PTEN loss of expression predicts cetuximab efficacy in metastatic colorectal cancer patients - PubMed (original) (raw)
PTEN loss of expression predicts cetuximab efficacy in metastatic colorectal cancer patients
M Frattini et al. Br J Cancer. 2007.
Abstract
To evaluate whether the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), K-Ras and PTEN, all members of the EGFR signalling pathway, may affect the clinical response in cetuximab-treated metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) patients. Twenty-seven cetuximab-treated mCRC patients were evaluated for drug response and investigated for EGFR protein expression and gene status, K-Ras mutational status and PTEN protein expression. Ten patients achieved a partial response (PR) to cetuximab-based therapy. All 27 patients showed EGFR protein overexpression. Epidermal growth factor receptor gene amplification was observed in eight out of 27 (30%) and chromosome 7 marked polysomy in 16 (59%) patients. Partial response was observed in six out of eight patients with EGFR gene amplification, four out of 16 with marked polysomy and none out of three with eusomy (P<0.05). The K-Ras wild-type sequence was observed in 17 patients, and nine of them experienced a PR. Conversely, K-Ras was mutated in 10 cases, of which one patient experienced a PR (P<0.05). The PTEN protein was normally expressed in 16 patients, and 10 of them achieved a PR. In contrast, no benefit was documented in 11 patients with loss of PTEN activity (P<0.001). Patients with EGFR gene amplification or chromosome 7 marked polysomy respond to cetuximab. In addition to K-Ras mutations, we demonstrate for the first time that the loss of PTEN protein expression is associated with nonresponsiveness to cetuximab.
Figures
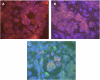
Figure 1
Epidermal growth factor receptor gene status evaluated by FISH in metastatic colorectal cancers. (A) Patient showing eusomy of chromosome 7. (B) Patient with marked polysomy on chromosome 7. (C) Patient with EGFR gene amplification in at least 10% of tumoral cells.
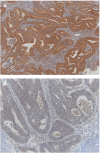
Figure 2
PTEN protein expression by immunohistochemistry in metastatic colorectal cancers. (A) Patient showing normal PTEN expression. (B) Patient with absent PTEN expression.
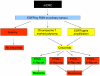
Figure 3
Algorithm in predicting response to cetuximab according to the EGFR and K-Ras status, and PTEN protein expression.
Similar articles
- Analysis of PTEN, BRAF, and EGFR status in determining benefit from cetuximab therapy in wild-type KRAS metastatic colon cancer.
Laurent-Puig P, Cayre A, Manceau G, Buc E, Bachet JB, Lecomte T, Rougier P, Lievre A, Landi B, Boige V, Ducreux M, Ychou M, Bibeau F, Bouché O, Reid J, Stone S, Penault-Llorca F. Laurent-Puig P, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2009 Dec 10;27(35):5924-30. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.21.6796. Epub 2009 Nov 2. J Clin Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19884556 - Recommendations from the EGAPP Working Group: can testing of tumor tissue for mutations in EGFR pathway downstream effector genes in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer improve health outcomes by guiding decisions regarding anti-EGFR therapy?
Evaluation of Genomic Applications in Practice and Prevention (EGAPP) Working Group. Evaluation of Genomic Applications in Practice and Prevention (EGAPP) Working Group. Genet Med. 2013 Jul;15(7):517-27. doi: 10.1038/gim.2012.184. Epub 2013 Feb 21. Genet Med. 2013. PMID: 23429431 - Markers for EGFR pathway activation as predictor of outcome in metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with or without cetuximab.
Tol J, Dijkstra JR, Klomp M, Teerenstra S, Dommerholt M, Vink-Börger ME, van Cleef PH, van Krieken JH, Punt CJ, Nagtegaal ID. Tol J, et al. Eur J Cancer. 2010 Jul;46(11):1997-2009. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2010.03.036. Epub 2010 Apr 21. Eur J Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20413299 Clinical Trial. - EGFR gene gain and PTEN protein expression are favorable prognostic factors in patients with KRAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer treated with cetuximab.
Razis E, Pentheroudakis G, Rigakos G, Bobos M, Kouvatseas G, Tzaida O, Makatsoris T, Papakostas P, Bai M, Goussia A, Samantas E, Papamichael D, Romanidou O, Efstratiou I, Tsolaki E, Psyrri A, De Roock W, Bafaloukos D, Klouvas G, Tejpar S, Kalogeras KT, Pectasides D, Fountzilas G. Razis E, et al. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2014 May;140(5):737-48. doi: 10.1007/s00432-014-1626-2. Epub 2014 Mar 5. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24595598 - The predictive value of KRAS, NRAS, BRAF, PIK3CA and PTEN for anti-EGFR treatment in metastatic colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Therkildsen C, Bergmann TK, Henrichsen-Schnack T, Ladelund S, Nilbert M. Therkildsen C, et al. Acta Oncol. 2014 Jul;53(7):852-64. doi: 10.3109/0284186X.2014.895036. Epub 2014 Mar 25. Acta Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24666267 Review.
Cited by
- mCOPA: analysis of heterogeneous features in cancer expression data.
Wang C, Taciroglu A, Maetschke SR, Nelson CC, Ragan MA, Davis MJ. Wang C, et al. J Clin Bioinforma. 2012 Dec 10;2(1):22. doi: 10.1186/2043-9113-2-22. J Clin Bioinforma. 2012. PMID: 23216803 Free PMC article. - CDK4/6 inhibition to resensitize BRAF/EGFR inhibitor in patient-derived BRAF/PTEN-mutant colon cancer cells.
Lim SH, Lee SY, Hong JY, Lee J, Kim ST. Lim SH, et al. Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Jul 31;13(7):3695-3703. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-20. Epub 2024 Jul 12. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39145064 Free PMC article. - Mechanisms of resistance to anti-epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors in metastatic colorectal cancer.
Sforza V, Martinelli E, Ciardiello F, Gambardella V, Napolitano S, Martini G, Della Corte C, Cardone C, Ferrara ML, Reginelli A, Liguori G, Belli G, Troiani T. Sforza V, et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Jul 28;22(28):6345-61. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i28.6345. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27605871 Free PMC article. Review. - Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor Is a Molecular Determinant of the Anti-EGFR Monoclonal Antibody Cetuximab Resistance in Human Colorectal Cancer Cells.
Russo R, Matrone N, Belli V, Ciardiello D, Valletta M, Esposito S, Pedone PV, Ciardiello F, Troiani T, Chambery A. Russo R, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2019 Sep 25;11(10):1430. doi: 10.3390/cancers11101430. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31557914 Free PMC article. - Panitumumab: the evidence for its use in the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer.
Berardi R, Onofri A, Pistelli M, Maccaroni E, Scartozzi M, Pierantoni C, Cascinu S. Berardi R, et al. Core Evid. 2010 Oct 21;5:61-76. doi: 10.2147/ce.s7035. Core Evid. 2010. PMID: 21042543 Free PMC article.
References
- Atkins D, Reiffen KA, Tegtmeier CL, Winther H, Bonato MS, Storkel S (2004) Immunohistochemical detection of EGFR in paraffin-embedded tumor tissues: variation in staining intensity due to choice of fixative and storage time of tissue sections. J Histochem Cytochem 52: 890–893 - PubMed
- Baselga J (2001) The EGFR as a target for anticancer therapy: focus on cetuximab. Eur J Cancer 37(Suppl 4): S16–S22 - PubMed
- Borner M, Mingrone W, Koeberle D, Von Moos R, Rauch D, Saletti P, Herrmann R, Dietrich D, Lanz D, Roth A (2006) The impact of cetuximab on the capecitabine plus oxaliplatin (XELOX) combination in first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer (MCC): a randomised phase II trial of the Swiss Group for Clinical Cancer Research (SAKK). J Clin Oncol 24(18S): 3551 - PubMed
- Chung KY, Shia J, Kemeny NE, Shah M, Schwartz GK, Tse A, Hamilton A, Pan D, Schrag D, Schwartz L, Klimstra DS, Fridman D, Kelsen DP, Saltz LB (2005) Cetuximab shows activity in colorectal cancer patients with tumors that do not express the epidermal growth factor receptor by immunohistochemistry. J Clin Oncol 23: 1803–1810 - PubMed
- Cunningham D, Humblet Y, Siena S, Khayat D, Bleiberg H, Santoro A, Bets D, Mueser M, Harstrick A, Verslype C, Chau I, Van Cutsem E (2004) Cetuximab monotherapy and cetuximab plus irinotecan in irinotecan-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 351: 337–345 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous