Oligonucleotide microarray analysis of genomic imbalance in children with mental retardation - PubMed (original) (raw)
doi: 10.1086/507471. Epub 2006 Jul 25.
Agnes Baross, Allen D Delaney, Adrian Ally, Laura Arbour, Linlea Armstrong, Jennifer Asano, Dione K Bailey, Sarah Barber, Patricia Birch, Mabel Brown-John, Manqiu Cao, Susanna Chan, David L Charest, Noushin Farnoud, Nicole Fernandes, Stephane Flibotte, Anne Go, William T Gibson, Robert A Holt, Steven J M Jones, Giulia C Kennedy, Martin Krzywinski, Sylvie Langlois, Haiyan I Li, Barbara C McGillivray, Tarun Nayar, Trevor J Pugh, Evica Rajcan-Separovic, Jacqueline E Schein, Angelique Schnerch, Asim Siddiqui, Margot I Van Allen, Gary Wilson, Siu-Li Yong, Farah Zahir, Patrice Eydoux, Marco A Marra
Affiliations
- PMID: 16909388
- PMCID: PMC1559542
- DOI: 10.1086/507471
Oligonucleotide microarray analysis of genomic imbalance in children with mental retardation
J M Friedman et al. Am J Hum Genet. 2006 Sep.
Erratum in
- Am J Hum Genet. 2006 Dec;79(6):1135. Armstrong, Linlea [added]
Abstract
The cause of mental retardation in one-third to one-half of all affected individuals is unknown. Microscopically detectable chromosomal abnormalities are the most frequently recognized cause, but gain or loss of chromosomal segments that are too small to be seen by conventional cytogenetic analysis has been found to be another important cause. Array-based methods offer a practical means of performing a high-resolution survey of the entire genome for submicroscopic copy-number variants. We studied 100 children with idiopathic mental retardation and normal results of standard chromosomal analysis, by use of whole-genome sampling analysis with Affymetrix GeneChip Human Mapping 100K arrays. We found de novo deletions as small as 178 kb in eight cases, de novo duplications as small as 1.1 Mb in two cases, and unsuspected mosaic trisomy 9 in another case. This technology can detect at least twice as many potentially pathogenic de novo copy-number variants as conventional cytogenetic analysis can in people with mental retardation.
Figures
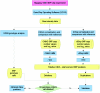
Figure 1.
Flow diagram showing algorithm used for detection of CNVs by use of WGSA with Mapping 100K arrays. HMM = hidden Markov model.
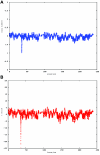
Figure 2.
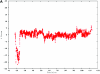
A CNV on chromosome 2 in the affected child of family 7551. A, dChip-smoothed copy-number (CN) estimate with a window of 38 SNPs, showing a 1-copy deletion. B, Diagram showing t scores calculated for a sliding window of 38 SNPs that compare the copy number estimated by dChip for SNPs within the window with the copy number estimated for all other SNPs on the same chromosome. The high (negative) t scores associated with the deletion indicate that this deviation in copy number is unlikely to have occurred by chance. In both panels, the _X_-axis shows the nucleotide position in Mb.
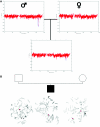
Figure 3.
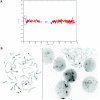
Inherited CNV demonstrated by WGSA with Mapping 100K arrays. A, Plot of t scores for chromosome 2 in father, mother, and child in family 0674, by use of a 21-SNP window. The SNPs are ordered along the _X_-axis from pter to qter, with the location shown in Mb. The child with MR inherited the CNV (blue oval) from his unaffected father. B, FISH confirmation of the inherited CNV on 2q34. In the father and child, one chromosome 2 (white arrowheads) lacks a signal for probe RP11-93G7, whereas the signal is present on the other chromosome 2 (red arrowheads). In the mother, the signal for probe RP11-93G7 is seen on both chromosomes 2 (red arrowheads).
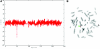
Figure 4.
De novo submicroscopic genomic deletion, del(2)(p16.3p16.3), identified by WGSA with Mapping 100K arrays in family 5003. A, The t scores for the CNV in comparison with the rest of the chromosome, by use of a window size of 20 SNPs. The SNPs are ordered along the _X_-axis from pter to qter, with the location shown in Mb. B, FISH confirmation of the CNV in the affected child by use of probe RP11-1151G3. The white arrowhead indicates the deletion-containing chromosome 2 without the signal. The green arrowhead indicates the normal homologue, which shows the signal.
Figure 5.
De novo submicroscopic genomic deletions identified by WGSA with Mapping 100K arrays in the affected child of families 1895, 3476, 4818, 5566, 6545, and 7807. Panels A, C, E, G, I, K, and M show the t scores for each CNV in comparison with the rest of the chromosome, by use of the window size given below. The SNPs are ordered along the _X_-axis from pter to qter, with the location shown in Mb. Panels B, D, F, H, J, L, and N show FISH confirmation of the CNV in the affected child, by use of the probe given below. The white arrowhead indicates the deleted chromosome without the signal. The red or green arrowhead indicates the normal homologue, which shows the signal. A, Family 1895, chromosome 13, window of 20 SNPs. B, Family 1895, probe RP11-26D3, del(13)(q12.11q12.13). C, Family 3476, chromosome 4, window of 30 SNPs. D, Family 3476, probe RP11-7G22, del(4)(q21.21q22.1). E, Family 4818, chromosome 12, window of 20 SNPs. F, Family 4818, probe RP11-91K23, del(12)(q14.2q15). G, Family 5566, chromosome 14, window of 5 SNPs. The de novo CNV is shown inside the blue oval. H, Family 5566, probe CTD-2136K6, del(14)(q11.2q11.2). I, Family 6545, chromosome 7, window of 20 SNPs. J, Family 6545, probe RP11-802L1, del(7)(p22.2p22.1). K, Family 7807, chromosome 22, window of 20 SNPs. L, Family 7807, probe RP11-79G21, del(22)(q12.1q12.1). M, Family 8326, chromosome 14, window of 20 SNPs. N, Family 8326, probe RP11-340M24, del(14)(q11.2q11.2).
Figure 5.
De novo submicroscopic genomic deletions identified by WGSA with Mapping 100K arrays in the affected child of families 1895, 3476, 4818, 5566, 6545, and 7807. Panels A, C, E, G, I, K, and M show the t scores for each CNV in comparison with the rest of the chromosome, by use of the window size given below. The SNPs are ordered along the _X_-axis from pter to qter, with the location shown in Mb. Panels B, D, F, H, J, L, and N show FISH confirmation of the CNV in the affected child, by use of the probe given below. The white arrowhead indicates the deleted chromosome without the signal. The red or green arrowhead indicates the normal homologue, which shows the signal. A, Family 1895, chromosome 13, window of 20 SNPs. B, Family 1895, probe RP11-26D3, del(13)(q12.11q12.13). C, Family 3476, chromosome 4, window of 30 SNPs. D, Family 3476, probe RP11-7G22, del(4)(q21.21q22.1). E, Family 4818, chromosome 12, window of 20 SNPs. F, Family 4818, probe RP11-91K23, del(12)(q14.2q15). G, Family 5566, chromosome 14, window of 5 SNPs. The de novo CNV is shown inside the blue oval. H, Family 5566, probe CTD-2136K6, del(14)(q11.2q11.2). I, Family 6545, chromosome 7, window of 20 SNPs. J, Family 6545, probe RP11-802L1, del(7)(p22.2p22.1). K, Family 7807, chromosome 22, window of 20 SNPs. L, Family 7807, probe RP11-79G21, del(22)(q12.1q12.1). M, Family 8326, chromosome 14, window of 20 SNPs. N, Family 8326, probe RP11-340M24, del(14)(q11.2q11.2).
Figure 5.
De novo submicroscopic genomic deletions identified by WGSA with Mapping 100K arrays in the affected child of families 1895, 3476, 4818, 5566, 6545, and 7807. Panels A, C, E, G, I, K, and M show the t scores for each CNV in comparison with the rest of the chromosome, by use of the window size given below. The SNPs are ordered along the _X_-axis from pter to qter, with the location shown in Mb. Panels B, D, F, H, J, L, and N show FISH confirmation of the CNV in the affected child, by use of the probe given below. The white arrowhead indicates the deleted chromosome without the signal. The red or green arrowhead indicates the normal homologue, which shows the signal. A, Family 1895, chromosome 13, window of 20 SNPs. B, Family 1895, probe RP11-26D3, del(13)(q12.11q12.13). C, Family 3476, chromosome 4, window of 30 SNPs. D, Family 3476, probe RP11-7G22, del(4)(q21.21q22.1). E, Family 4818, chromosome 12, window of 20 SNPs. F, Family 4818, probe RP11-91K23, del(12)(q14.2q15). G, Family 5566, chromosome 14, window of 5 SNPs. The de novo CNV is shown inside the blue oval. H, Family 5566, probe CTD-2136K6, del(14)(q11.2q11.2). I, Family 6545, chromosome 7, window of 20 SNPs. J, Family 6545, probe RP11-802L1, del(7)(p22.2p22.1). K, Family 7807, chromosome 22, window of 20 SNPs. L, Family 7807, probe RP11-79G21, del(22)(q12.1q12.1). M, Family 8326, chromosome 14, window of 20 SNPs. N, Family 8326, probe RP11-340M24, del(14)(q11.2q11.2).
Figure 5.
De novo submicroscopic genomic deletions identified by WGSA with Mapping 100K arrays in the affected child of families 1895, 3476, 4818, 5566, 6545, and 7807. Panels A, C, E, G, I, K, and M show the t scores for each CNV in comparison with the rest of the chromosome, by use of the window size given below. The SNPs are ordered along the _X_-axis from pter to qter, with the location shown in Mb. Panels B, D, F, H, J, L, and N show FISH confirmation of the CNV in the affected child, by use of the probe given below. The white arrowhead indicates the deleted chromosome without the signal. The red or green arrowhead indicates the normal homologue, which shows the signal. A, Family 1895, chromosome 13, window of 20 SNPs. B, Family 1895, probe RP11-26D3, del(13)(q12.11q12.13). C, Family 3476, chromosome 4, window of 30 SNPs. D, Family 3476, probe RP11-7G22, del(4)(q21.21q22.1). E, Family 4818, chromosome 12, window of 20 SNPs. F, Family 4818, probe RP11-91K23, del(12)(q14.2q15). G, Family 5566, chromosome 14, window of 5 SNPs. The de novo CNV is shown inside the blue oval. H, Family 5566, probe CTD-2136K6, del(14)(q11.2q11.2). I, Family 6545, chromosome 7, window of 20 SNPs. J, Family 6545, probe RP11-802L1, del(7)(p22.2p22.1). K, Family 7807, chromosome 22, window of 20 SNPs. L, Family 7807, probe RP11-79G21, del(22)(q12.1q12.1). M, Family 8326, chromosome 14, window of 20 SNPs. N, Family 8326, probe RP11-340M24, del(14)(q11.2q11.2).
Figure 5.
De novo submicroscopic genomic deletions identified by WGSA with Mapping 100K arrays in the affected child of families 1895, 3476, 4818, 5566, 6545, and 7807. Panels A, C, E, G, I, K, and M show the t scores for each CNV in comparison with the rest of the chromosome, by use of the window size given below. The SNPs are ordered along the _X_-axis from pter to qter, with the location shown in Mb. Panels B, D, F, H, J, L, and N show FISH confirmation of the CNV in the affected child, by use of the probe given below. The white arrowhead indicates the deleted chromosome without the signal. The red or green arrowhead indicates the normal homologue, which shows the signal. A, Family 1895, chromosome 13, window of 20 SNPs. B, Family 1895, probe RP11-26D3, del(13)(q12.11q12.13). C, Family 3476, chromosome 4, window of 30 SNPs. D, Family 3476, probe RP11-7G22, del(4)(q21.21q22.1). E, Family 4818, chromosome 12, window of 20 SNPs. F, Family 4818, probe RP11-91K23, del(12)(q14.2q15). G, Family 5566, chromosome 14, window of 5 SNPs. The de novo CNV is shown inside the blue oval. H, Family 5566, probe CTD-2136K6, del(14)(q11.2q11.2). I, Family 6545, chromosome 7, window of 20 SNPs. J, Family 6545, probe RP11-802L1, del(7)(p22.2p22.1). K, Family 7807, chromosome 22, window of 20 SNPs. L, Family 7807, probe RP11-79G21, del(22)(q12.1q12.1). M, Family 8326, chromosome 14, window of 20 SNPs. N, Family 8326, probe RP11-340M24, del(14)(q11.2q11.2).
Figure 5.
De novo submicroscopic genomic deletions identified by WGSA with Mapping 100K arrays in the affected child of families 1895, 3476, 4818, 5566, 6545, and 7807. Panels A, C, E, G, I, K, and M show the t scores for each CNV in comparison with the rest of the chromosome, by use of the window size given below. The SNPs are ordered along the _X_-axis from pter to qter, with the location shown in Mb. Panels B, D, F, H, J, L, and N show FISH confirmation of the CNV in the affected child, by use of the probe given below. The white arrowhead indicates the deleted chromosome without the signal. The red or green arrowhead indicates the normal homologue, which shows the signal. A, Family 1895, chromosome 13, window of 20 SNPs. B, Family 1895, probe RP11-26D3, del(13)(q12.11q12.13). C, Family 3476, chromosome 4, window of 30 SNPs. D, Family 3476, probe RP11-7G22, del(4)(q21.21q22.1). E, Family 4818, chromosome 12, window of 20 SNPs. F, Family 4818, probe RP11-91K23, del(12)(q14.2q15). G, Family 5566, chromosome 14, window of 5 SNPs. The de novo CNV is shown inside the blue oval. H, Family 5566, probe CTD-2136K6, del(14)(q11.2q11.2). I, Family 6545, chromosome 7, window of 20 SNPs. J, Family 6545, probe RP11-802L1, del(7)(p22.2p22.1). K, Family 7807, chromosome 22, window of 20 SNPs. L, Family 7807, probe RP11-79G21, del(22)(q12.1q12.1). M, Family 8326, chromosome 14, window of 20 SNPs. N, Family 8326, probe RP11-340M24, del(14)(q11.2q11.2).
Figure 5.
De novo submicroscopic genomic deletions identified by WGSA with Mapping 100K arrays in the affected child of families 1895, 3476, 4818, 5566, 6545, and 7807. Panels A, C, E, G, I, K, and M show the t scores for each CNV in comparison with the rest of the chromosome, by use of the window size given below. The SNPs are ordered along the _X_-axis from pter to qter, with the location shown in Mb. Panels B, D, F, H, J, L, and N show FISH confirmation of the CNV in the affected child, by use of the probe given below. The white arrowhead indicates the deleted chromosome without the signal. The red or green arrowhead indicates the normal homologue, which shows the signal. A, Family 1895, chromosome 13, window of 20 SNPs. B, Family 1895, probe RP11-26D3, del(13)(q12.11q12.13). C, Family 3476, chromosome 4, window of 30 SNPs. D, Family 3476, probe RP11-7G22, del(4)(q21.21q22.1). E, Family 4818, chromosome 12, window of 20 SNPs. F, Family 4818, probe RP11-91K23, del(12)(q14.2q15). G, Family 5566, chromosome 14, window of 5 SNPs. The de novo CNV is shown inside the blue oval. H, Family 5566, probe CTD-2136K6, del(14)(q11.2q11.2). I, Family 6545, chromosome 7, window of 20 SNPs. J, Family 6545, probe RP11-802L1, del(7)(p22.2p22.1). K, Family 7807, chromosome 22, window of 20 SNPs. L, Family 7807, probe RP11-79G21, del(22)(q12.1q12.1). M, Family 8326, chromosome 14, window of 20 SNPs. N, Family 8326, probe RP11-340M24, del(14)(q11.2q11.2).
Figure 5.
De novo submicroscopic genomic deletions identified by WGSA with Mapping 100K arrays in the affected child of families 1895, 3476, 4818, 5566, 6545, and 7807. Panels A, C, E, G, I, K, and M show the t scores for each CNV in comparison with the rest of the chromosome, by use of the window size given below. The SNPs are ordered along the _X_-axis from pter to qter, with the location shown in Mb. Panels B, D, F, H, J, L, and N show FISH confirmation of the CNV in the affected child, by use of the probe given below. The white arrowhead indicates the deleted chromosome without the signal. The red or green arrowhead indicates the normal homologue, which shows the signal. A, Family 1895, chromosome 13, window of 20 SNPs. B, Family 1895, probe RP11-26D3, del(13)(q12.11q12.13). C, Family 3476, chromosome 4, window of 30 SNPs. D, Family 3476, probe RP11-7G22, del(4)(q21.21q22.1). E, Family 4818, chromosome 12, window of 20 SNPs. F, Family 4818, probe RP11-91K23, del(12)(q14.2q15). G, Family 5566, chromosome 14, window of 5 SNPs. The de novo CNV is shown inside the blue oval. H, Family 5566, probe CTD-2136K6, del(14)(q11.2q11.2). I, Family 6545, chromosome 7, window of 20 SNPs. J, Family 6545, probe RP11-802L1, del(7)(p22.2p22.1). K, Family 7807, chromosome 22, window of 20 SNPs. L, Family 7807, probe RP11-79G21, del(22)(q12.1q12.1). M, Family 8326, chromosome 14, window of 20 SNPs. N, Family 8326, probe RP11-340M24, del(14)(q11.2q11.2).
Figure 5.
De novo submicroscopic genomic deletions identified by WGSA with Mapping 100K arrays in the affected child of families 1895, 3476, 4818, 5566, 6545, and 7807. Panels A, C, E, G, I, K, and M show the t scores for each CNV in comparison with the rest of the chromosome, by use of the window size given below. The SNPs are ordered along the _X_-axis from pter to qter, with the location shown in Mb. Panels B, D, F, H, J, L, and N show FISH confirmation of the CNV in the affected child, by use of the probe given below. The white arrowhead indicates the deleted chromosome without the signal. The red or green arrowhead indicates the normal homologue, which shows the signal. A, Family 1895, chromosome 13, window of 20 SNPs. B, Family 1895, probe RP11-26D3, del(13)(q12.11q12.13). C, Family 3476, chromosome 4, window of 30 SNPs. D, Family 3476, probe RP11-7G22, del(4)(q21.21q22.1). E, Family 4818, chromosome 12, window of 20 SNPs. F, Family 4818, probe RP11-91K23, del(12)(q14.2q15). G, Family 5566, chromosome 14, window of 5 SNPs. The de novo CNV is shown inside the blue oval. H, Family 5566, probe CTD-2136K6, del(14)(q11.2q11.2). I, Family 6545, chromosome 7, window of 20 SNPs. J, Family 6545, probe RP11-802L1, del(7)(p22.2p22.1). K, Family 7807, chromosome 22, window of 20 SNPs. L, Family 7807, probe RP11-79G21, del(22)(q12.1q12.1). M, Family 8326, chromosome 14, window of 20 SNPs. N, Family 8326, probe RP11-340M24, del(14)(q11.2q11.2).
Figure 5.
De novo submicroscopic genomic deletions identified by WGSA with Mapping 100K arrays in the affected child of families 1895, 3476, 4818, 5566, 6545, and 7807. Panels A, C, E, G, I, K, and M show the t scores for each CNV in comparison with the rest of the chromosome, by use of the window size given below. The SNPs are ordered along the _X_-axis from pter to qter, with the location shown in Mb. Panels B, D, F, H, J, L, and N show FISH confirmation of the CNV in the affected child, by use of the probe given below. The white arrowhead indicates the deleted chromosome without the signal. The red or green arrowhead indicates the normal homologue, which shows the signal. A, Family 1895, chromosome 13, window of 20 SNPs. B, Family 1895, probe RP11-26D3, del(13)(q12.11q12.13). C, Family 3476, chromosome 4, window of 30 SNPs. D, Family 3476, probe RP11-7G22, del(4)(q21.21q22.1). E, Family 4818, chromosome 12, window of 20 SNPs. F, Family 4818, probe RP11-91K23, del(12)(q14.2q15). G, Family 5566, chromosome 14, window of 5 SNPs. The de novo CNV is shown inside the blue oval. H, Family 5566, probe CTD-2136K6, del(14)(q11.2q11.2). I, Family 6545, chromosome 7, window of 20 SNPs. J, Family 6545, probe RP11-802L1, del(7)(p22.2p22.1). K, Family 7807, chromosome 22, window of 20 SNPs. L, Family 7807, probe RP11-79G21, del(22)(q12.1q12.1). M, Family 8326, chromosome 14, window of 20 SNPs. N, Family 8326, probe RP11-340M24, del(14)(q11.2q11.2).
Figure 5.
De novo submicroscopic genomic deletions identified by WGSA with Mapping 100K arrays in the affected child of families 1895, 3476, 4818, 5566, 6545, and 7807. Panels A, C, E, G, I, K, and M show the t scores for each CNV in comparison with the rest of the chromosome, by use of the window size given below. The SNPs are ordered along the _X_-axis from pter to qter, with the location shown in Mb. Panels B, D, F, H, J, L, and N show FISH confirmation of the CNV in the affected child, by use of the probe given below. The white arrowhead indicates the deleted chromosome without the signal. The red or green arrowhead indicates the normal homologue, which shows the signal. A, Family 1895, chromosome 13, window of 20 SNPs. B, Family 1895, probe RP11-26D3, del(13)(q12.11q12.13). C, Family 3476, chromosome 4, window of 30 SNPs. D, Family 3476, probe RP11-7G22, del(4)(q21.21q22.1). E, Family 4818, chromosome 12, window of 20 SNPs. F, Family 4818, probe RP11-91K23, del(12)(q14.2q15). G, Family 5566, chromosome 14, window of 5 SNPs. The de novo CNV is shown inside the blue oval. H, Family 5566, probe CTD-2136K6, del(14)(q11.2q11.2). I, Family 6545, chromosome 7, window of 20 SNPs. J, Family 6545, probe RP11-802L1, del(7)(p22.2p22.1). K, Family 7807, chromosome 22, window of 20 SNPs. L, Family 7807, probe RP11-79G21, del(22)(q12.1q12.1). M, Family 8326, chromosome 14, window of 20 SNPs. N, Family 8326, probe RP11-340M24, del(14)(q11.2q11.2).
Figure 5.
De novo submicroscopic genomic deletions identified by WGSA with Mapping 100K arrays in the affected child of families 1895, 3476, 4818, 5566, 6545, and 7807. Panels A, C, E, G, I, K, and M show the t scores for each CNV in comparison with the rest of the chromosome, by use of the window size given below. The SNPs are ordered along the _X_-axis from pter to qter, with the location shown in Mb. Panels B, D, F, H, J, L, and N show FISH confirmation of the CNV in the affected child, by use of the probe given below. The white arrowhead indicates the deleted chromosome without the signal. The red or green arrowhead indicates the normal homologue, which shows the signal. A, Family 1895, chromosome 13, window of 20 SNPs. B, Family 1895, probe RP11-26D3, del(13)(q12.11q12.13). C, Family 3476, chromosome 4, window of 30 SNPs. D, Family 3476, probe RP11-7G22, del(4)(q21.21q22.1). E, Family 4818, chromosome 12, window of 20 SNPs. F, Family 4818, probe RP11-91K23, del(12)(q14.2q15). G, Family 5566, chromosome 14, window of 5 SNPs. The de novo CNV is shown inside the blue oval. H, Family 5566, probe CTD-2136K6, del(14)(q11.2q11.2). I, Family 6545, chromosome 7, window of 20 SNPs. J, Family 6545, probe RP11-802L1, del(7)(p22.2p22.1). K, Family 7807, chromosome 22, window of 20 SNPs. L, Family 7807, probe RP11-79G21, del(22)(q12.1q12.1). M, Family 8326, chromosome 14, window of 20 SNPs. N, Family 8326, probe RP11-340M24, del(14)(q11.2q11.2).
Figure 5.
De novo submicroscopic genomic deletions identified by WGSA with Mapping 100K arrays in the affected child of families 1895, 3476, 4818, 5566, 6545, and 7807. Panels A, C, E, G, I, K, and M show the t scores for each CNV in comparison with the rest of the chromosome, by use of the window size given below. The SNPs are ordered along the _X_-axis from pter to qter, with the location shown in Mb. Panels B, D, F, H, J, L, and N show FISH confirmation of the CNV in the affected child, by use of the probe given below. The white arrowhead indicates the deleted chromosome without the signal. The red or green arrowhead indicates the normal homologue, which shows the signal. A, Family 1895, chromosome 13, window of 20 SNPs. B, Family 1895, probe RP11-26D3, del(13)(q12.11q12.13). C, Family 3476, chromosome 4, window of 30 SNPs. D, Family 3476, probe RP11-7G22, del(4)(q21.21q22.1). E, Family 4818, chromosome 12, window of 20 SNPs. F, Family 4818, probe RP11-91K23, del(12)(q14.2q15). G, Family 5566, chromosome 14, window of 5 SNPs. The de novo CNV is shown inside the blue oval. H, Family 5566, probe CTD-2136K6, del(14)(q11.2q11.2). I, Family 6545, chromosome 7, window of 20 SNPs. J, Family 6545, probe RP11-802L1, del(7)(p22.2p22.1). K, Family 7807, chromosome 22, window of 20 SNPs. L, Family 7807, probe RP11-79G21, del(22)(q12.1q12.1). M, Family 8326, chromosome 14, window of 20 SNPs. N, Family 8326, probe RP11-340M24, del(14)(q11.2q11.2).
Figure 5.
De novo submicroscopic genomic deletions identified by WGSA with Mapping 100K arrays in the affected child of families 1895, 3476, 4818, 5566, 6545, and 7807. Panels A, C, E, G, I, K, and M show the t scores for each CNV in comparison with the rest of the chromosome, by use of the window size given below. The SNPs are ordered along the _X_-axis from pter to qter, with the location shown in Mb. Panels B, D, F, H, J, L, and N show FISH confirmation of the CNV in the affected child, by use of the probe given below. The white arrowhead indicates the deleted chromosome without the signal. The red or green arrowhead indicates the normal homologue, which shows the signal. A, Family 1895, chromosome 13, window of 20 SNPs. B, Family 1895, probe RP11-26D3, del(13)(q12.11q12.13). C, Family 3476, chromosome 4, window of 30 SNPs. D, Family 3476, probe RP11-7G22, del(4)(q21.21q22.1). E, Family 4818, chromosome 12, window of 20 SNPs. F, Family 4818, probe RP11-91K23, del(12)(q14.2q15). G, Family 5566, chromosome 14, window of 5 SNPs. The de novo CNV is shown inside the blue oval. H, Family 5566, probe CTD-2136K6, del(14)(q11.2q11.2). I, Family 6545, chromosome 7, window of 20 SNPs. J, Family 6545, probe RP11-802L1, del(7)(p22.2p22.1). K, Family 7807, chromosome 22, window of 20 SNPs. L, Family 7807, probe RP11-79G21, del(22)(q12.1q12.1). M, Family 8326, chromosome 14, window of 20 SNPs. N, Family 8326, probe RP11-340M24, del(14)(q11.2q11.2).
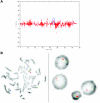
Figure 6.
De novo submicroscopic genomic duplication, dup(16)(p13.3p13.3), identified by WGSA with Mapping 100K arrays in family 4794. A, The t scores for the CNV in comparison with the rest of the chromosome, by use of a window size of 20 SNPs. The SNPs are ordered along the _X_-axis from pter to qter, with the location shown in Mb. The de novo CNV is shown inside the blue oval. B, FISH confirmation of the CNV in the affected child, by use of probe G248P82513E10 in metaphase cells (left) and probe RP11-397B22 in interphase cells (right). In the metaphase spread, the duplication is indicated by the red arrowhead, and the normal chromosome is indicated by the blue arrowhead. The signal is duplicated on one chromosome 16.
Figure 7.
De novo submicroscopic genomic duplication, dup(17)(q21.33q21.33), identified by WGSA with Mapping 100K arrays in family 6168. A, The t scores for each CNV in comparison with the rest of the chromosome, by use of a window size of 8 SNPs. The SNPs are ordered along the _X_-axis from pter to qter, with the location shown in Mb. The de novo CNV is shown inside the blue oval. B, FISH confirmation of the CNV in the affected child, by use of probes RP11-962N5 (green) and RP11-121F10 (red) in metaphase (left) and interphase (right) cells. In the metaphase spread, the duplication is shown at the red arrowhead, and the normal chromosome is shown at the blue arrowhead. The red signal is duplicated on one chromosome 17; the green signal does not appear duplicated but cross-hybrizes to chromosome 6qter.
Similar articles
- Whole-genome array-CGH identifies novel contiguous gene deletions and duplications associated with developmental delay, mental retardation, and dysmorphic features.
Aradhya S, Manning MA, Splendore A, Cherry AM. Aradhya S, et al. Am J Med Genet A. 2007 Jul 1;143A(13):1431-41. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.31773. Am J Med Genet A. 2007. PMID: 17568414 - Molecular karyotyping in patients with mental retardation using 100K single-nucleotide polymorphism arrays.
Hoyer J, Dreweke A, Becker C, Göhring I, Thiel CT, Peippo MM, Rauch R, Hofbeck M, Trautmann U, Zweier C, Zenker M, Hüffmeier U, Kraus C, Ekici AB, Rüschendorf F, Nürnberg P, Reis A, Rauch A. Hoyer J, et al. J Med Genet. 2007 Oct;44(10):629-36. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2007.050914. Epub 2007 Jun 29. J Med Genet. 2007. PMID: 17601928 Free PMC article. - Detection of pathogenic copy number variants in children with idiopathic intellectual disability using 500 K SNP array genomic hybridization.
Friedman J, Adam S, Arbour L, Armstrong L, Baross A, Birch P, Boerkoel C, Chan S, Chai D, Delaney AD, Flibotte S, Gibson WT, Langlois S, Lemyre E, Li HI, MacLeod P, Mathers J, Michaud JL, McGillivray BC, Patel MS, Qian H, Rouleau GA, Van Allen MI, Yong SL, Zahir FR, Eydoux P, Marra MA. Friedman J, et al. BMC Genomics. 2009 Nov 16;10:526. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-526. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19917086 Free PMC article. - Oligonucleotide arrays for high-resolution analysis of copy number alteration in mental retardation/multiple congenital anomalies.
Shaikh TH. Shaikh TH. Genet Med. 2007 Sep;9(9):617-25. doi: 10.1097/gim.0b013e318148bb81. Genet Med. 2007. PMID: 17873650 Review. - Application of array-based comparative genome hybridization in children with developmental delay or mental retardation.
Liang JS, Shimojima K, Yamamoto T. Liang JS, et al. Pediatr Neonatol. 2008 Dec;49(6):213-7. doi: 10.1016/S1875-9572(09)60013-9. Pediatr Neonatol. 2008. PMID: 19166117 Review.
Cited by
- Identifying Genetic Etiology in Patients with Intellectual Disability: An Experience in Public Health Services in Northeastern Brazil.
de Carvalho AFL, Alves ES, Pitanga PML, Ribeiro EM, Doriqui MJR, Toralles MBP, Topázio BA, Dos Santos JF, de Lima RLLF, Kulikowski LD, Acosta AX. de Carvalho AFL, et al. J Pediatr Genet. 2022 Nov 14;13(2):90-98. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-1757888. eCollection 2024 Jun. J Pediatr Genet. 2022. PMID: 38721574 Free PMC article. - Post-transcriptional microRNA repression of PMP22 dose in severe Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1.
Pipis M, Won S, Poh R, Efthymiou S, Polke JM, Skorupinska M, Blake J, Rossor AM, Moran JJ, Munot P, Muntoni F, Laura M, Svaren J, Reilly MM. Pipis M, et al. Brain. 2023 Oct 3;146(10):4025-4032. doi: 10.1093/brain/awad203. Brain. 2023. PMID: 37337674 Free PMC article. - A Novel 13q12 Microdeletion Associated with Familial Syndromic Corneal Opacification.
Serpen JY, Presley W, Beil A, Armenti ST, Johnson K, Mian SI, Innis JW, Prasov L. Serpen JY, et al. Genes (Basel). 2023 May 1;14(5):1034. doi: 10.3390/genes14051034. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37239394 Free PMC article. - NRXN1 depletion in the medial prefrontal cortex induces anxiety-like behaviors and abnormal social phenotypes along with impaired neurite outgrowth in rat.
Wu D, Zhu J, You L, Wang J, Zhang S, Liu Z, Xu Q, Yuan X, Yang L, Wang W, Tong M, Hong Q, Chi X. Wu D, et al. J Neurodev Disord. 2023 Feb 3;15(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s11689-022-09471-9. J Neurodev Disord. 2023. PMID: 36737720 Free PMC article. - Common Variable Immunodeficiency and Neurodevelopmental Delay Due to a 13Mb Deletion on Chromosome 4 Including the NFKB1 Gene: A Case Report.
Franco-Jarava C, Valenzuela I, Riviere JG, Garcia-Prat M, Martínez-Gallo M, Dieli-Crimi R, Castells N, Batlle-Masó L, Soler-Palacin P, Colobran R. Franco-Jarava C, et al. Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 17;13:897975. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.897975. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35784294 Free PMC article.
References
Web Resources
- Affymetrix GeneChip Human Mapping 100K Assay Manual, http://www.affymetrix.com/support/downloads/manuals/100k_manual.pdf - PMC - PubMed
- Database of Genomic Variants, http://projects.tcag.ca/variation/
- GeneChip DNA Analysis Software (GDAS) Version 3.0, http://www.affymetrix.com/Auth/support/downloads/manuals/gdas_manual.zip
References
- Roeleveld N, Zielhuis G, Gabreels F (1997) The prevalence of mental retardation: a critical review of recent literature. Dev Med Child Neurol 39:125–132 - PubMed
- Pope A, Tarlov A (1991) Disability in America: toward a national agenda for prevention. Institute of Medicine, Washington, DC
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous