Sno/scaRNAbase: a curated database for small nucleolar RNAs and cajal body-specific RNAs - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2007 Jan;35(Database issue):D183-7.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl873. Epub 2006 Nov 11.
Affiliations
- PMID: 17099227
- PMCID: PMC1669756
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl873
Sno/scaRNAbase: a curated database for small nucleolar RNAs and cajal body-specific RNAs
Jun Xie et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 Jan.
Abstract
Small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) and Cajal body-specific RNAs (scaRNAs) are named for their subcellular localization within nucleoli and Cajal bodies (conserved subnuclear organelles present in the nucleoplasm), respectively. They have been found to play important roles in rRNA, tRNA, snRNAs, and even mRNA modification and processing. All snoRNAs fall in two categories, box C/D snoRNAs and box H/ACA snoRNAs, according to their distinct sequence and secondary structure features. Box C/D snoRNAs and box H/ACA snoRNAs mainly function in guiding 2'-O-ribose methylation and pseudouridilation, respectively. ScaRNAs possess both box C/D snoRNA and box H/ACA snoRNA sequence motif features, but guide snRNA modifications that are transcribed by RNA polymerase II. Here we present a Web-based sno/scaRNA database, called sno/scaRNAbase, to facilitate the sno/scaRNA research in terms of providing a more comprehensive knowledge base. Covering 1979 records derived from 85 organisms for the first time, sno/scaRNAbase is not only dedicated to filling gaps between existing organism-specific sno/scaRNA databases that are focused on different sno/scaRNA aspects, but also provides sno/scaRNA scientists with an opportunity to adopt a unified nomenclature for sno/scaRNAs. Derived from a systematic literature curation and annotation effort, the sno/scaRNAbase provides an easy-to-use gateway to important sno/scaRNA features such as sequence motifs, possible functions, homologues, secondary structures, genomics organization, sno/scaRNA gene's chromosome location, and more. Approximate searches, in addition to accurate and straightforward searches, make the database search more flexible. A BLAST search engine is implemented to enable blast of query sequences against all sno/scaRNAbase sequences. Thus our sno/scaRNAbase serves as a more uniform and friendly platform for sno/scaRNA research. The database is free available at http://gene.fudan.sh.cn/snoRNAbase.nsf.
Figures
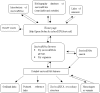
Figure 1
The schematic illustration of the sno/scaRNAbase.
Figure 2
The sno/scaRNAbase browse page. a. Browsing result ordered by organism. b. Sorting buttons. c. Browsing selection I: browsing sno/scaRNAs by organism. d. A collapsing or expanding button. e. Browsing selection II: browsing sno/scaRNAs by three categories. f. Buttons for viewing previous or next pages.
Figure 3
An example of a sno/scaRNA record page. a. Links to home/main pages, the previous/next sno/scaRNA record page, and the help page. b. A selected sno/scaRNA name. c. Possible homologues found in the sno/scaRNAbase. d. A link to the predicted secondary structure.
Similar articles
- snoRNA-LBME-db, a comprehensive database of human H/ACA and C/D box snoRNAs.
Lestrade L, Weber MJ. Lestrade L, et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Jan 1;34(Database issue):D158-62. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj002. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16381836 Free PMC article. - A common sequence motif determines the Cajal body-specific localization of box H/ACA scaRNAs.
Richard P, Darzacq X, Bertrand E, Jády BE, Verheggen C, Kiss T. Richard P, et al. EMBO J. 2003 Aug 15;22(16):4283-93. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg394. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12912925 Free PMC article. - scaRNAs and snoRNAs: Are they limited to specific classes of substrate RNAs?
Deryusheva S, Gall JG. Deryusheva S, et al. RNA. 2019 Jan;25(1):17-22. doi: 10.1261/rna.068593.118. Epub 2018 Oct 9. RNA. 2019. PMID: 30301832 Free PMC article. - Assembly and trafficking of box C/D and H/ACA snoRNPs.
Massenet S, Bertrand E, Verheggen C. Massenet S, et al. RNA Biol. 2017 Jun 3;14(6):680-692. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1243646. Epub 2016 Oct 7. RNA Biol. 2017. PMID: 27715451 Free PMC article. Review. - Beyond rRNA and snRNA: tRNA as a 2'-O-methylation target for nucleolar and Cajal body box C/D RNPs.
Nostramo RT, Hopper AK. Nostramo RT, et al. Genes Dev. 2019 Jul 1;33(13-14):739-740. doi: 10.1101/gad.328443.119. Genes Dev. 2019. PMID: 31262844 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- The infinite possibilities of RNA therapeutics.
Mollocana-Lara EC, Ni M, Agathos SN, Gonzales-Zubiate FA. Mollocana-Lara EC, et al. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Dec 23;48(9-10):kuab063. doi: 10.1093/jimb/kuab063. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34463324 Free PMC article. - The small nucleolar ribonucleoprotein (snoRNP) database.
Ellis JC, Brown DD, Brown JW. Ellis JC, et al. RNA. 2010 Apr;16(4):664-6. doi: 10.1261/rna.1871310. Epub 2010 Mar 2. RNA. 2010. PMID: 20197376 Free PMC article. - snOPY: a small nucleolar RNA orthological gene database.
Yoshihama M, Nakao A, Kenmochi N. Yoshihama M, et al. BMC Res Notes. 2013 Oct 23;6:426. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-6-426. BMC Res Notes. 2013. PMID: 24148649 Free PMC article. - Informatic resources for identifying and annotating structural RNA motifs.
George AD, Tenenbaum SA. George AD, et al. Mol Biotechnol. 2009 Feb;41(2):180-93. doi: 10.1007/s12033-008-9114-z. Epub 2008 Nov 1. Mol Biotechnol. 2009. PMID: 18979204 Free PMC article. Review. - Biomolecule and Bioentity Interaction Databases in Systems Biology: A Comprehensive Review.
Baltoumas FA, Zafeiropoulou S, Karatzas E, Koutrouli M, Thanati F, Voutsadaki K, Gkonta M, Hotova J, Kasionis I, Hatzis P, Pavlopoulos GA. Baltoumas FA, et al. Biomolecules. 2021 Aug 20;11(8):1245. doi: 10.3390/biom11081245. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34439912 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Bachellerie J.P., Cavaille J., Huttenhofer A. The expanding snoRNA world. Biochimie. 2002;84:775–790. - PubMed
- Kiss T. Small nucleolar RNAs: an abundant group of noncoding RNAs with diverse cellular functions. Cell. 2002;109:145–148. - PubMed
- Cavaille J., Buiting K., Kiefmann M., Lalande M., Brannan C.I., Horsthemke B., Bachellerie J.P., Brosius J., Huttenhofer A. Identification of brain-specific and imprinted small nucleolar RNA genes exhibiting an unusual genomic organization. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2000;97:14311–14316. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials