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37445209 Free PMC article. - Comparisons of α2-Adrenergic Agents, Medetomidine and Xylazine, with Pentobarbital for Anesthesia: Important Pitfalls in Diabetic and Nondiabetic Rats.
Connell AR, Hookham MB, Fu D, Brazil DP, Lyons TJ, Yu JY. Connell AR, et al. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Mar;38(2):156-166. doi: 10.1089/jop.2021.0084. Epub 2021 Dec 29. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 34964655 Free PMC article. - Polydopamine nanoparticles attenuate retina ganglion cell degeneration and restore visual function after optic nerve injury.
Lou X, Hu Y, Zhang H, Liu J, Zhao Y. Lou X, et al. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021 Dec 20;19(1):436. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-01199-3. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021. PMID: 34930292 Free PMC article.
References
- Ahmed FA, Hegazy K, Chaudhary P, et al. Neuroprotective effect of alpha(2) agonist (brimonidine) on adult rat retinal ganglion cells after increased intraocular pressure. Brain Res 2001;913:133–9. - PubMed
- Morrison JC, Nylander KB, Lauer AK, et al. Glaucoma drops control intraocular pressure and protect optic nerves in a rat model of glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1998;39:526–31. - PubMed
- Wheeler LA, Woldemussie E. Alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonists are neuroprotective in experimental models of glaucoma. Eur J Ophthalmol 2001;11:S30–35. - PubMed
- WoldeMussie E, Ruiz G, Wijono M, et al. Neuroprotection of retinal ganglion cells by brimonidine in rats with laser-induced chronic ocular hypertension. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2001;42:2849–55. - PubMed
- Donello JE, Padillo EU, Webster ML, et al. Alpha(2)-adrenoceptor agonists inhibit vitreal glutamate and aspartate accumulation and preserve retinal function after transient ischemia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2001;296:216–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials