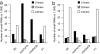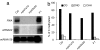Role of RNA polymerase IV in plant small RNA metabolism - PubMed (original) (raw)
Role of RNA polymerase IV in plant small RNA metabolism
Xiaoyu Zhang et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007.
Abstract
In addition to the three RNA polymerases (RNAP I-III) shared by all eukaryotic organisms, plant genomes encode a fourth RNAP (RNAP IV) that appears to be specialized in the production of siRNAs. Available data support a model in which dsRNAs are generated by RNAP IV and RNA-dependent RNAP 2 (RDR2) and processed by DICER (DCL) enzymes into 21- to 24-nt siRNAs, which are associated with different ARGONAUTE (AGO) proteins for transcriptional or posttranscriptional gene silencing. However, it is not yet clear what fraction of genomic siRNA production is RNAP IV-dependent, and to what extent these siRNAs are preferentially processed by certain DCL(s) or associated with specific AGOs for distinct downstream functions. To address these questions on a genome-wide scale, we sequenced approximately 335,000 siRNAs from wild-type and RNAP IV mutant Arabidopsis plants by using 454 technology. The results show that RNAP IV is required for the production of >90% of all siRNAs, which are faithfully produced from a discrete set of genomic loci. Comparisons of these siRNAs with those accumulated in rdr2 and dcl2 dcl3 dcl4 and those associated with AGO1 and AGO4 provide important information regarding the processing, channeling, and functions of plant siRNAs. We also describe a class of RNAP IV-independent siRNAs produced from endogenous single-stranded hairpin RNA precursors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The lengths of sRNAs that perfectly matched the Arabidopsis genomic sequence in wild-type, nrpd1a/1b, nrpd2a/2b, and the F1 progenies from a cross between nrpd1a/1b and nrpd2a/2b. (a) All sRNAs. (b) siRNAs (miRNAs and tasiRNAs were excluded). y axis, the number of individual sRNA sequences of a certain size.
Fig. 2.
The locus IR71 as an example of siRNAs produced from single-stranded hairpin RNA precursors. (a) All individual siRNAs at IR71 that matched a unique position in the genome isolated from wild type (454 or MPSS), nrpd1a/1b (454), and rdr2 (MPSS). Vertical color bars, individual siRNAs; pink horizontal bars, the two arms of the inverted repeat. siRNAs shown above the inverted repeats matched the Watson strand, and those below matched the Crick strand of the genome. (b) Examples of siRNAs produced from the imperfectly matched regions (red dots) of the predicted single-stranded hairpin of IR71. Horizontal bars, siRNAs that match the left (above the alignment) or right arm (below the alignment).
Fig. 3.
Immediate restoration of siRNA production and RNA-directed DNA methylation. (a) Northern blot analysis of siRNAs derived from the FWA and siRNA02 loci (16, 19, 38). miRNA 159 is shown as control. (b) Bisulfite sequencing analysis of DNA methylation at MEA-ISR.
Similar articles
- Distinct and concurrent pathways of Pol II- and Pol IV-dependent siRNA biogenesis at a repetitive trans-silencer locus in Arabidopsis thaliana.
Sasaki T, Lee TF, Liao WW, Naumann U, Liao JL, Eun C, Huang YY, Fu JL, Chen PY, Meyers BC, Matzke AJ, Matzke M. Sasaki T, et al. Plant J. 2014 Jul;79(1):127-38. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12545. Epub 2014 Jun 13. Plant J. 2014. PMID: 24798377 - Reaction Mechanisms of Pol IV, RDR2, and DCL3 Drive RNA Channeling in the siRNA-Directed DNA Methylation Pathway.
Singh J, Mishra V, Wang F, Huang HY, Pikaard CS. Singh J, et al. Mol Cell. 2019 Aug 8;75(3):576-589.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.07.008. Mol Cell. 2019. PMID: 31398324 Free PMC article. - Analysis of siRNA Precursors Generated by RNA Polymerase IV and RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase 2 in Arabidopsis.
Blevins T, Podicheti R, Pikaard CS. Blevins T, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1933:33-48. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9045-0_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30945177 - Cell biology of the Arabidopsis nuclear siRNA pathway for RNA-directed chromatin modification.
Pikaard CS. Pikaard CS. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:473-80. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.046. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381329 Review. - The expanding world of small RNAs in plants.
Borges F, Martienssen RA. Borges F, et al. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Dec;16(12):727-41. doi: 10.1038/nrm4085. Epub 2015 Nov 4. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26530390 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- The RNA-binding domain of DCL3 is required for long-distance RNAi signaling.
Li J, Zhang BS, Wu HW, Liu CL, Guo HS, Zhao JH. Li J, et al. aBIOTECH. 2023 Nov 28;5(1):17-28. doi: 10.1007/s42994-023-00124-6. eCollection 2024 Mar. aBIOTECH. 2023. PMID: 38576436 Free PMC article. - The unusual predominance of maintenance DNA methylation in Spirodela polyrhiza.
Harkess A, Bewick AJ, Lu Z, Fourounjian P, Michael TP, Schmitz RJ, Meyers BC. Harkess A, et al. G3 (Bethesda). 2024 Apr 3;14(4):jkae004. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkae004. G3 (Bethesda). 2024. PMID: 38190722 Free PMC article. - KSHV-encoded LANA bypasses transcriptional block through the stabilization of RNA Pol II in hypoxia.
Bose D, Singh RK, Robertson ES. Bose D, et al. mBio. 2024 Jan 16;15(1):e0277423. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02774-23. Epub 2023 Dec 14. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38095447 Free PMC article. - Small RNA-mediated DNA methylation during plant reproduction.
Chow HT, Mosher RA. Chow HT, et al. Plant Cell. 2023 May 29;35(6):1787-1800. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koad010. Plant Cell. 2023. PMID: 36651080 Free PMC article. Review. - Transcriptome Profiling Reveals Role of MicroRNAs and Their Targeted Genes during Adventitious Root Formation in Dark-Pretreated Micro-Shoot Cuttings of Tetraploid Robinia pseudoacacia L.
Uddin S, Munir MZ, Gull S, Khan AH, Khan A, Khan D, Khan MA, Wu Y, Sun Y, Li Y. Uddin S, et al. Genes (Basel). 2022 Feb 27;13(3):441. doi: 10.3390/genes13030441. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35327995 Free PMC article.
References
- Wassenegger M. Cell. 2005;122:13–16. - PubMed
- Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP, Bartel B. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2006;57:19–53. - PubMed
- Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP, Anderson TA. Dev Biol. 2006;289:3–16. - PubMed
- Meins F, Jr, Si-Ammour A, Blevins T. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2005;21:297–318. - PubMed
- Vaucheret H. Genes Dev. 2006;20:759–771. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R37 GM060398/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM 60398/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM060398/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HG 003523/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG003523/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials