The cargo-binding domain regulates structure and activity of myosin 5 - PubMed (original) (raw)
The cargo-binding domain regulates structure and activity of myosin 5
Kavitha Thirumurugan et al. Nature. 2006.
Abstract
Myosin 5 is a two-headed motor protein that moves cargoes along actin filaments. Its tail ends in paired globular tail domains (GTDs) thought to bind cargo. At nanomolar calcium levels, actin-activated ATPase is low and the molecule is folded. Micromolar calcium concentrations activate ATPase and the molecule unfolds. Here we describe the structure of folded myosin and the GTD's role in regulating activity. Electron microscopy shows that the two heads lie either side of the tail, contacting the GTDs at a lobe of the motor domain (approximately Pro 117-Pro 137) that contains conserved acidic side chains, suggesting ionic interactions between motor domain and GTD. Myosin 5 heavy meromyosin, a constitutively active fragment lacking the GTDs, is inhibited and folded by a dimeric GST-GTD fusion protein. Motility assays reveal that at nanomolar calcium levels heavy meromyosin moves robustly on actin filaments whereas few myosins bind or move. These results combine to show that with no cargo, the GTDs bind in an intramolecular manner to the motor domains, producing an inhibited and compact structure that binds weakly to actin and allows the molecule to recycle towards new cargoes.
Figures
Figure 1
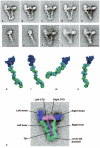
Structure of switched-off myosin 5 and HMM-GTD complex. a-e, averaged images of negative-stained, folded whole myosin molecules; 46-53 molecules per class. f, g, averaged images of myosin 5 S1 stained in the presence of ATP; f shows the pre-powerstroke conformation (63 molecules), g the post-rigor conformation (58 molecules). h, i, averaged images of myosin in presence of ADP or no nucleotide, respectively; 21 and 55 molecules. j, averaged images of the complex of myosin 5 HMM and GST-GTD dimer; 28 molecules. Scale bar in j is 20 nm and applies to panels a-j. k-n, atomic models of myosin 5 head; heavy chain shaded dark blue, the six calmodulins shaded alternately cyan and green, the putative GTD-binding region of the motor domain (Pro117-Pro137) shaded pink. k, model using scallop motor domain containing ADP.vanadate oriented to try to match left head of folded myosin in image averages. l, model using myosin 5 motor domain containing ADP.BeFx oriented to match left head. m, same model as l, oriented to match right head. Pro117-Pro137 lies behind the converter subdomain in this view. n, same model as k, oriented to try to match right head motor domain appearance. k-n created using PyMOL (DeLano Scientific). o, enlargement of a, coloured and labelled to show domains within folded myosin 5.
Figure 2
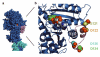
GTD-binding region of myosin 5 motor domain. a, motor domain region of myosin 5.ADP.BeFx complex, with putative GTD-binding region pink and proximal calmodulin cyan. b, enlargement of GTD-binding region of the motor domain of a to show spatial relationship to bound nucleotide; polypeptide chain shown in cartoon form, except the four acidic residues (E121, D122, D134, D136) shown in spacefill with carbons yellow, orange, green and cyan respectively and carboxylate oxygens red; bound MgADP.BeFx as spacefilling model, ADP in CPK colours, BeFx olive, Mg2+ green. Created using PyMOL (DeLano Scientific).
Figure 3
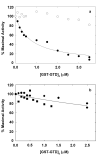
Regulation of actin-activated myosin 5 ATPase activity by GST-GTD dimers. a, myosin 5 HMM; solid circles at nanomolar calcium, open circles with 0.1 mM free calcium. Fitted line gives Ki 0.75μM. b, myosin 5 S1 at nanomolar calcium, squares and circles represent independent experiments. Ca2+ did not greatly affect the Km values for actin activation of HMM MgATPase which were generally in the range of 0.3-0.7 μM in the presence of 50 mM KCl.
Similar articles
- The Globular Tail Domain of Myosin-5a Functions as a Dimer in Regulating the Motor Activity.
Zhang WB, Yao LL, Li XD. Zhang WB, et al. J Biol Chem. 2016 Jun 24;291(26):13571-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.724328. Epub 2016 Apr 28. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27129208 Free PMC article. - Myosin V: regulation by calcium, calmodulin, and the tail domain.
Krementsov DN, Krementsova EB, Trybus KM. Krementsov DN, et al. J Cell Biol. 2004 Mar 15;164(6):877-86. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200310065. Epub 2004 Mar 8. J Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15007063 Free PMC article. - Ca2+-induced activation of ATPase activity of myosin Va is accompanied with a large conformational change.
Li XD, Mabuchi K, Ikebe R, Ikebe M. Li XD, et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004 Mar 12;315(3):538-45. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.01.084. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004. PMID: 14975734 - Calcium and cargoes as regulators of myosin 5a activity.
Sellers JR, Thirumurugan K, Sakamoto T, Hammer JA 3rd, Knight PJ. Sellers JR, et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008 Apr 25;369(1):176-81. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.11.109. Epub 2007 Dec 3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008. PMID: 18060865 Review. - The tail that wags the dog: the globular tail domain defines the function of myosin V/XI.
Li JF, Nebenführ A. Li JF, et al. Traffic. 2008 Mar;9(3):290-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2007.00687.x. Epub 2007 Dec 9. Traffic. 2008. PMID: 18088322 Review.
Cited by
- The microtubule plus-end localization of Aspergillus dynein is important for dynein-early-endosome interaction but not for dynein ATPase activation.
Zhang J, Zhuang L, Lee Y, Abenza JF, Peñalva MA, Xiang X. Zhang J, et al. J Cell Sci. 2010 Oct 15;123(Pt 20):3596-604. doi: 10.1242/jcs.075259. Epub 2010 Sep 28. J Cell Sci. 2010. PMID: 20876661 Free PMC article. - Autoregulation and dual stepping mode of MYA2, an Arabidopsis myosin XI responsible for cytoplasmic streaming.
Haraguchi T, Ito K, Morikawa T, Yoshimura K, Shoji N, Kimura A, Iwaki M, Tominaga M. Haraguchi T, et al. Sci Rep. 2022 Feb 24;12(1):3150. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-07047-0. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35210477 Free PMC article. - Functions of class V myosins in neurons.
Hammer JA 3rd, Wagner W. Hammer JA 3rd, et al. J Biol Chem. 2013 Oct 4;288(40):28428-34. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R113.514497. Epub 2013 Aug 29. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23990471 Free PMC article. Review. - Identification of a third myosin-5a-melanophilin interaction that mediates the association of myosin-5a with melanosomes.
Pan J, Zhou R, Yao LL, Zhang J, Zhang N, Cao QJ, Sun S, Li XD. Pan J, et al. Elife. 2024 Jun 20;13:RP93662. doi: 10.7554/eLife.93662. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38900147 Free PMC article. - Loss of cargo binding in the human myosin VI deafness mutant (R1166X) leads to increased actin filament binding.
Arden SD, Tumbarello DA, Butt T, Kendrick-Jones J, Buss F. Arden SD, et al. Biochem J. 2016 Oct 1;473(19):3307-19. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20160571. Epub 2016 Jul 29. Biochem J. 2016. PMID: 27474411 Free PMC article.
References
- Sellers JR, Veigel C. Walking with myosin V. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2006;18:68–73. - PubMed
- Cheney RE, et al. Brain myosin-V is a 2-headed unconventional myosin with motor-activity. Cell. 1993;75:13–23. - PubMed
- Wang F, et al. Regulated conformation of myosin V. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:2333–2336. - PubMed
- Li XD, Mabuchi K, Ikebe R, Ikebe M. Ca2+-induced activation of ATPase activity of myosin Va is accompanied with a large conformational change. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 2004;315:538–545. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials