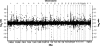Identification by full-coverage array CGH of human DNA copy number increases relative to chimpanzee and gorilla - PubMed (original) (raw)
Comparative Study
Identification by full-coverage array CGH of human DNA copy number increases relative to chimpanzee and gorilla
Gary M Wilson et al. Genome Res. 2006 Feb.
Abstract
Duplication of chromosomal segments and associated genes is thought to be a primary mechanism for generating evolutionary novelty. By comparative genome hybridization using a full-coverage (tiling) human BAC array with 79-kb resolution, we have identified 63 chromosomal segments, ranging in size from 0.65 to 1.3 Mb, that have inferred copy number increases in human relative to chimpanzee. These segments span 192 Ensembl genes, including 82 gene duplicates (41 reciprocal best BLAST matches). Synonymous and nonsynonymous substitution rates across these pairs provide evidence for general conservation of the amino acid sequence, consistent with the maintenance of function of both copies, and one case of putative positive selection for an uncharacterized gene. Surprisingly, the core histone genes H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 have been duplicated in the human lineage since our split with chimpanzee. The observation of increased copy number of a human cluster of core histone genes suggests that altered dosage, even of highly constrained genes, may be an important evolutionary mechanism.
Figures
Figure 1.
Human chimpanzee DNA copy number ratio determined by full-coverage BAC array CGH.
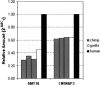
Figure 2.
Relative copy number of the AMY1A and CNTNAP3 loci in three unrelated chimpanzees and a single gorilla compared to a single pooled sample of human gDNA.
Similar articles
- Identification of large-scale human-specific copy number differences by inter-species array comparative genomic hybridization.
Goidts V, Armengol L, Schempp W, Conroy J, Nowak N, Müller S, Cooper DN, Estivill X, Enard W, Szamalek JM, Hameister H, Kehrer-Sawatzki H. Goidts V, et al. Hum Genet. 2006 Mar;119(1-2):185-98. doi: 10.1007/s00439-005-0130-9. Epub 2006 Jan 5. Hum Genet. 2006. PMID: 16395594 - Identification of human specific gene duplications relative to other primates by array CGH and quantitative PCR.
Armengol G, Knuutila S, Lozano JJ, Madrigal I, Caballín MR. Armengol G, et al. Genomics. 2010 Apr;95(4):203-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2010.02.003. Epub 2010 Feb 11. Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20153417 - Duplication of the CD8 beta-chain gene as a marker of the man-gorilla-chimpanzee clade.
Delarbre C, Nakauchi H, Bontrop R, Kourilsky P, Gachelin G. Delarbre C, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):7049-53. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.7049. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993. PMID: 8346216 Free PMC article. - Structural divergence between the human and chimpanzee genomes.
Kehrer-Sawatzki H, Cooper DN. Kehrer-Sawatzki H, et al. Hum Genet. 2007 Feb;120(6):759-78. doi: 10.1007/s00439-006-0270-6. Epub 2006 Oct 26. Hum Genet. 2007. PMID: 17066299 Review. - Evolution and demography of the great apes.
Kuhlwilm M, de Manuel M, Nater A, Greminger MP, Krützen M, Marques-Bonet T. Kuhlwilm M, et al. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2016 Dec;41:124-129. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2016.09.005. Epub 2016 Oct 4. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2016. PMID: 27716526 Review.
Cited by
- The evolutionary significance of copy number variation in the human genome.
Perry GH. Perry GH. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2008;123(1-4):283-7. doi: 10.1159/000184719. Epub 2009 Mar 11. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2008. PMID: 19287166 Free PMC article. Review. - Measurements of salivary alpha amylase and salivary cortisol in hominoid primates reveal within-species consistency and between-species differences.
Behringer V, Borchers C, Deschner T, Möstl E, Selzer D, Hohmann G. Behringer V, et al. PLoS One. 2013 Apr 17;8(4):e60773. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060773. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23613746 Free PMC article. - What makes us human: revisiting an age-old question in the genomic era.
Mekel-Bobrov N, Lahn BT. Mekel-Bobrov N, et al. J Biomed Discov Collab. 2006 Nov 29;1:18. doi: 10.1186/1747-5333-1-18. J Biomed Discov Collab. 2006. PMID: 17134487 Free PMC article. - Great ape genomics.
Wall JD. Wall JD. ILAR J. 2013;54(2):82-90. doi: 10.1093/ilar/ilt048. ILAR J. 2013. PMID: 24174434 Free PMC article. Review. - Online resources for genomic structural variation.
Sneddon TP, Church DM. Sneddon TP, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;838:273-89. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-507-7_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22228017 Free PMC article.
References
- Adams, R. and Bischof, L. 1994. Seeded region growing. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Machine Intell. 16 641-647.
- Bailey, J.A., Gu, Z., Clark, R.A., Reinert, K., Samonte, R.V., Schwartz, S., Adams, M.D., Myers, E.W., Li, P.W., and Eichler, E.E. 2002. Recent segmental duplications in the human genome. Science 297 1003-1007. - PubMed
- Chimpanzee Sequencing and Analysis Consortium. 2005. Initial sequence of the chimpanzee genome and comparison with the human genome. Nature 437 69-87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous