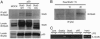Suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 selectively inhibits LPS-induced IL-6 production by regulating JAK-STAT - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
. 2005 Nov 22;102(47):17089-94.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0508517102. Epub 2005 Nov 15.
Affiliations
- PMID: 16287972
- PMCID: PMC1288004
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0508517102
Comparative Study
Suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 selectively inhibits LPS-induced IL-6 production by regulating JAK-STAT
Akihiro Kimura et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005.
Abstract
Suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 (SOCS-1) is one of the negative-feedback regulators of Janus kinase (JAK)-signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) signaling. We previously showed that SOCS-1 participates in LPS signaling, but it is not entirely clear yet how SOCS-1 suppresses LPS signaling. In this study, we demonstrate that SOCS-1 selectively inhibits LPS-induced IL-6 production through regulation of JAK-STAT but not production of TNF-alpha, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, IFN-beta, and other cytokines. We found that LPS directly activated Jak2 and Stat5, whereas SOCS-1 inhibited LPS-induced Jak2 and Stat5 activation. Furthermore, AG490, a Jak-specific inhibitor, and dominant negative Stat5 only reduced LPS-induced IL-6 production. Additionally, Stat5 interacted with p50, resulting in recruitment of Stat5 to the IL-6 promoter together with p50 in response to LPS stimulation. These findings suggest that the JAK-STAT pathway participates in LPS-induced IL-6 production and that SOCS-1 suppresses LPS signaling by regulating JAK-STAT.
Figures
Fig. 1.
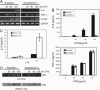
SOCS-1 selectively inhibits IL-6 production by LPS. (A) Raw/Neo and Raw/SOCS-1 cells were stimulated by LPS at the indicated time points. Expression of LPS-induced cytokines genes was examined by RT-PCR. (B) Raw/Neo and Raw/SOCS-1 cells were stimulated by LPS as indicated. IL-6 and TNF-α production was measured by using ELISA. (C) SOCS-1 He mice and WT mice were injected i.p. with 1 mg of LPS. Serum IL-6 levels were measured by ELISA at 2 h. Data show means ± SE of three independent experiments.
Fig. 2.
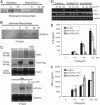
Jak2 participates directly in LPS-induced IL-6 production. (A) Raw/Neo and Raw/SOCS-1 cells were stimulated by LPS at the indicated time points. Tyrosine phosphorylation of Jak2 was analyzed by immunoprecipitation and Western blotting. (B) COS-7 cells were cotransfected with MyD88-Flag, TLR4-Flag, and Jak2. After 2 days, the cells were lysed and immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag Ab, followed by detection of Jak2 by means of Western blotting. Raw cells were stimulated by LPS with or without AG490. (C) Cytokine induction by LPS was examined by using RT-PCR. (D) LPS-induced IL-6 production was measured by means of ELISA. Data show means ± SE of three independent experiments.
Fig. 3.
Stat5 participates directly in LPS-induced IL-6 production. (A) Raw/Neo and Raw/SOCS-1 cells were incubated with LPS at the indicated time points. Whole-cell lysates were used for immunoblotting (IB) analysis with anti-phospho-tyrosine Stat5 Ab. (B) Peritoneal macrophages were isolated from BALB/c mice and stimulated by LPS at the indicated time points. Tyrosine phosphorylation of Stat5 was examined by means of immunoprecipitation (IP) and Western blotting. (C) The interaction of Stat5 with TLR4 was examined by immunoprecipitation and Western blotting in COS-7 cells, which were inducted with Stat5, TLR4, and Raw cells. Raw/Neo, Raw/Stat5 1*6, and Raw/Stat5 DN were stimulated by LPS at the indicated time points, followed by an examination of IL-6 and TNF-α induction by means of RT-PCR (D) and ELISA (E and F). Data show means ± SE of three independent experiments.
Fig. 4.
Stat5 associates with p50 and mediates LPS-induced IL-6 production. (A) COS-7 cells were cotransfected with Stat5 WT, Stat5 1*6, or Stat5 DN and p50. Whole-cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-p50 Ab after which Stat5 was detected with Western blotting. (B) Raw/Stat5 1*6 cells were stimulated by LPS followed by examination of the association of Stat5 with endogenous p50 by means of immunoprecipitation (IP) and Western blotting. (C) Raw cells were stimulated with LPS for 2 h, and the ChIP assay was performed by using anti-Stat5a, anti-Stat5, and anti-p50 Abs. Purified DNA fragments were amplified by using primers specific for the IL-6 promoter, as described in Materials and Methods. IB, immunoblotting.
Similar articles
- The JAK-inhibitor, JAB/SOCS-1 selectively inhibits cytokine-induced, but not v-Src induced JAK-STAT activation.
Iwamoto T, Senga T, Naito Y, Matsuda S, Miyake Y, Yoshimura A, Hamaguchi M. Iwamoto T, et al. Oncogene. 2000 Sep 28;19(41):4795-801. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203829. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 11032030 - Endoplasmic reticulum stress prolongs GH-induced Janus kinase (JAK2)/signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT5) signaling pathway.
Flores-Morales A, Fernández L, Rico-Bautista E, Umana A, Negrín C, Zhang JG, Norstedt G. Flores-Morales A, et al. Mol Endocrinol. 2001 Sep;15(9):1471-83. doi: 10.1210/mend.15.9.0699. Mol Endocrinol. 2001. PMID: 11518796 - Involvement of suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 as a mediator of the inhibitory effects of IL-10 on lipopolysaccharide-induced macrophage activation.
Berlato C, Cassatella MA, Kinjyo I, Gatto L, Yoshimura A, Bazzoni F. Berlato C, et al. J Immunol. 2002 Jun 15;168(12):6404-11. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.12.6404. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12055259 - Suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS): inhibitors of the JAK/STAT pathway.
Cooney RN. Cooney RN. Shock. 2002 Feb;17(2):83-90. doi: 10.1097/00024382-200202000-00001. Shock. 2002. PMID: 11837794 Review. - SOCS proteins and caveolin-1 as negative regulators of endocrine signaling.
Jasmin JF, Mercier I, Sotgia F, Lisanti MP. Jasmin JF, et al. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2006 May-Jun;17(4):150-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2006.03.007. Epub 2006 Apr 17. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2006. PMID: 16616514 Review.
Cited by
- Anti-inflammatory effect of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 is associated with crosstalk between signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 and the vitamin D receptor in human monocytes.
Yang M, Yang BO, Gan H, Li X, Xu J, Yu J, Gao L, Li F. Yang M, et al. Exp Ther Med. 2015 May;9(5):1739-1744. doi: 10.3892/etm.2015.2321. Epub 2015 Mar 2. Exp Ther Med. 2015. PMID: 26136886 Free PMC article. - The role of JAK-3 in regulating TLR-mediated inflammatory cytokine production in innate immune cells.
Wang H, Brown J, Gao S, Liang S, Jotwani R, Zhou H, Suttles J, Scott DA, Lamont RJ. Wang H, et al. J Immunol. 2013 Aug 1;191(3):1164-74. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1203084. Epub 2013 Jun 24. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23797672 Free PMC article. - Disease-dependent local IL-10 production ameliorates collagen induced arthritis in mice.
Henningsson L, Eneljung T, Jirholt P, Tengvall S, Lidberg U, van den Berg WB, van de Loo FA, Gjertsson I. Henningsson L, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49731. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049731. Epub 2012 Nov 16. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23166758 Free PMC article. - IFN-α-Induced Downregulation of miR-221 in Dendritic Cells: Implications for HCV Pathogenesis and Treatment.
Sehgal M, Zeremski M, Talal AH, Ginwala R, Elrod E, Grakoui A, Li QG, Philip R, Khan ZK, Jain P. Sehgal M, et al. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2015 Sep;35(9):698-709. doi: 10.1089/jir.2014.0211. Epub 2015 Jun 19. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2015. PMID: 26090579 Free PMC article. - IL-6-dependent and -independent pathways in the development of interleukin 17-producing T helper cells.
Kimura A, Naka T, Kishimoto T. Kimura A, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Jul 17;104(29):12099-104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0705268104. Epub 2007 Jul 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17623780 Free PMC article.
References
- Beutler, B. & Rietschel, E. T. (2003) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 3, 169-176. - PubMed
- Akira, S. & Takeda, K. (2004) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 4, 499-511. - PubMed
- Medzhitov, R., Preston-Hurlbrt, P., Kopp, E., Stadlen, A., Chen, C., Ghosh, S. & Janeway, C. A., Jr. (1998) Mol. Cell 2, 253-258. - PubMed
- Yamamoto, M., Sato, S., Hemmi, H., Sanjyo, H., Uematsu, S., Kaisho, T., Hoshino, K., Takeuchi, O., Kobayashi, M., Fujita, T., et al. (2002) Nature 420, 324-329. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous