Candidate genes for expansion and transformation of hematopoietic stem cells by NUP98-HOX fusion genes - PubMed (original) (raw)
Candidate genes for expansion and transformation of hematopoietic stem cells by NUP98-HOX fusion genes
Lars Palmqvist et al. PLoS One. 2007.
Abstract
Background: Hox genes are implicated in hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) regulation as well as in leukemia development through translocation with the nucleoporin gene NUP98. Interestingly, an engineered NUP98-HOXA10 (NA10) fusion can induce a several hundred-fold expansion of HSCs in vitro and NA10 and the AML-associated fusion gene NUP98-HOXD13 (ND13) have a virtually indistinguishable ability to transform myeloid progenitor cells in vitro and to induce leukemia in collaboration with MEIS1 in vivo.
Methodology/principal findings: These findings provided a potentially powerful approach to identify key pathways mediating Hox-induced expansion and transformation of HSCs by identifying gene expression changes commonly induced by ND13 and NA10 but not by a NUP98-Hox fusion with a non-DNA binding homedomain mutation (N51S). The gene expression repertoire of purified murine bone marrow Sca-1+Lin- cells transduced with retroviral vectors encoding for these genes was established using the Affymetrix GeneChip MOE430A. Approximately seventy genes were differentially expressed in ND13 and NA10 cells that were significantly changed by both compared to the ND13(N51S) mutant. Intriguingly, several of these potential Hox target genes have been implicated in HSC expansion and self-renewal, including the tyrosine kinase receptor Flt3, the prion protein, Prnp, hepatic leukemia factor, Hlf and Jagged-2, Jag2. Consistent with these results, FLT3, HLF and JAG2 expression correlated with HOX A cluster gene expression in human leukemia samples.
Conclusions: In conclusion this study has identified several novel Hox downstream target genes and provides important new leads to key regulators of the expansion and transformation of hematopoietic stem cells by Hox.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
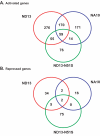
Figure 1. Venn diagram of genes significantly activated (A) or repressed (B) in Sca1+, Lin- BM cells expressing the ND13, NA10 or ND13(N51S) mutant fusion genes compared to GFP control.
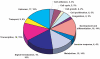
Figure 2. Annotation of differentially expressed genes.
Genes that were differentially expressed by both ND13 and NA10 but not the mutant ND13(N51S) mutant were classified according to involvement in different biological processes. Some genes are classified in more than one category resulting in the total number of genes indicated in the figures being greater than the total number of differentially expressed genes.
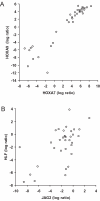
Figure 3. Correlation between HOXA7 and HOXA9 (A) and JAG2 and HLF (B) gene expression in human AML analyzed with TaqMan Low Density Array (TLDA).
Spearman rank correlation analysis was done on the log ratio values obtained from the TLDA assay and calculated with the 2−ΔΔCT method (n = 34).
Similar articles
- Hox genes: from leukemia to hematopoietic stem cell expansion.
Abramovich C, Pineault N, Ohta H, Humphries RK. Abramovich C, et al. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005 Jun;1044:109-16. doi: 10.1196/annals.1349.014. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005. PMID: 15958703 Review. - Linkage of Meis1 leukemogenic activity to multiple downstream effectors including Trib2 and Ccl3.
Argiropoulos B, Palmqvist L, Yung E, Kuchenbauer F, Heuser M, Sly LM, Wan A, Krystal G, Humphries RK. Argiropoulos B, et al. Exp Hematol. 2008 Jul;36(7):845-59. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2008.02.011. Epub 2008 Apr 2. Exp Hematol. 2008. PMID: 18375036 - Constitutive activation of Flt3 and STAT5A enhances self-renewal and alters differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells.
Moore MA, Dorn DC, Schuringa JJ, Chung KY, Morrone G. Moore MA, et al. Exp Hematol. 2007 Apr;35(4 Suppl 1):105-16. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2007.01.018. Exp Hematol. 2007. PMID: 17379095 - NUP98-NSD1 links H3K36 methylation to Hox-A gene activation and leukaemogenesis.
Wang GG, Cai L, Pasillas MP, Kamps MP. Wang GG, et al. Nat Cell Biol. 2007 Jul;9(7):804-12. doi: 10.1038/ncb1608. Epub 2007 Jun 24. Nat Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17589499 - NUP98 dysregulation in myeloid leukemogenesis.
Moore MA, Chung KY, Plasilova M, Schuringa JJ, Shieh JH, Zhou P, Morrone G. Moore MA, et al. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007 Jun;1106:114-42. doi: 10.1196/annals.1392.019. Epub 2007 Apr 18. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007. PMID: 17442773 Review.
Cited by
- Nuclear pore proteins and cancer.
Xu S, Powers MA. Xu S, et al. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2009 Jul;20(5):620-30. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2009.03.003. Epub 2009 Mar 18. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2009. PMID: 19577736 Free PMC article. Review. - Transcription factor-mediated reprogramming toward hematopoietic stem cells.
Ebina W, Rossi DJ. Ebina W, et al. EMBO J. 2015 Mar 12;34(6):694-709. doi: 10.15252/embj.201490804. Epub 2015 Feb 20. EMBO J. 2015. PMID: 25712209 Free PMC article. Review. - Identification of GSX2 and AF10 as NUP98 partner genes in myeloid malignancies.
Soler G, Kaltenbach S, Dobbelstein S, Broccardo C, Radford I, Mozziconacci MJ, Bernard OA, Penard-Lacronique V, Delabesse E, Romana SP. Soler G, et al. Blood Cancer J. 2013 Jul 12;3(7):e124. doi: 10.1038/bcj.2013.20. Blood Cancer J. 2013. PMID: 23852159 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Effects of the NUP98-DDX10 oncogene on primary human CD34+ cells: role of a conserved helicase motif.
Yassin ER, Abdul-Nabi AM, Takeda A, Yaseen NR. Yassin ER, et al. Leukemia. 2010 May;24(5):1001-11. doi: 10.1038/leu.2010.42. Epub 2010 Mar 25. Leukemia. 2010. PMID: 20339440 Free PMC article. - Enforced expression of Hoxa5 in haematopoietic stem cells leads to aberrant erythropoiesis in vivo.
Yang D, Zhang X, Dong Y, Liu X, Wang T, Wang X, Geng Y, Fang S, Zheng Y, Chen X, Chen J, Pan G, Wang J. Yang D, et al. Cell Cycle. 2015;14(4):612-20. doi: 10.4161/15384101.2014.992191. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 25590986 Free PMC article.
References
- Abramovich C, Humphries RK. Hox regulation of normal and leukemic hematopoietic stem cells. Curr Opin Hematol. 2005;12:210–216. - PubMed
- Grier DG, Thompson A, Kwasniewska A, McGonigle GJ, Halliday HL, et al. The pathophysiology of HOX genes and their role in cancer. J Pathol. 2005;205:154–171. - PubMed
- Slape C, Aplan PD. The role of NUP98 gene fusions in hematologic malignancy. Leuk Lymphoma. 2004;45:1341–1350. - PubMed
- Borrow J, Stanton VP, Jr, Andresen JM, Becher R, Behm FG, et al. The translocation t(8;16)(p11;p13) of acute myeloid leukaemia fuses a putative acetyltransferase to the CREB-binding protein. Nat Genet. 1996;14:33–41. - PubMed
- Raza-Egilmez SZ, Jani-Sait SN, Grossi M, Higgins MJ, Shows TB, et al. NUP98-HOXD13 gene fusion in therapy-related acute myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Res. 1998;58:4269–4273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous