TRRAP and GCN5 are used by c-Myc to activate RNA polymerase III transcription - PubMed (original) (raw)
TRRAP and GCN5 are used by c-Myc to activate RNA polymerase III transcription
Niall S Kenneth et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007.
Abstract
Activation of RNA polymerase (pol) II transcription by c-Myc generally involves recruitment of histone acetyltransferases and acetylation of histones H3 and H4. Here, we describe the mechanism used by c-Myc to activate pol III transcription of tRNA and 5S rRNA genes. Within 2 h of its induction, c-Myc appears at these genes along with the histone acetyltransferase GCN5 and the cofactor TRRAP. At the same time, occupancy of the pol III-specific factor TFIIIB increases and histone H3 becomes hyperacetylated, but increased histone H4 acetylation is not detected at these genes. The rapid acetylation of histone H3 and promoter assembly of TFIIIB, c-Myc, GCN5, and TRRAP are followed by recruitment of pol III and transcriptional induction. The selective acetylation of histone H3 distinguishes pol III activation by c-Myc from mechanisms observed in other systems.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Fig. 1.
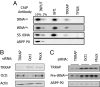
TRRAP binds tRNA genes and stimulates their expression in vivo. (A) ChIP using Brf1, TRRAP, and TFIIB antibodies with HEK293 cells and primers to the indicated genes. (B) Immunoblot for TRRAP, Oct1, and actin in extracts of HeLa cells transfected with siRNAs against TRRAP or Oct1 mRNAs (lanes 1 and 2, respectively) or mock-transfected (lane 3). (C) RT-PCR of pre-tRNA and the TRRAP and ARPP P0 mRNAs in HeLa cells transfected with siRNAs against TRRAP mRNA (lanes 1 and 2), Oct1 mRNA (lanes 3 and 4), or mock-transfected (lanes 5 and 6).
Fig. 2.
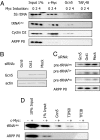
TRRAP is recruited to pol III templates in response to c-Myc. (A) ChIP using RPC155, TRRAP, and TFIIB antibodies with wild-type and c-Myc null fibroblasts. (B) ChIP using c-Myc and TAFI48 antibodies with MycER-expressing fibroblasts after 0, 2, or 4 h of OHT treatment. (C) ChIP using TRRAP and TAFI48 antibodies with MycER-expressing fibroblasts after 0, 2, or 4 h of OHT treatment.
Fig. 3.
GCN5 is recruited to tRNA genes in response to c-Myc and stimulates their expression. (A) ChIP using c-Myc, GCN5, and TAFI48 antibodies with MycER-expressing fibroblasts after 0, 2, or 4 h of treatment with OHT. (B) Western blot for GCN5 and actin in extracts of HeLa cells transfected with siRNAs against GCN5 or Oct1 mRNAs (lanes 1 and 2, respectively) or mock-transfected (lane 3). (C) RT-PCR to compare levels of pre-tRNA and ARPP P0 mRNAs in HeLa cells transfected with siRNAs against GCN5 mRNA (lane 1), Oct1 mRNA (lane 2), or mock-transfected (lane 3). (D) ChIP using GCN5, TIP60, and TFIIB antibodies with matched wild-type and c-Myc knockout fibroblasts.
Fig. 4.
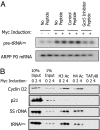
Induction of c-Myc stimulates H3 acetylation at pol III-transcribed genes. (A) RT-PCR of pre-tRNA and ARPP P0 mRNA in MycER-expressing fibroblasts after 0 (lanes 1 and 2) or 4 h (lanes 3–8) of OHT treatment. Where indicated, cells were pretreated for 24 h with 50 μM H3-Ac-20-Tat control peptide (lanes 5 and 6) or H3-CoA-20-Tat GCN5/PCAF inhibitor peptide (lanes 7 and 8). (B) ChIP using antibodies against TAFI48 and acetylated histones H3 and H4 with MycER-expressing fibroblasts after 0, 2, or 4 h of treatment with OHT, as indicated. Immunoprecipitated DNA was PCR-amplified by using the indicated gene primers.
Fig. 5.
Pol III and TFIIIB are recruited selectively in response to c-Myc and TSA. (A) ChIP assay using antibodies against TAFI48, RPC155, Brf1, TFIIIC220, and acetylated histones H3 and H4 with MycER-expressing fibroblasts after 0 or 4 h of treatment with OHT. Immunoprecipitated DNA was PCR-amplified by using the indicated gene primers. (B) ChIP using antibodies against Brf1 and Bdp1, TFIIIC220 and TFIIIC110, RPC155 and TAFI48, with MycER-expressing fibroblasts after 0, 2, or 4 h of treatment with OHT. Immunoprecipitated DNA was PCR-amplified by using the indicated gene primers. (C) ChIP using 5S and tRNA gene primers and antibodies against acetylated histones H3 and H4, TFIIIC (TFIIIC110), TFIIIB (Brf1), pol III (RPC155), and TFIIB with fibroblasts treated for 0, 6, 12, or 24 h with TSA.
References
- Grandori C, Cowley SM, James LP, Eisenman RN. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2000;16:653–699. - PubMed
- Adhikary S, Eilers M. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:635–645. - PubMed
- Oskarsson T, Trumpp A. Nat Cell Biol. 2005;7:215–217. - PubMed
- Gomez-Roman N, Grandori C, Eisenman RN, White RJ. Nature. 2003;421:290–294. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous